 This
EarthCache is located in Forestville State Park
Link located approximately 6 miles south of Wykoff. Entrance to
the park is 4 miles south of State Highway 16 on Fillmore County
Highway 5, then 2 miles east on Fillmore County 118.
This
EarthCache is located in Forestville State Park
Link located approximately 6 miles south of Wykoff. Entrance to
the park is 4 miles south of State Highway 16 on Fillmore County
Highway 5, then 2 miles east on Fillmore County 118.
Since this Earthcache is located in a Minnesota State Park, a
Park Sticker is required when visiting this Park.
Two to five hundred million years ago material was deposited in
the bottom of shallow seas which intermittently covered large
portions of North America. As the deposits increased in thickness,
the layers on the bottom were compressed to form limestone, shale
and sandstone. Today in the park, these rocks are 1300 feet above
the sea. They are an important factor in the development of the
terrain which exists now.
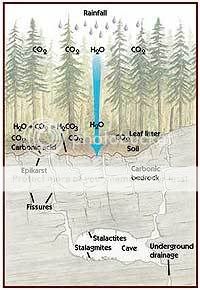
Forestville State Park is located within the karst region of
Minnesota. Karst occurs in areas of soluble rocks, usually
limestone or dolomite. As rainwater percolates through the soil, it
is rendered slightly acidic as it picks up carbon dioxide from
microbial decay of organic soil material. This fortified water has
the capacity to dissolve the rock. The effects of this dissolving
action are minute from the perspective of a human’s lifetime.
However, over the course of many thousands of years, dramatic
changes occur; the typical features of karst develop – caves
and sinkholes form; underground drainage occurs. The park exhibits
many karst features including one of the most outstanding karst
features in the state, Mystery Cave. The cave is a maze of linear
corridors. Over twelve miles of passage exist in two rock layers
with strikingly different compositions. During dry years, the
entire South Branch Root River sinks into the cave through gravel
filled crevices in the river bottom. Forestville also exhibits
features of the unglaciated or “driftless” region. Of
the four major glacial advances during the last million years, only
the first two covered the vicinity of Forestville. Downcutting of
stream valleys by powerful glacial meltwater created the steep
hills and bluffs we see in the park and surrounding area today.
In order to claim credit for this EarthCache, you must do the
following:
Please e-mail me the following:
1.Measure the pH of the water coming right from the cave.
(pH testing strips are available at any pool supply store)
2.Please explain to me why this water is either acidic or
basic.
Then:
3.If you would like, take a picture of yourself/ team
with the cave in the background and your gps clearly visible and
post it when logging the cache.
The elevated terrain rating is due to the fact that a 1.3 mile
hike is required to reach the spring's source which includes a
shallow water crossing of appoximately 20 metres.
Please note, at no time do you need to leave the trail, please
respect this area's special ecology and STAY ON THE
TRAIL!