
 The closest shuttle stop is E5, the Four Mile Trail Head on the El Capitan Shuttle. This route runs only during the summer season.
The closest shuttle stop is E5, the Four Mile Trail Head on the El Capitan Shuttle. This route runs only during the summer season.
Many of the geologic features commonly associated with Yosemite Valley were formed hundreds of thousands to millions of years ago. However, the story of Yosemite Valley did not stop. Geologic processes continue to reshape the landscape of Yosemite. The Merced River continues to flow through the valley causing erosion and deposition in various locations and at different times. This EarthCache examines the formation of river meanders in the Merced River as it flows across the valley floor.
But the current geologic processes must work on the landscape that has its origins in the past glaciations of the valley. Various glaciations carved the steep-walled Yosemite Valley. Following the last glaciations, an end moraine formed across the valley from about El Capitan to Bridalveil Falls. This moraine dammed the Merced River forming a lake that extended 5.5 miles up the valley. While this lake existed for only a few thousand years (very short in geologic time), between a few hundred feet to almost 2000 feet of sediment was washed into the valley filling in the floor. This lake sediment creates the relatively flat floor of the valley, which is actually not characteristic of a U-shaped glacial valley.
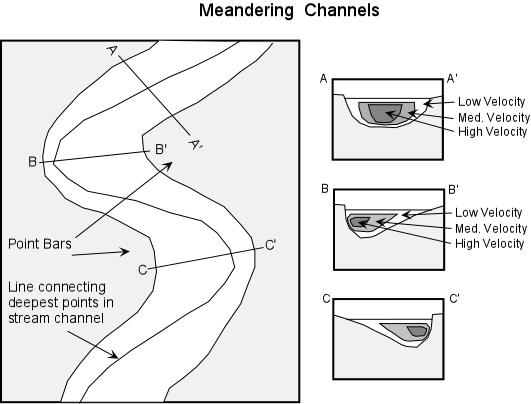 It is on this flat topography that the Merced River slows and begins to meander. In areas of low slope, the path of a river begins to wander back and forth creating meanders, or curves. Along each curve, the flow of the river is constantly eroding the outside bank of the meander, while at the same time depositing material on the inside. This is because the area of fastest flow in the river is forced to the outside bank on the curves and the slowest flow is on the inside. Faster water carries more sediment causing the erosion. The slower water is unable to carry as much sediment, so some sediment drops out of the water. The result is a steep bank on the outer edge of a meander and a gentle slope on the inner edge.
It is on this flat topography that the Merced River slows and begins to meander. In areas of low slope, the path of a river begins to wander back and forth creating meanders, or curves. Along each curve, the flow of the river is constantly eroding the outside bank of the meander, while at the same time depositing material on the inside. This is because the area of fastest flow in the river is forced to the outside bank on the curves and the slowest flow is on the inside. Faster water carries more sediment causing the erosion. The slower water is unable to carry as much sediment, so some sediment drops out of the water. The result is a steep bank on the outer edge of a meander and a gentle slope on the inner edge.
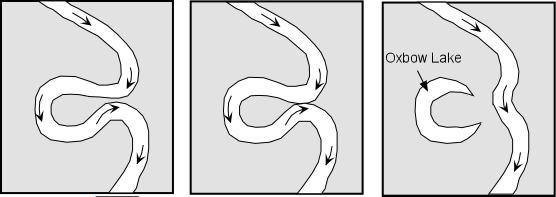 Over time, meanders get larger more pronounced as the outer edge is eroded away and the inner edge has material deposited on it. Given enough time, the meanders could get so curvy that they bend back and touch itself creating an oxbow lake.
Over time, meanders get larger more pronounced as the outer edge is eroded away and the inner edge has material deposited on it. Given enough time, the meanders could get so curvy that they bend back and touch itself creating an oxbow lake.
An animation of river meander formation can be found at http://www.cleo.net.uk/resources/displayframe.php?src=309/consultants_resources%2F_files%2Fmeander4.swf
In an area that floods regularly such as the meadows on the floor of Yosemite Valley, oxbow lakes quickly fill in with sediment to become part of surrounding meadow.
Logging requirements:
Send me a note with :
- The text "GC1QN2P Yosemite Valley River Meander" on the first line
- The number of people in your group.
- At this location, where is the area of most erosion and why do you think it is located there?
- How far are you from the highest velocity water flow?
- What material are you standing on and why is it located here?
- How close to creating an oxbow lake is this meander?
The above information was compiled from the following sources:
- All images from Prof. Stephen A. Nelson, Tulane University. http://www.yosemite.ca.us/library/geology_of_yosemite_valley/
Trial listing approved by
Yosemite National Park