I 75 Drinking Fountain? EarthCache
-
Difficulty:
-

-
Terrain:
-

Size:  (not chosen)
(not chosen)
Please note Use of geocaching.com services is subject to the terms and conditions
in our disclaimer.
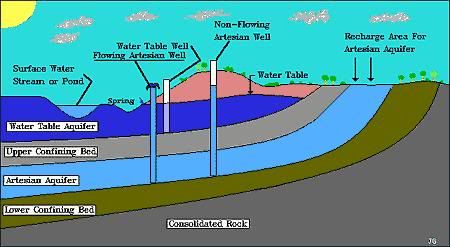
Flowing artesian wells are created when the pressure in a confined
aquifer (water- bearing geologic formation) forces ground water
above the ground surface so that the well will flow without a pump.
This water is forced up through either man-made holes or natural
fissures (cracks). An aquifer is a layer of permeable material in
which water can easily move such as unconsolidated sand, gravel,
clay or silt. It can also be composed of soft rock like fractured
limestone or sandstone that absorbs water from an inlet path. Large
solution openings that are produced when part of the rock is
dissolved by ground water are common in carbonate rocks. Carbonate
rocks are a class of sedimentary rocks composed primarily of
carbonate minerals. The two major types are limestone and dolomite.
These openings store and transmit large quantities of water. Porous
stone is crushed between impermeable rocks or clay. This keeps the
pressure high, so when the water finds a hole, it overcomes gravity
and is forced up and out. The principal water-yielding aquifers of
North America can be grouped into five types: unconsolidated and
semi-consolidated sand and gravel aquifers, sandstone aquifers,
carbonate-rock aquifers, aquifers in interbedded sandstone and
carbonate rocks, and aquifers in igneous and metamorphic rocks.
This well and others in the area are produced from a Carbonate-Rock
aquifer (sometimes referred to as a Silurian-Devonian aquifer). The
average thickness of the carbonate rocks that compose most of the
Silurian-Devonian aquifer is about 300 to 400 feet; the aquifer
also contains some sandstone, shale, and evaporite beds (rock and
mineral deposits left over from evaporation process when Michigan
was covered by sea water). Water movement is primarily through
secondary openings, such as joints, fractures, and bedding-plane
openings, many of which have been enlarged by dissolution
(dissolving of underground rocks). The pH of the groundwater is
affected by the type of rock material it moves through and how long
it remains in contact before it is released. The indicator for
acidity or alkalinity, or basic, is known as the pH value. A pH
value of 7 means a substance is neutral. The lower value indicates
acidity, and a higher value is a sign of alkalinity. To display the
range in pH, take a look at these examples: Lemon- 2.5 Coffee-5-6.5
Milk- 6.2 Soapy water-7-10 Beer- 4.5 So, what does pH mean for
water? Basically, the pH value determines whether water is hard or
soft. The pH of pure water is 7. In general, water with a pH lower
than 7 is considered acidic, and with a pH greater than 7, basic.
The normal range for pH in surface water systems is 6.5 to 8.5 and
for groundwater systems 6 to 8.5. According to U.S. Environmental
Protection Agency criteria, water for domestic use should have a pH
between 5.5 and 9. Alkalinity is a measure of the capacity of the
water to resist a change in pH that would tend to make the water
more acidic. The measurement of alkalinity and pH is needed to
determine the corrosiveness of the water. In general, water with a
low pH ( 8.5 could indicate that the water is hard. Hard water does
not pose a health risk, but can cause aesthetic problems. These
problems include an alkali taste to the water (making that morning
coffee taste bitter!), formation of a deposit on dishes, utensils,
and laundry basins, difficulty in getting soaps and detergents to
lather, and formation of insoluble precipitates on clothing. While
the ideal pH level of drinking water should be between 6-8.5, the
human body maintains pH equilibrium on a constant basis and will
not be affected by water consumption. For example our stomachs have
a naturally low pH level of 2 which is beneficial acid that helps
us with food digestion. To claim a find, e-mail me through my
profile after completing the following tasks. You will need a
camera, tape measure, and pH testing strips. 1). What is the
distance from the ground to the tip of the pipe where the water
exits? 2). Take a picture of you/your team and/OR your GPSr at the
location. 3). What is the pH level of the water?
Additional Hints
(No hints available.)
Treasures
You'll collect a digital Treasure from one of these collections when you find and log this geocache:

Loading Treasures