Unconformity
The rocks above an unconformity are younger than the rocks beneath (unless the sequence has been overturned). An unconformity represents time during which no sediments were preserved in a region. The interval of geologic time not represented is called a hiatus.
This “unconformity between the Ordovician Jefferson City Dolomite (white rock at the bottom) and Devonian Cedar Valley Limestone (Dark rock on top).” (Spencer) Here you will witness the hiatus of the Silurian Period, that is 28 million years’ worth gone.
The Silurian period was about 443.7 to 416.0 million years ago. It was a time when the Earth experienced substantial changes that had important effects for the environment and life. One result of these changes was the thawing of large glaciers. This added to a considerable rise in the levels of the major seas. The Silurian saw a relative balance of the Earth's overall climate, ending the pattern of unpredictable climatic fluctuations.
Types of unconformities
Disconformity
A disconformity is an unconformity between parallel layers of sedimentary rocks which represents a period of erosion or non-deposition. Disconformities are marked by features of subaerial erosion. This type of erosion can leave channels in the rock record.

Nonconformity
A nonconformity exists between sedimentary rocks and metamorphic or igneous rocks when the sedimentary rock lies above and was deposited on the pre-existing and eroded metamorphic or igneous rock. Namely, if the rock below the break is igneous or has lost its bedding by metamorphism; then it’s a nonconformity type of unconformity.
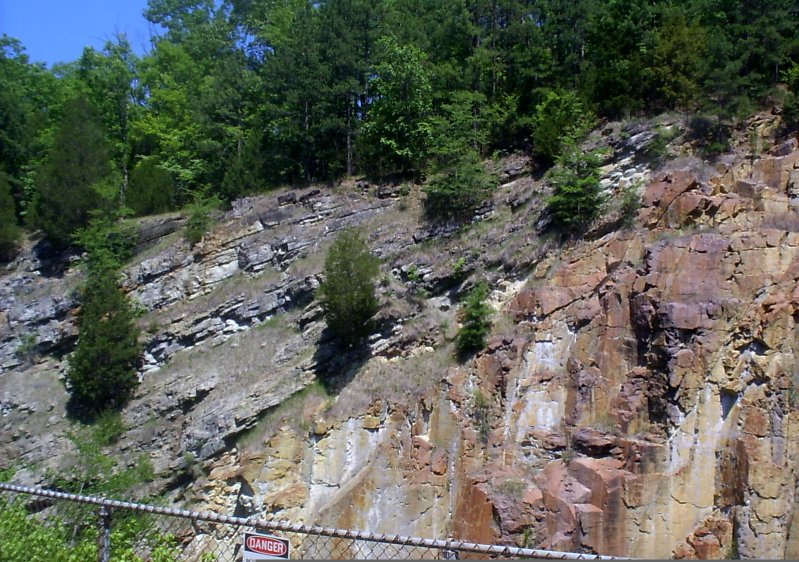

Angular unconformity
An angular unconformity is an unconformity where horizontally parallel strata of sedimentary rock are deposited on tilted and eroded layers, producing an angular discordance with the overlying horizontal layers. The whole sequence may later be deformed and tilted by further plate tectonic activity.

Paraconformity
A paraconformity is a type of unconformity in which strata are parallel; there is little apparent erosion and the unconformity surface resembles a simple bedding plane.
Types of geological structure folds
Anticline
An anticline is a fold that is convex up and has its oldest beds at its core. The term is not to be confused with antiform, which is a purely descriptive term for any fold that is convex up.
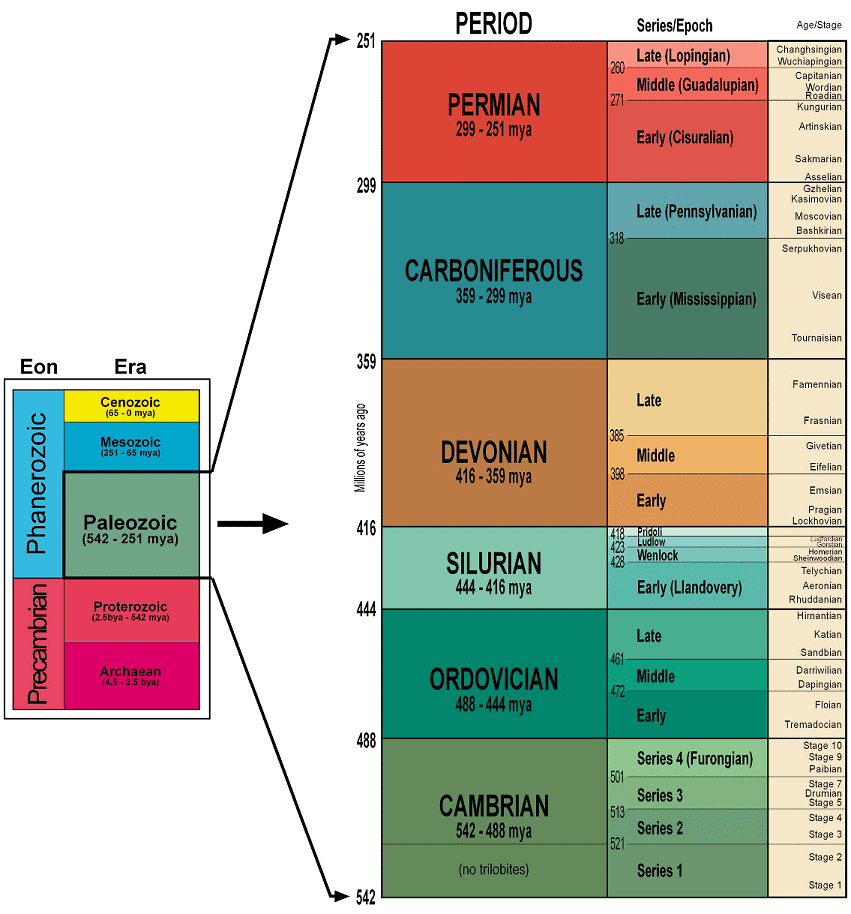
Homocline
A homocline or homoclinal structure, is a geological structure in which the bedding of a sequence of rock strata, either sedimentary or igneous, dips uniformly in a single direction having the same general inclination in terms of direction and angle.

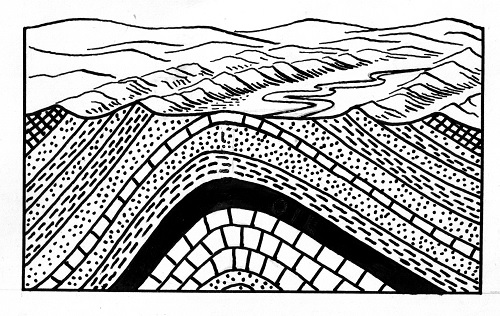
Syncline
A syncline is a fold with younger layers closer to the center of the structure. Synclines are typically a downward fold.
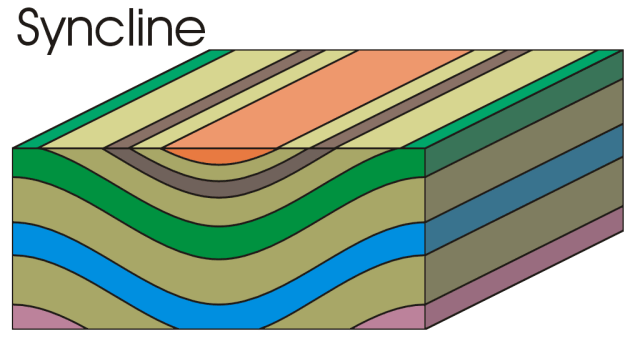
Monocline
A monocline is a step-like fold in rock strata consisting of a zone of steeper dip within an otherwise horizontal or gently-dipping sequence.
**Logging requirements**
DO NOT POST ANSWERS IN YOUR LOG.
Send the following answers to me via email.
- The text "GC5E0H5 Millions of years missing" on the first line
- What type of unconformity is presented here, (look at the Northside road cut for clues)?
- What has caused geological time to be wiped off the earth in this area?
- The entire road cut here from east to west is what kind of fold?
| I have earned GSA's highest level: |
 |
Sources
- Spencer, Charles G. Roadside Geology of Missouri. Missoula, Mont.: Mountain Pub., 2011. Print.
- Beveridge, Thomas. Geologic Wonders and Curiosities of Missouri. 2nd. Rolla, Missouri: Missouri Department of Natural Resources, 1990. Print.