Svedsmossen Earthcache


En insjö bildas.
Den enorma tyngd som isen utgjorde pressade ner jordskorpan. De beräkningar som gjorts tyder på att isen var som tjockast, ända upp till 3 km, i området mellan Ångermanland och Vasatrakten i Finland. Allt eftersom isen avsmälte började jordskorpan höjas pga. det lättade trycket. Landhöjningstakten var i början någon dm om året för att succesivt avta. Idag har landhöjningen slutat i Skåne, medan den ligger på ungefär 4 mm per år kring trakten av Stockholm och omkring 8 mm i Luleåområdet. De senaste årtiondena har det faktiskt observerats en landsänkning med l mm per år i Skåne. Orsaken tror man beror på en förskjutning av de sk kontinentala plattorna, vilket även tros vara en del av orsaken till dagens landhöjning.
Avsmältningen av inlandsisen i Sverige pågick under ungefär 3 000 år. Från början var större delen av vårt land täckt av vatten, för i takt med att jordskorpan höjdes ökade även vattenmängden i havet pga. allt smältvatten. Den högsta nivå havet hade kan man fortfarande se i form av strandterasser, klapperstensfält, kalspolade berghällar och kalottberg. De här historiska lämningarna i vår natur uppkom då det forna havets vågsvall och bränningar sköljde bort en stor del av allt finmaterial. Den nivå havet nådde till som högst kallas Högsta kustlinjen och förkortas HK. När landskapet började höja sig ännu mer ur havet bildades sk fornsjöar och issjöar där håligheter i jordskorpan fanns. Klimatet var fortfarande arktiskt och tillrinningen till sjöarna innehöll mest grus, sand, mo. Med tiden började tundran “vegeteras” och tillrinningen innehöll mer organiskt material. Ett lager med näringsrikt sediment började avsättas på botten och sjöarna var förhållandevis näringsrika då jorden ännu inte börjat urlakas. Där många ursjöar låg är det idag ett bördigt marklager som kom att lämpa sig bra för odling. Den primära ekologiska successionen kunde börja sin utveckling, dvs ett nytt ekosystem tar form där det tidigare aldrig funnits något ekosystem. Det slam som bildades av tillrinnande organiskt material fylldes på av sjöarnas egna växter och började efterhand sedimenteras. Med hjälp av bottenlevande organismers inverkan uppstod gyttjebottnar i de mer näringsrika sjöarna och dybottnar i näringsfattiga sjöar. Näringsfattiga sjöar uppstod där tillrinningen innehöll lite organiskt material och sjöns egen växlighet var mindre frodig.
En mosse bildas.
Med ordet mosse i vidsträckt betydelse, det vill säga torvmark, torvmosse eller myr, menar man vanligen en i markytan liggande avlagring som huvudsakligen består av jordarter som bildats av delvis nedbrutna växtdelar som producerats av platsens vegetation och som ansamlats under en lång tid. Torvmarker uppstår nästan uteslutande i trakter med tempererat klimat, men rikligast förekommer de i områden där en forntida nedisning har skapat en småkuperad terräng av den typ, som är karaktäristisk för Skandinavien. Nästan alla delar av Sverige har därför torvmarker, från en storlek på några få ar till flera kvadratmils utsträckning. Sveriges torvavlagringar är utan undantag bildade under tiden efter den sista istiden. På ett par platser i södra Norrland (Härnösand och Bollnäs) har man dock träffat gyttjelager som härstammar från äldre torvmossar som förstörts av inlandsisen. I sjömossarna kommer underst i lagerföljden jordarter som är avsatta i öppet vatten (till exempel gyttjor och sjötorv) och som innehåller rester av vattenväxter.
När formlig tallskog uppträder på mossen, innebär detta vanligtvis att den nått sin utvecklings slutpunkt. Torvytan har nämligen då nått en höjd att torvlagrets tillväxt avstannar, för att de döda växtdelar som produceras där, nu bryts ned nästan fullständigt, precis som på vanlig fast mark.
För att logga:
För att få logga denna  (Earthcache) som
(Earthcache) som  (found) skall du göra följande:
(found) skall du göra följande:
1. Valfritt (men önskat!): Ta ett kort på dig med din GPS i handen med mossen i bakgrunden och posta det tillsammans med loggen.
2. Skicka ett mail till cacheägaren med svaret på frågorna.
Frågor:
1. I vilket skede av sin utveckling befinner sig denna mosse?
2. Hur länge pågick avsmältningen i Sverige?
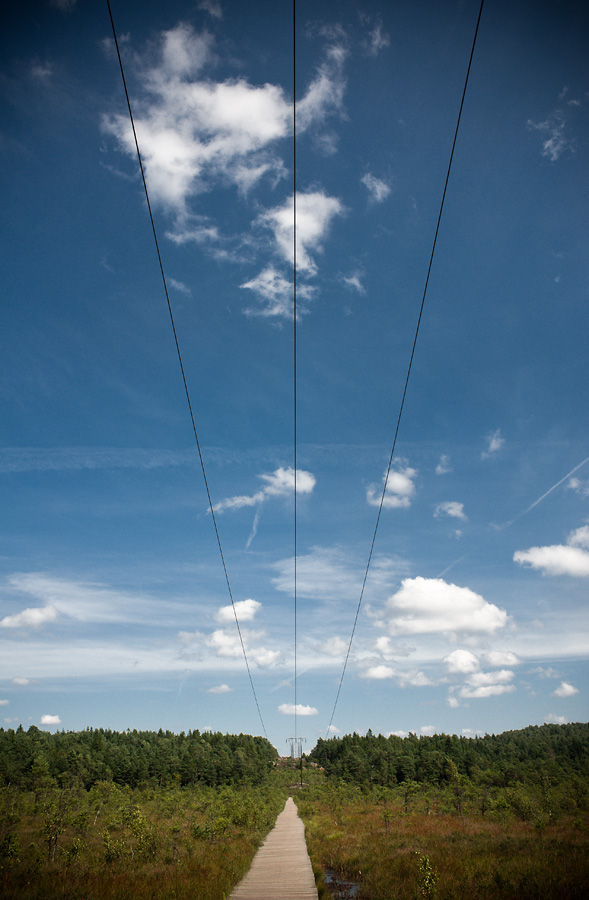
3. Hur lång är spången som du har besökt?
Du behöver inte vänta på godkännande av cacheägaren för att få logga som found. Om jag behöver kompletterande uppgifter hör jag av mig. Kom ihåg att bifoga en bild och att inte skriva svaren i din logg!


A lake is formed.
The enormous weight of the ice pressed onto the earth’s crust. The calculations performed indicate that the ice was at its thickest, up to 3 km, in the area between Ångermanland and Vaasa area in Finland. As the ice melted the earth’s crust began to rise because of the eased pressure. The uplift pace was in the beginning a dm a year to gradually decline. Today, the uplift stopped in southern Sweden, while it is around 4 mm per year around the area of Stockholm and about 8 mm in the Luleå area. In recent decades there has actually been observed a reduction of l mm / year in southern Sweden. The reason is believed due to a shift in the so-called continental plates, which also is believed to be a part of the reason for the current uplift.
The melting of the ice in Sweden lasted for about 3 000 years. Originally, most of our land was covered by water, for as the earth’s crust was increased also increased water in the ocean due to all melt. The highest level of the sea is still marked, you can still see as beach terraces, rubble fields, bare washed mountain tops and cap rock. These historical remnants of our nature occurred when the ancient sea’s waves and breakers swept away much of the smallest materials. The sea level reached a peak called the Supreme coastline and shortened HK. When the landscape began to rise even further from the sea formed the so-called ancient lakes and ice lakes where excavation of the earth’s crust where. The climate was still arctic and inflow to the lakes contained mostly gravel, sand and fine sand. In time the tundra began to “vegetate” and the inflow contained more organic material. A layer of nutrient-rich sediment was disposed of on the ground and the lakes were relatively nutrient-rich soil which has not yet begun to leach. Where many ancient lakes laid, it is now a fertile soil layer, which came to be suitable for cultivation. The primary ecological succession could begin their development, ie a new ecosystem takes shape, where it has never been any ecosystem before. The sludge formed by the stream of organic material filled with the lakes own plants and subsequently began to settle. With the help of benthic organisms mud bottom occurred in the more nutrient-rich lakes and sludge bottoms in nutrient-poor lakes. Nutrient-poor lakes arose where inflow contained little organic matter and the lake’s self vegetation were less lush.
A bog is formed.
The word bog of vast importance, namely peat soils, peat moss or bog, we mean usually in the ground underlying deposit consisting predominantly of soils formed from partially degraded plant parts produced by the site’s vegetation and accumulated over a long period of time. Peatlands occur almost exclusively in areas with temperate climate, but most abundant are those in areas where an ancient glaciation has created a little hilly terrain of the type, which is characteristic of Scandinavia. Almost all parts of Sweden have peatlands, from a size of a few square meters to several square miles extent. Swedish peat deposits are invariably formed in the period after the last ice age. In a few places in southern Norrland (Härnösand and Bollnäs) has however met with mudlayers derived from older peat lands destroyed by the ice sheet. In lakebogs the bottom of the stock rotation soils that are committed in open water (such as mud and lakepeat) and containing residues of aquatic plants.
When veritable pine forest occurs in bogs, this usually means that the development reached its end point. Peat surface when in fact reached a height that the peat layer growth stagnation, to the dead plant parts that are produced there, now broken down almost completely, just as in conventional solid ground.
How to log:
To log this  (Earthcache) as
(Earthcache) as  (found) you must do the following:
(found) you must do the following:
1. Optional: (but wanted!) Take a picture of yourself with your GPS in your hand and the bog in the background and post it along with the log.
2. Send an email to the cache owner with the answer to these three questions.
Questions:
1. At what stage of its development is this bog?
2. How long was the melting of the ice in Sweden?
3. How long is the footbridge that you have visited?
You do not need to wait for approval from the cacheowner to log as found. If I need additional information, I let you know. Remember to post a picture and not to write answers in your log!

Visit my other Earthcaches:
Sweden:  Ersdalen Earthcache
Ersdalen Earthcache  Svavelbruket
Svavelbruket  Kalkbrottet
Kalkbrottet  Rosenlunds bankar
Rosenlunds bankar  Gautelfr
Gautelfr  Druim
Druim  Kamlungeforsen
Kamlungeforsen
Cape Verde:  As dunas de Bubista
As dunas de Bubista
Montenegro:  Vapnenac
Vapnenac
Croatia:  Kolac natural arch
Kolac natural arch
Cuba:  Mirador de Bacunayagua
Mirador de Bacunayagua
Greece:  Afantou beach
Afantou beach
Italy:  Torre pendente di Pisa
Torre pendente di Pisa