
Deutsch
Der Hülser Berg ist mit 63 Metern die höchste natürliche Erhebung in der Stadt Krefeld und liegt etwa zwei Kilometer nordöstlich der 1975 eingemeindeten Ortschaft Hüls
Entstehung
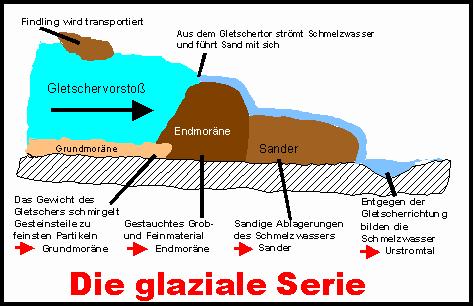
Der Hülser Berg entstand während des Drenthe-Vorstoßes der Saale-Eiszeit vor ca. 150 000 Jahre . Das aufgeschichtete Geröll, welches die Gletscher von Skandinavien kommend vor und unter sich her- und mitschoben, blieb nach Abtauen derselben in Form einer Stauchendmoräne zurück. Stauchendmoränen, die sich oft durch sehr hohe Reliefenergie auszeichnen, entstehen, wenn durch den Druck eines vorstoßenden Gletschers älteres Material, das vor der Gletscherfront abgelagert wurde, unter horizontalen und vertikalen Druck gerät und dabei gestaucht und aufgeworfen wird. Je nach der Beschaffenheit des älteren Materials bestehen Stauchendmoränen aus verschiedensten Sedimenten. Meist handelt es sich um ältere glaziale Ablagerungen wie Sand, Eisstauseesedimente oder ältere Geschiebemergel. Auf die gleiche Weise entstand auch der nahegelegene Wolfsberg, der Teil des sich nach Norden fortsetzenden Schaephuysener Höhenzuges ist.
Historisches
Die ältesten menschlichen Spuren am Hülser Berg wurden um 1979 von Dipl-Ing. Detlef Stender gefunden. Es handelt sich um mesolithische Fundstellen vom Ende der letzten Eiszeit (ca. 8000 v. Chr.) bis Beginn der Jungsteinzeit (ca. 5500 v. Chr.). Gefunden wurden Feuersteinartefakte (Pfeilspitzen und Feuersteinabschläge). Die höchste Artefaktkonzentration fand sich hierbei am östlichen Hang. Auf Grund der hohen Fundkonzentration und der Art der Funde schließt man, dass sich die Menschen am Hülser Berg längere Zeit aufhielten. Die Funde befinden sich heute im Museum Burg Linn (Krefeld).
1909 wurden auf dem Hülser Berg die Reste eines Keltenlagers ausgegraben. Es bestand aus einem 400 Meter langen Doppelwall. Brandstätten und Werkzeuge wurden gefunden. Eine Dokumentation dieser Befunde wurden in einem Aufsatz von Dipl.-Ing. Detlef Stender und Dr. Thomas Ruppel verfasst.
Überall auf dem Hülser Berg befinden sich sogenannte Tonkuhlen: Runde Erdvertiefungen von 10 bis 20 Meter Durchmesser geben Zeugnis von den ehemaligen Abbaustellen der Lehmstecher, welche die Hülser Pott- und Pannebäcker (Töpfer und Hersteller von Dachziegeln) mit Rohstoff für deren Produktion versorgten. Hüls war vom 17. bis 19. Jahrhundert eines der bedeutendsten Pottbäckerdörfer am linken Niederrhein.
In der Zeit von 1600 bis 1800 gab es am Hülser Berg eine Hinrichtungsstätte, den sog. Galgenberg. Sie befand sich dort, wo heute die Schluff genannte Eisenbahnlinie den Hülser Berg an seinen nordwestlichen Ausläufern anschneidet. Hier wurden Räuber und Schwerverbrecher am Galgen oder durch Enthauptung hingerichtet. Ferner fanden hier Hinrichtungen von vermeintlichen Hexen statt.

Parken könnt ihr bei N 51°23.334, E 006°32.201.
Auf dem Weg zur oben genannten Koordinate kommt ihr bei N 51°23.286, E 006° 32.210 vorbei, wo ihr ein Bild von euch an dem Denkmal machen könnt.
Um diesen Cache zu loggen, sollten folgenden 3 Aufgaben beantwortet werden!
Loggen des Cache´s:
1. Bei N 51°23.330 und E 6°32.205 befindet sich eine Informationstafel.
Wie wird das Naturdenkmal noch auf der Tafel genannt ?.
2.Am Naturdenkmal bei N 51° 23.290 und E 6°32.192 hat man einige Findlinge des Hülser Bergs platziert. .
Was unterscheidet den Findling ca. 2m rechts vom Schild, gegenüber den anderen Findlingen und welche Farbe hat er?.
3.Bei N 51°23.143 und E 6°32.166 befinden sich einige der sogenannten Tonkuhlen..
Wie viele Tonkuhlen befinden sich in unmittelbarer Nähe und welche ist die größte von Ihnen ?
Bitte schickt uns eine E-Mail an unser Profil mit den Antworten für die Fragen. Bitte wartet dann auf die Log-Freigabe bevor ihr euren Log-Eintrag macht und wenn ihr wollt, hängt - freiwillig - ein Foto an euerem Log.

English
The Hülser Hill with its 430 hectares is the biggest nature reserve of Krefeld since 2002. It lies about four km to the north of the Krefeld city center of and about two km northeast of Hüls.
Emergence
The Hülser Hill originated during the Drenthe thrust of the hall ice age approx. 150,000 years ago. The stacked stone which the glaciers of Scandinavia moved over and copushed coming before and under themselves stayed behind on defrosting the same in form of a Stauchendmoräne.

Historical
The oldest human tracks in the Hülser Hill were found about 1979 by dipl. engineer Detlef Stender. It concerns mesolithische finding places from the end of the last ice age (approx. 8,000 B.C.) till the beginning of the Neolithic Age (approx. 5,500 B.C.). Flint artefacts (heads of the arrow and flint reductions) were found. The highest artefact concentration was found, on this occasion, in the eastern slope. On grounds of the high finding concentration and the kind of the findings one closes that the people in the Hülser Hill stayed longer time. Today the findings are in the museum castle Linn (Krefeld).
In 1909 the rests of a Celt's camp were dug out on the Hülser Hill. There was of a 400-metre-long double embankment. Fire sites and tools were found. A documentation of these findings were written in an article by qualified engineer Detlef Stender and Dr. Thomas Ruppel.
Everywhere so-called sound hollows are on the Hülser Hill: Round earth deepening of 10 to 20 metres of diameter give report of the former dismantling places of the mucky engravers which the Hülser pot and breakdown bakers (potter and manufacturer of roofing tiles) supplied with raw material for their production. Hüls was from the 17-th to the 19-th century one of the most significant pot baker villages on the left Lower Rhine.
In the time of from 1600 to 1800 there was in the Hülser mountain an execution site, the so-called. Gallows mountain. She was where today the Schluff called railway line cuts the Hülser Hill in his northwest runners. Here robbers and dangerous criminals in the gallows or by decapitation were executed. Further executions of putative witches took place here.

You can park on N 51°23.334, E 006°32.201.
On your way to N 51° 23. 286, E 006° 32. 210 you can take a photo of the memorial .
To log these Cache, 3 tasks should be answered.
1. With N 51°23,330 and E 6°32.205 there is a board of information .
How the natural monument is still called on the board?
2. In the natural monument with N 51° 23,290 and E 6°32.192 one has placed some erratic blocks of the Hülser mountain .
What distinguishes the erratic block approx. 2 m on the right from the sign, towards the other erratic blocks and which colour he has ?
3. With N 51°23.143 and E 6°32.166 there are some of the so-called sound hollows .
How many sound hollows are in immediate nearness and which is biggest from you ?
Please send me an email containing the answers of the questions and if you want - thats free - add the photo to your log.