
 Rest
stops are available on either side of the freeway. A paved walking
path has been constructed for each side. I walked along the path on
the north-bound side, but similar features can be found along the
south-bound rest stop.
Rest
stops are available on either side of the freeway. A paved walking
path has been constructed for each side. I walked along the path on
the north-bound side, but similar features can be found along the
south-bound rest stop.
Hot spots are thought to be caused by a plume of hot magma
flowing up to the crust. This plume is for some reason sustained
over long geologic periods. Volcanoes then form over these hot
spots. Over time, the plates of the earth move over these hot spots
leaving a trail of volcanoes.
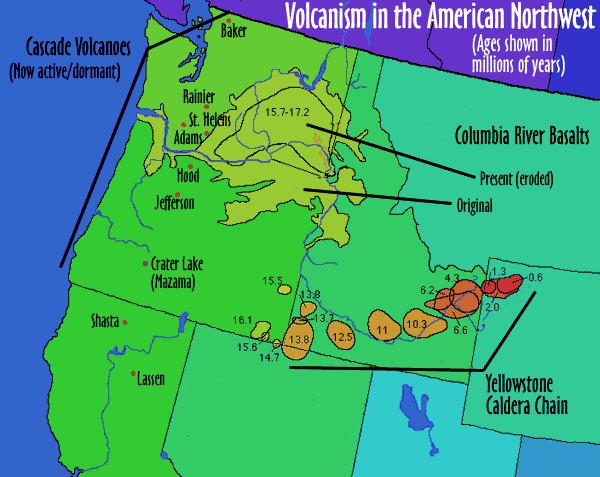 A trail of volcanic activity can be found all the
way through Idaho to Oregon and Nevada. The oldest of this
activity, the McDermitt volcanic field 70 miles north of
Winnemucca, Nevada, is about 16 million years old. The youngest is
the Yellowstone Caldera and is only about 600,000 years old. Other
volcanic fields in this chain include the Picabo volcanic field,
and the Heise volcanic field.
A trail of volcanic activity can be found all the
way through Idaho to Oregon and Nevada. The oldest of this
activity, the McDermitt volcanic field 70 miles north of
Winnemucca, Nevada, is about 16 million years old. The youngest is
the Yellowstone Caldera and is only about 600,000 years old. Other
volcanic fields in this chain include the Picabo volcanic field,
and the Heise volcanic field.
Basaltic lava from this hot spot erupted northwest of here and
covered this area with Pahoehoe lava. This is a smooth ropey lava.
This is compared to Aa lava, a sharp angular lava.
While there is no chemical difference between the two types of
basalt, a combination of temperature, viscosity (how well a liquid
flows), and gas content appears to play a part. Hot, low viscosity
lava with little gas tends to form pahoehoe while a cooler, high
viscosity, gaseous lava tends to form Aa.
The informational signs point out various other features that
can be found along the paths. Some of these features include
squeeze-ups, vesicles and flow patterns.
Since this lava flow is so young, little soil has developed.
This makes it difficult for plants to take root and grow. This area
is an example of the recolonization of plants to fresh rock
surfaces.
Logging requirements:
Send me a note with :
- The text "GC15FHV Hell's Half Acre" on the first line
- The number of people in your group.
- The name of the crescent shaped depression that this hot spot
created and it's approximate length.
- Post the name of one of the features that is described in the
informational panels.
- Send me a note of how this feature is formed.
- If possible, post a picture of the feature
- from the informational panels (the large brown ones in the
parking lots at the coordinates)what is the main way soil is formed
at this location.
The above information was compiled from the
following sources:
- Global Volcanism Program, Hell's Half Acre,
Smithsonian National Natural History Museum,
http://www.volcano.si.edu/world/volcano.cfm?vnum=1204-04- Idaho
Natural History Museum informational panels.