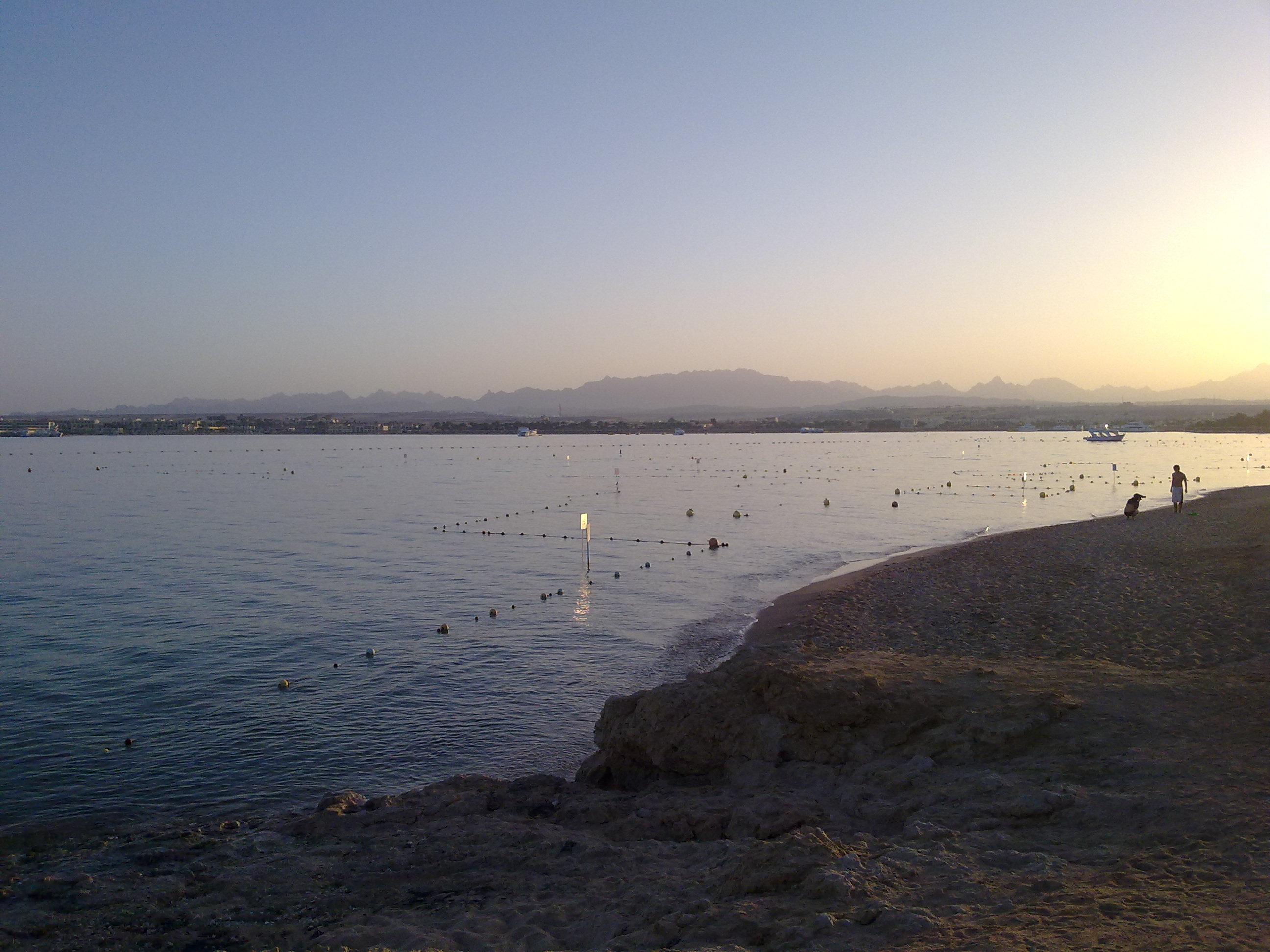
 بيت الشعاب المرجانية خليج مقادي
بيت الشعاب المرجانية خليج مقادي
مكادي بأي منتجع مدينة في مصر. ويقع المصنع على بعد حوالي 30 كم جنوب مدينة الغردقة على البحر الأحمر.
بحتة السياحية الوجهة متميزة تسوية تقع على حوالي 4 كيلومترات من الساحل على خليج صغير وخليج مكادي وعلى المنحدرات الجنوبية.
لمكان حصرا تقريبا من حوالي 20 من مرافق الفندق والنادي الرئيسية. وهناك في وسط الخليج شاطئ رملي المنحدرة بلطف. على مسافة قصيرة أمام الشاطئ يمكن ملاحظة بعض الشعاب المرجانية البيت البسيطة والشعب المرجانية الهدابيه أطول قليلاً وتمتد في الجناح الشمالي للخليج ويوفر فرص الغوص. الصحراء العربية يبدأ مباشرة خلف مرافق الفندق.
البحر الأحمر
 البحر الأحمر شهدت منطقة انتشار نشطة جيولوجيا جداً مع الصهارة سويلابل على (تناظري ريدج وسط المحيط الأطلسي)، ومما يؤدي الانجراف بعيداً من البلدان الأفريقية والعربية لوحة لسنوات 130 مليون. . التدريب الحوض وقد "فقط" 38 مليون سنة مضت في أوليجوسيني، ما زال في الصدع الذي "حدث في شرق أفريقيا" والعديد من ملايين السنين سوف يؤدي إلى محيطجديد. البحر حاليا إلى 1.6 سم سنوياً في الشمال حوالي 0.8 سم، في الجنوب. بعد عزلة المتكررة من المحيط الهندي، واتصال مؤقت مع البحر الأبيض المتوسط وحتى التجفيف، وصلت البحر الأحمر إلى حالتها الراهنة قبل 5000 سنة تقريبا.
البحر الأحمر شهدت منطقة انتشار نشطة جيولوجيا جداً مع الصهارة سويلابل على (تناظري ريدج وسط المحيط الأطلسي)، ومما يؤدي الانجراف بعيداً من البلدان الأفريقية والعربية لوحة لسنوات 130 مليون. . التدريب الحوض وقد "فقط" 38 مليون سنة مضت في أوليجوسيني، ما زال في الصدع الذي "حدث في شرق أفريقيا" والعديد من ملايين السنين سوف يؤدي إلى محيطجديد. البحر حاليا إلى 1.6 سم سنوياً في الشمال حوالي 0.8 سم، في الجنوب. بعد عزلة المتكررة من المحيط الهندي، واتصال مؤقت مع البحر الأبيض المتوسط وحتى التجفيف، وصلت البحر الأحمر إلى حالتها الراهنة قبل 5000 سنة تقريبا.
ما هو الشعب المرجانية؟
الشعب المرجانية ارتفاع طويلة، ضيقة في الجزء السفلي. قد تكون الشعاب المرجانية العميقة تحت سطح الماء حتى أنها قريبة أو خارج
الشعاب الهدابيه
هذه الشعاب المرجانية هي دائماً قريبة من الساحل، وتنمو عبوره. الشعب المرجانية الهدابيه يمتد على طول ساحل البر الرئيسي أو من جزيرة. هو النوع الأكثر شيوعاً من الشعاب المرجانية في البحر الأحمر، وواحد فقط تقريبا. التهديب المرجانية الممتدة على طول من السواحل، ويمكن أن يكون العديد من كم. أن العرض عادة يمكن أن يكون أقل من 100 متر ولكن أيضا عدة مئات من الأمتار. تحدث أولاً مباشرة على الشاطئ في ذروة الحدود المائية المرجانية الهدابيه وتمتد أنفسهم مع نموها دائماً أكثر عبوره. على العرض النهائي يعتمد على حيث قاع البحر ينخفض انخفاضا حادا. ويظل سطح هذه الشعاب الهدابيه ضيق أدناه المائي دائماً في نفس الارتفاع.
كل الشعب المرجانية يمكن أن يكون موجوداً في مختلف مناطق كسر حيث هناك السائدة في ظروف مختلفة من النباتات والحيوانات الحية. هذه المناطق هي وضوحاً بطريقة مختلفة في أنواع مختلفة من الشعاب المرجانية، وأيضا داخل الشعب المرجانية قد يختلف نوع من البناء. هيكل نموذجي للشعب المرجانية الهدابيه مفسرة أدناه.
تجاور منطقة الشاطئ مباشرة إلى البر الرئيسي. انخفاض المد الجافة مرتين طوال اليوم لعدة ساعات.
نحو البحر، الشعاب المرجانية كريست، الجزء الأفقي من الشعاب المرجانية، الانضمام إلى. منطقة الخارجي بين المنحدر المرجاني الداخلية والحافه الخارجية الشعاب المرجانية تقع ابدأ الجافة. وهو في متوسط 10 أقدام، وقد عمق مياه من 40 سم إلى 1 متر. اقتراح موجه قوية يمنع ذلك الرمل ومواد أخرى فضفاضة المودعة. وتشكل قنوات وإنفاق تدفق قوي. الحافة الخارجية للشعاب المرجانية تتعرض للأمواج القوية.
قبل الشعاب المرجانية، مما يمثل الانتقال من منحدر الشعاب المرجانية إلى البحر المفتوح، ويمكن الاطلاع على ركائز منفصلة من الشعاب المرجانية التي هي متضخمة مزدحمة بالمرجان عن طريق تمتد من الرمل. في المياه العميقة أمام أركان الشعاب المرجانية سوف تجد العديد من الأنواع من الصخور والشعاب المرجانية الناعمة، الترقيم مع زيادة انخفاض عمق المياه.
منزل صغير العديد من الشعاب المرجانية، التي المنبع من الساحل وحتى مثيرة للاهتمام لجعل استكشاف الشعاب المرجانية مع تاوتشينبريلي أو معدات الغوص فريدة من نوعها في خليج مقادي. في عروض المد والجزر المنخفضة رحلة على الأقدام، ولكن يرجى ارتداء النعال، الأرض جزئيا حادة جداً.
الآن إلى المهمة الخاصة بك. تسجيل ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت هذه الأرض للإجابة على الأسئلة التالية:
1السؤال: يقع لماذا الشعب المرجانية ومن الذي هو الصخرة الشعاب المرجانية أساسا؟
2السؤال: ماذا الصخرة على الشعاب المرجانية؟
3السؤال: باختصار وصف بنية للصخرة؟
4السؤال: كيف بعيدة عن الشاطئ يبدأ البيت الشعب المرجانية في خليج مقادي؟
5السؤال: سوف تشاهد من الشاطئ على شكل L رصيف، من حيث يمكنك الوصول إلى الشعاب المرجانية. كم من الوقت هذا جيتي على وشك وكم عدد الوظائف أزواج هو الجزء القصير للأم؟
اختياري: جعل صورة لك والخاص بك لتحديد المواقع على الجسر والجسر في الخلفية
الرجاء إرسال إلى العنوان الموجود في ملف التعريف الخاص بي إجاباتك والرجاء كتابة بلوق الدخول الخاص بك باللغة الإنجليزية أو الألمانية. يمكنك تسجيل الدخول مباشرة. ينبغي أن لا تكون موافق على الإجابات أنا سوف يوقع معك.
المتعة مع ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت هذه الأرض!
المصادر: ويكيبيديا, www.starfish.ch, www.BG-Bab.AC.at\/Jordan\/German\/korallen.htm.
صور: مالك من ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت
 Reef Makadi Bay
Reef Makadi Bay
Makadi Bay is a holiday resort in Egypt. The complex is located about 30 kilometers south of Hurghada at the Red Sea.
This place is spread on about 4 kilometers of coast line in a small bay, the Makadi Bay and its southern branches. It is almost only used by tourists.
.
The place consists of 20 larger hotels and clubs. A slightly shelving beach is situated in the center of the bay. In a short distance from this beach you can find smaller house reefs and a larger fringing reef at the northern side of the bay with a lot of diving opportunities. Directly behind the hotel resort the Arabian Desert opens.
The Red Sea
The Red Sea marks a geologically highly active spreading zone with macerating magma (similar to the Mid-Atlantic Ridge) which causes the divergence of the African and the Arabian Plates since 130 millions years. The formation of a sink could “only” be foreseen 38 million years ago, in the Oligocene, and it continues into the Rift Valley and will finally lead to a new ocean in a million of years. At the moment, the ocean expands by 0,8 cm in the North and by 1,6 cm in the South each year. After several isolations from the Indian Ocean and a temporary connection to the Mediterranean Sea and even dehydration the Red Sea keeps its recent state since 5000 years only.
What is a reef?
A reef is a long, narrow elevation at the bottom of the sea. Reefs can be deep below the surface of the water, they can reach or even go above the surface of the sea.
Fringing reef
These reefs are always situated close to the coast and are growing seawards. Fringing reefs extend along the coast of the mainland or an island. It is the most common type of reef in the Red Sea and almost the only one. Fringing reefs can be found along the coasts and can have a length of several kilometers. There width is mostly below 100 meters but sometimes they also can have a width of several hundred meters. At first, fringing reefs will occur close to the cost at the height of the low-water line and will expand towards the sea when growing. Their final width depends from the ocean bed and its slope. The surface of the fringing reef still remains at the same height, close beneath the water surface.
Each reef can be divided into different zones where due to the predominant conditions different plants and animals are living. These zones are varying from reef type to type and also within one reef type the  structure of these zones may vary. Within the following text a typical type of fringe reef will be explained:
structure of these zones may vary. Within the following text a typical type of fringe reef will be explained:
The main land will be directly followed by the beach zone. At low tide this area will be dry for several hours twice a day.
Towards the sea the reef roof, the horizontal part of the reef, will follow up. The outer area between the inner reef slope and the outer reef slope will never fall dry. This area is about 10 meters wide and usually has a depth of about 40 cm up to one meter. A strong undulation prevents from accumulation of sand and other loose material. Tide strong tunnels and cannels will occur. The outer reef slope will be exposed to strong surf.
In the inner reef where the reef slope descends to the open sea you can find reef pillars covered by corals. These pillars are separated from each other by sandy areas.
In the deepening water in front of the pillars a lot of hard and soft corals can be found, there amount decreases with the water depth.
The various small house reefs offshore unique for Makadi Bay are offering many opportunities to explore the reef with the help of diver eyeglasses or with a complete diving gear. At low tide it is also possible to explore the reef by foot, but please keep in mind the wear bathing shoes due to the underground which can be very sharp at some areas.
Now your task. To log this Earth Cache please answer the following questions:
Question1: What kind of reef is it about and of what kind of rock mostly?
Question 2: What does the rock arise in the reef from?
Question 3: Briefly describe the structure of the rock?
Question 4: What is the distance between the beach and the reef in Makadi Bay?
Question 5: From the beach you can see an L-shaped base from where you can reach the reef. How long is this base approximately and of how many pairs of pillars the shorter part of the “L” is build on?
Optional: Take a photo of you and your GPS on the base or with the base in the background.
Please send your answers to the address in my profile and create your visit log-in in English or German. You can login immediately. If the answers are not OK, I’ll get in touch with you.
Have fun with this Earth Cache!
Sources: Wikipedia www.starfish.ch, www.bg-bab.ac.at/jordan/german/korallen.htm
Photos: Owner of the cache

Hausriff Makadi Bay
Makadi Bay ist ein Ferienort in Ägypten. Die Anlage liegt rund 30 Kilometer südlich von Hurgahada am Roten Meer.
Die rein touristisch geprägte Ansiedlung liegt auf rund 4 Kilometer Küstenlänge an einer kleinen Bucht, der Makadi Bay und ihren südlichen Ausläufern.
Der Ort besteht fast ausschließlich aus rund 20 größeren Hotel- und Clubanlagen. Im Zentrum der Bucht gibt es einen flach abfallenden Sandstrand. In kurzer Entfernung vor dem Strand sind einige kleinere Hausriffs zu beobachten und ein etwas längeres Saumriff zieht sich an der nördlichen Flanke der Bucht hinaus und bietet Tauchmöglichkeiten. Direkt hinter den Hotelanlagen beginnt die Arabische Wüste.
Das Rote Meer
Das Rote Meer markiert eine geologisch hochaktive Spreizungszone mit aufquellendem Magma (analog dem Mittelatlantischen Rücken) und bewirkt dadurch das Auseinanderdriften der Afrikanischen und der Arabischen Platte seit 130 Millionen Jahren. Die Ausbildung einer Senke verdeutlichte sich „erst“ vor 38 Millionen Jahren im Oligozän, setzt sich im Ostafrikanischen Graben fort und wird in vielen Millionen Jahren zu einem neuen Ozean führen. Zurzeit wird das Meer jedes Jahr im Norden um 0,8 cm, im Süden um 1,6 cm breiter. Nach mehrfacher Isolierung vom Indischen Ozean, vorübergehender Verbindung mit dem Mittelmeer und sogar Austrocknung erreichte das Rote Meer seinen jetzigen Zustand erst vor knapp 5000 Jahren.
Was ist ein Riff?
Ein Riff ist eine langgestreckte, schmale Erhebung auf dem Gewässerboden. Riffe können tief unter der Wasseroberfläche liegen, bis an sie heran reichen oder darüber hinaus ragen.
Saumriff
Diese Riffe verlaufen immer in Küstennähe und wachsen seewärts. Ein Saumriff erstreckt sich entlang der Küste des Festlandes oder einer Insel. Es ist der am weitesten  verbreitete Rifftyp und im Roten Meer fast der einzige. Saumriffe erstrecken sich entlang von Küsten und können viele Kilometer lang sein. Ihre Breite beträgt meist unter 100 Meter kann jedoch auch mehrere hundert Meter betragen. Saumriffe entstehen zunächst unmittelbar am Ufer auf Höhe der Niedrigwassergrenze und dehnen sich mit ihrem Wachstum immer mehr seewärts aus. Ihre Endbreite hängt davon ab, wo der Meeresboden steil abfällt. Die Oberfläche des Saumriffs bleibt dabei immer auf gleicher Höhe dicht unterhalb der Wasserlinie.
verbreitete Rifftyp und im Roten Meer fast der einzige. Saumriffe erstrecken sich entlang von Küsten und können viele Kilometer lang sein. Ihre Breite beträgt meist unter 100 Meter kann jedoch auch mehrere hundert Meter betragen. Saumriffe entstehen zunächst unmittelbar am Ufer auf Höhe der Niedrigwassergrenze und dehnen sich mit ihrem Wachstum immer mehr seewärts aus. Ihre Endbreite hängt davon ab, wo der Meeresboden steil abfällt. Die Oberfläche des Saumriffs bleibt dabei immer auf gleicher Höhe dicht unterhalb der Wasserlinie.
Jedes Riff lässt sich in verschiedene Zonen gliedern, in denen aufgrund der dort vorherrschenden Bedingungen unterschiedliche Pflanzen und Tiere leben. Diese Zonen sind bei den verschiedenen Rifftypen unterschiedlich stark ausgeprägt, und auch innerhalb eines Rifftyps kann der Aufbau variieren. Nachfolgend wird der typische Aufbau eines Saumriffs erläutert.
Die Strandzone schließt sich direkt an das Festland an. Bei Ebbe fällt sie im Tagesverlauf zweimal für mehrere Stunden trocken.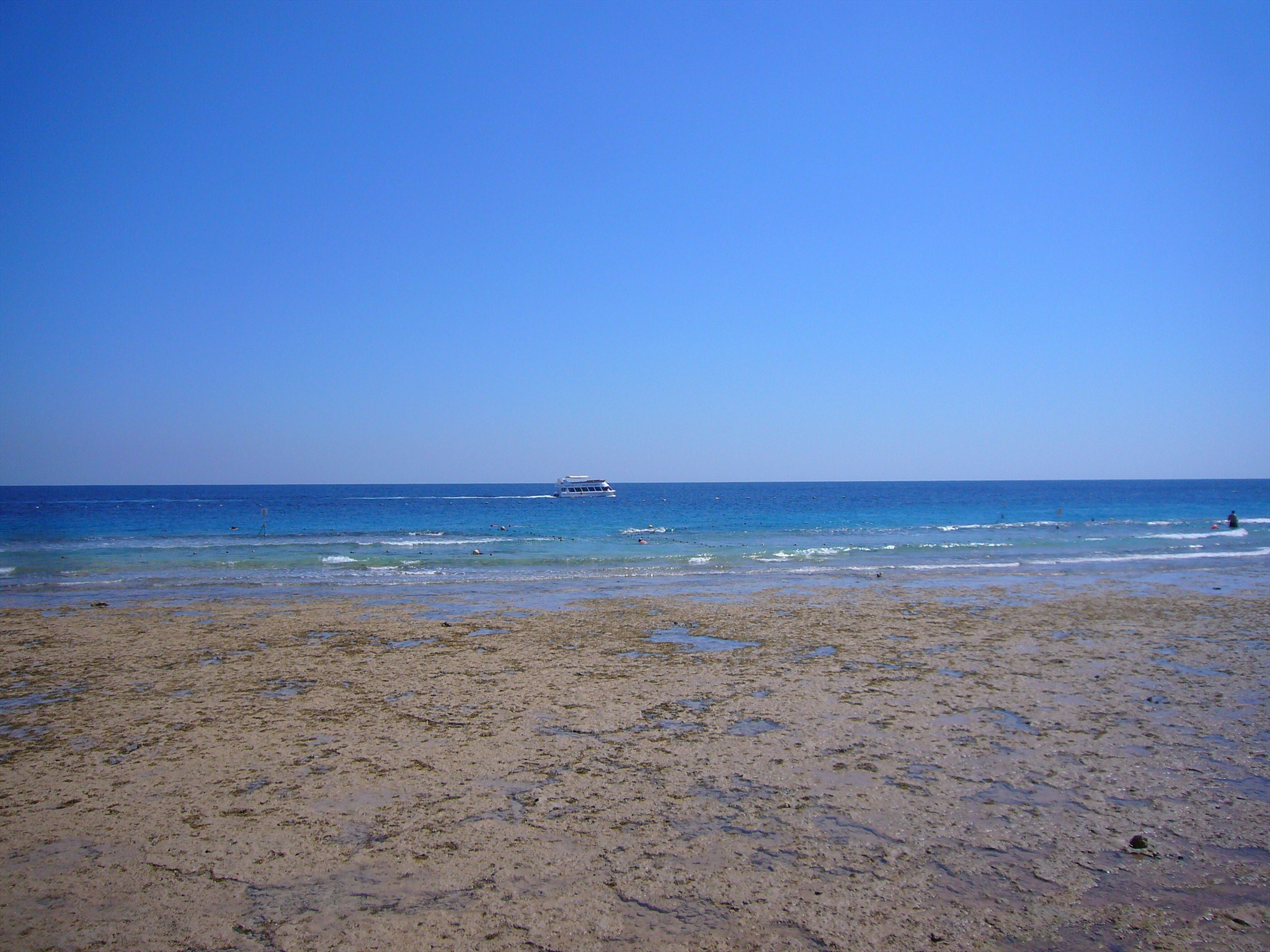 
In Richtung Meer schließt sich das Riffdach, der horizontale Teil des Riffs, an. Der äußere Bereich zwischen Innenriffhang und der Außenriffkante fällt niemals trocken. Er ist durchschnittlich 10 Meter breit, und weist eine Wassertiefe von 40 cm bis zu einem Meter auf. Eine starke Wellenbewegung verhindert, dass sich Sand und anderes loses Material ablagert. Es bilden sich strömungsstarke Tunnel und Kanäle. Die Außenriffkante ist starker
Brandung ausgesetzt.
Im Vorriff, das den Übergang vom Riffhang zur offenen See darstellt, finden sich durch Sandflächen voneinander getrennte Riffpfeiler, die dicht von Korallen bewachsen sind. Im tiefer werdenden Wasser vor den Riffpfeilern finden sich viele Gattungen von Stein- und Weichkorallen, deren Anzahl mit zunehmender Wassertiefe abnimmt.
Nun zu deiner Aufgabe.Um diesen Earth Cache zu loggen beantworte bitte folgende Fragen:
Frage 1: Um was für ein Riff handelt es sich und aus welchem Gestein besteht das Riff hauptsächlich?
Frage 2: Woraus entsteht das Gestein im Riff?
Frage 3: Beschreibe kurz die Struktur des Gesteins?
Frage 4: Wie weit vom Strand entfernt beginnt das Hausriff in Makadi Bay?
Frage 5: Vom Strand aus siehst du einen L-förmigen Steg, von dem aus man in das Riff gelangen kann. Wie lang ist dieser Steg ungefähr und auf wie vielen Pfosten Paaren steht der kurze Teil des L?
Freiwillig, aber erwünscht: Mache ein Foto von Dir und deinem GPS auf dem Steg oder mit dem Steg im Hintergrund.
Deine Antworten schick bitte an die Adresse in meinem Profil und verfasse deinen Logeintrag bitte in Englisch oder Deutsch. Du kannst sofort loggen. Sollten die Antworten nicht okay sein werde ich mich bei dir melden.
Viel Spaß mit diesem Earth Cache!
Quellen: Wikipedia, www.starfish.ch, www.bg-bab.ac.at/jordan/german/korallen.htm
Fotos: Owner des Cache