You can claim a "found it" and after, could you answer the following tasks (please text me a message, the picture is welcome and optional):
1-On which kind of earth layer are you walking? And why? (Please read the description)
2- Which kind of erosion shaped this sand "arm" into the ocean and which kind of layer is harder?
3- In wich direction flows the Canary current and why?
4-Where is the backshore and do you think that the sea can reach the building on the beach and why?
5-What is the name of the main island in the middle of this coastal lagoon?
Vous pouvez revendiquer un "trouvé" et après, pourriez-vous répondre aux questions suivantes (s'il vous plaît envoyez-moi un message, l'image est la bienvenue et facultative):
1-Sur quel type de couche de terre marchez-vous? Et pourquoi? (S'il vous plaît lire la description)
2- Quelle érosion donne la forme actuelle de cette barre de sable séparant la lagune de l'océan et quel type de sol est plus dur?
3- Dans quelle direction coule le Canarie courant et pourquoi?
4-Où est la limite haute de l'estran et pensez-vous que la mer peut atteindre les constructions en bas sur la plage et pourquoi?
5-Quel est le nom de l'île principale dans le milieu de cette lagune côtière?
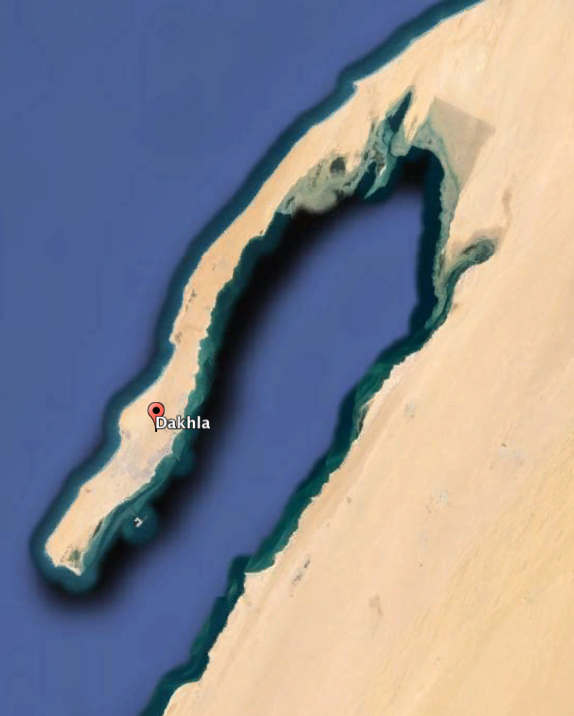
Dakhla coastal lagoon is a shallow inland marine water oriented parallel to the coast and connected to the ocean. This lagoon is delta-shaped. The longshore drift carries and deposits sediment across the concave coastline and creates this bay barrier. This sand bar was formed naturally with ocean current and wind. This current is called CANARY CURRENT. The north-wind shapes this lagoon too and produces circulation of water. Actually, this is great spot for kite-surfing.
Those features are divided into choked, restricted or leaky systems. This classification is based on the degree of water exchange.
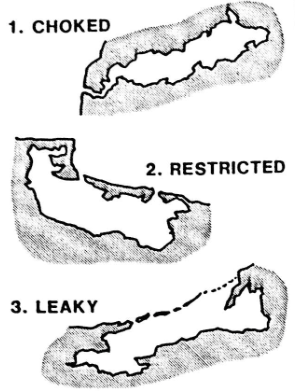
Here, the Dakhla coastal lagoon is a restricted one. This kind of lagoon is large with a wide water body , oriented shore parallel and with one or more inlet channel. This lagoon has a a well defined tidal circulation. The tidal currents maintain the inlet by removing incoming sands as a flush.
Dakhla Lagoon has a surface area of 315 Square Miles with a maximum depth of 65 ft
The productivity of these ecosystems has been recognized worldwide, and their natural resources have been exploited since many centuries (fisheries, gathering of plants and algae, salt extraction, aquaculture). Now, the lagoon is a no-fishing zone and motor boats are forbiden, excepted to rescue sailboarders or kite-surfers.
This mainland was formed in the Quaternary Period (Miocene-Pleistocene). This is the AAIUN BASIN. There is a friable earthy deposit consisting of clay and calcium carbonate called marl and a sedimentary rock containing shells called lumachelle. You can see two kinds of marl:
- white marl with sand
- yellow marl with clay.
Those are the only two layers (marl and lumachelle) you can see here.
From this observatory, you can sea the beach with the backshore and foreshore zones.
The backshore zone is the area of a beach normally affected by waves only during a storm at high tide and the foreshore zone is the area of a beach between the ordinary low tide mark and the high tide mark.
La lagune côtière de Dakhla est espace maritime intérieur peu profond orienté parallèlement à la côte et relié à l'océan. Cette lagune a une forme delta. Le courant littorale porte les dépôts de sédiments le long du littoral concave et crée cette barrière appelée lido. Cette barre de sable s'est donc formée naturellement avec le vent et les courants océaniques. Ce courant est appelé, le CANARIE courant. Le vent du nord façonne cette lagune et produit la circulation de l'eau. C'est un excellent endroit pour le kite-surf.
Ces lagons côtiers sont divisés en trois groupes: fermés, restreints ou ouverts. Cette classification est basée sur le taux d'échange de l'eau.
Ici, la lagune de Dakhla est une lagune restreinte. Ce genre de lagune est grande, avec un plan d'eau large, orientée parallèle à la rive océanique et avec un canal d'entrée. Cette lagune a une circulation des marées bien défini. Les courants de marée maintiennent l'entrée en enlevant sables entrants comme une chasse d'eau.
Le lagon de Dakhla a une superficie de 815 kilométres carrés avec une profondeur maximale de 65 pieds.
La productivité de ces écosystèmes a été reconnu dans le monde entier, et leurs ressources naturelles ont été exploitées depuis plusieurs siècles (pêche, cueillette de plantes et d'algues, l'extraction du sel, de l'aquaculture). Maintenant, la lagune est une zone de non-pêche et les bateaux à moteur sont interdits, sauf pour sauver les véliplanchistes ou les kite-surfeurs.
Ce continent a été formé dans le Quaternaire (Miocène-Pléistocène). Cette partie du Sahara Occidental appartient au BASSIN d'AAIUN. Il ya un dépôt de terre friable composé d'argile et de carbonate de calcium appelé marnes et une roche sédimentaire contenant des coquillages appelée lumachelle. Ce sont les deux seules types de couches géologiques observables. Les marnes sont de deux types:
- marnes blanches sableuses
- marnes jaunâtres avec des dépots d'argile
De cet observatoire, vous pouvez observer la plage avec les zones de marée maximale et la zone d'estran.
La zone de marée maximale est la zone de la plage normalement affectée par les marées les plus hautes et la zone d'estran est la zone de la plage entre la marée basse et haute alternativement couverte et découverte par l'océan.