Direction et accès :
L´Earthcache se trouve sur le site de l'Étang des Salines.L'accès se fait par la D9 depuis le rond point avant Sainte Anne. Vous prenez la route à gauche 200 mètres avant la Grande Anse. La route se transforme en piste mais cette dernière est en relativement bon état.
Géologie et Sol :
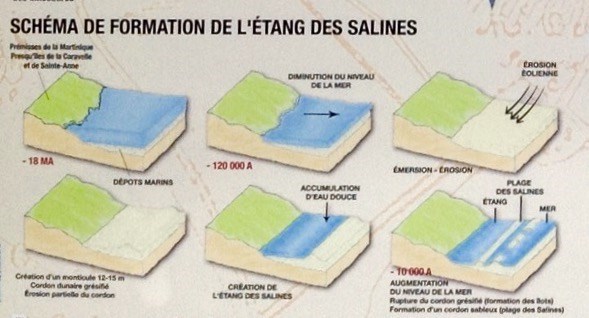
Situé à l’extrême sud de l’île, sur la commune de Sainte Anne, l’étang des Salines s’est formé sur l’une des deux plus anciennes formations terrestres de l’île (l’autre étant la Caravelle, à l'est de la Martinique), vieille de plus de 20 millions d'années. Cette formation, d’origine volcanique, a été transformée en plateau par l’érosion pour être ensuite recouverte de sédiments calcaires issus des récifs coralliens lors de l'immersion par la mer d'une importante partie de la baie de Sainte Anne au cours de l'Eernien. Apres carottage, le fond de l'étang révèle sa composition faite de vase argileuse à argile grumeleuse. Ce type d’argile présente une faible porosité et un risque d’érosion important en cas de pluie. Les berges de l'étang sont composées principalement de sable.
Topographie et Bathymétrie :
![]()
L’Etang des Salines est situé sur la presqu’île de Sainte Anne qui est constituée d’un plateau d’une altitude moyenne de 35 à 45 mètres. L'étang est circonscrit au nord par trois mornes dont les altitudes oscillent de 48 à 119 mètres. Les deux premiers édifices situés au nord-est de l'étang constituent une ceinture homogène. Sur sa bordure orientale, l'étang est circonscrit par deux petites buttes, aux versants concaves, dont les altitudes oscillent de 16 à 28 mètres. Sa profondeur varie entre 0,3 et 0.9 mètres selon les endroits, sachant que la profondeur la plus importante se situe en son centre. Le fond de l’étang est principalement constitué de vases. L’amas vaseux est plus épais dans la partie nord de l’étang (de 0,7 à 0,8 m) que dans la partie sud (de 0,3 à 0,4 m), cela pourrait s'expliquer par une forte érosion des versants septentrionaux.
Cette lagune de 207 hectares dont 97 hectares protégés, entourée de mangrove, de savane, de fourrés et forêt sèche fait l'objet d'une protection depuis 1998 par le conservatoire du littoral.
Hydrodynamique :

Le fonctionnement de l'étang s'effectue par des échanges avec le milieu marin de façon régulière par la marée, et exceptionnellement à l'occassion de fortes houles. Ces échanges se font principalement par :
- un canal sud, le plus court, 400 mètres de long pour une largeur moyenne de 6 mètres et une profondeur d'environ 1 mètre et communiquant directement avec l'Océan Atlantique.
- un second canal au nord, bien plus long et de plus faible section, qui s'étend sur plus de 1 km de long et traverse une zone marécageuse avant d'aboutir dans la mer des Caraïbes. Compte tenu de ses dimensions, et du fait qu’il traverse une mangrove avant d’aboutir à la mer, ce chenal n’alimente la lagune que lors de très fortes marées.
Le niveau d'eau de l'étang varie donc en fonction de la marée comme la mer :
- se remplissant avec la marée montante.
- et se vidant de son surplus à marée descendante. A marée basse on peut voir le fond de l'étang, constitué principalement de vase molle qui sèche et craquelle au soleil.
L’eau de l'étang des salines est saumâtre. En effet, l'étang est alimenté à la fois en eau douce provenant du ruissellement des versants alentours et en eau salée provenant des deux canaux.
Il faut noter une très forte salinité de l’eau de l’étang, supérieure à celle de l’eau de mer, pouvant s’expliquer par un apport trop faible d’eau douce couplé à une très forte évaporation.
Faune et Flore :
En s’introduisant dans cette lagune, les eaux de l’océan Atlantique et de la mer des Caraïbes, produisent des conditions écologiques spécifiques qui favorisent le développement de populations aquatiques riches et diversifiées.
Le site constitue la dernière étape pour de nombreuses espèces d’oiseaux en provenance d'Amérique du nord s’apprêtant à traverser le chenal de Sainte-Lucie. Des mangroves servent de zone d’alimentation pour beaucoup d'invertébrés et autres espèces marines.
L'Etang d'hier :
Cette zone a joué un rôle économique important entre le 18e et le 20e siècle grâce à la production de sel, d'où le nom attribué à l’étang. De part sa localisation et les ressourcent qu'il offre, l'étang a autrefois fait l'objet d'exploitations multiples et variés, jouant ainsi un rôle important dans la vie de l'époque.
L'Etang d'aujourd'hui :
En plus des menaces que constituent les pesticides et le ruissellement de produits polluants, le tourisme se révèle problématique car le site comprend une des plages les plus fréquentées de la Martinique avec près d'un million de visiteurs par an.
L'Etang des Salines a le label "Site Ramsar" et en voie de devenir "Grand Site"
Qu'est-ce qu'un site Ramsar ?
Depuis 1971, la Convention de Ramsar entend préserver les zones humides et promouvoir l'utilisation rationnelle de leurs ressources. Elle travaille à élaborer et maintenir un réseau international de zones humides importantes pour la conservation de la biodiversité mondiale et les services écosystémiques rendus.
Aujourd'hui plus de 2 100 zones humides d'importance mondiale sont inscrites sur la liste Ramsar dont 43 sites en France.
Pour mieux comprendre le fonctionnement de l’étang des Salines, le Conservatoire du littoral a réalisé :
- un observatoire aux oiseaux et ses panneaux de découverte de la faune et la flore
- un itinéraire de promenade sur pilotis avec des panneaux thématiques et ludiques
- un livret pédagogique sur la mangrove.
==================================================
POUR VALIDER VOTRE VISITE :
Après avoir visité le site :" Loguez cette cache "Found it" et envoyez-moi vos propositions de réponses soit via mon profil, soit via la messagerie geocaching.com (Message Center) en précisant bien le nom de l’earthcache, et je vous contacterai en cas de problème." ( pas de réponses dans les logs SVP) :
1 - Comment a été formé l'Etang des salines ? Et combien d'hectares sont protégés ?
2 - Comment fonctionne t-il ?
3 - Pourquoi le niveau de l'étang change t-il tout le temps ?
4 - Durant des siècles après sa formation, plusieurs variétés d'exploitation se sont succédées sur l'étang. Quelles sont elles ? Citez au moins cinq d'entre elles, et chacune de leur époque ? Pour cela vous devrez aller sur le site aux coordonnées suivantes pour trouver les réponses :( N 14 23.967 W 60 52.472 )
5 - Rendez vous aux coordonnées suivantes ( N 14 23.819 W 60 51.834 ), et admirez le paysage tout autour de vous :
a)- Que voyez-vous à votre gauche ?
b) - Et à votre droite ?
- Pour immortaliser votre visite , une photo du site, de vous ou votre GPS sera la bienvenue, bien que facultative.
Note :
Rappel concernant les « Earthcaches »: Il n'y a pas de conteneur à chercher ni de logbook à renseigner. Il suffit de se rendre sur les lieux, de répondre aux questions ci-dessus et de nous renvoyer les réponses.
============ENGLISH VERSION============
Direction and access:
Earthcache is on the site of the Etang des salines. The access is made by D9 since the traffic circle before the village of Sainte Anne. You set off to the left 200 meters before the Grand Anse. The road is transformed into track but the latter is in relatively good state.
Geology and Ground :
Situated extremely south of the island, on the municipality of Sainte Anne, the Etang des salines formed on one of the two more oldest formations of the island (being the other one the Caravel, east of Martinique), old of more than 20 million years. This formation, of volcanic origin, was transformed in the tray by the erosion to be then covered with calcareous sediments stemming from coral reefs during the dumping by the sea of an Important part of sainte Anne's bay during Eernien. After core drilling, the bottom of the pond reveals its composition made from clayey mud to lumpy clay. This type of clay presents a low porosity and a risk of erosion mattering in case of rain. The banks of the pond are mainly consisted of sand.
Topography and Bathymetry:
The Etang des salines is situated on the peninsula of Sainte Anne which is constituted by a tray(plateau) of an average height from 35 to 45 meters. The pond is confined in the North by sad three the heights of which oscillate from 48 to 119 meters. The first two buildings situated in the northeast of the pond constitute a homogeneous belt. On its oriental border, the pond is confined by two small mounds, in the concave hillsides, the heights of which oscillate from 16 to 28 meters. Its depth varies between 0,3 and 0.9 meters according to places, knowing that the most important depth is situated in its center. The bottom of the pond is mainly constituted by vases.The muddy heap is more thick in the north part of the pond (from 0,7 to 0,8 m) than in the southern part from 0,3 to 0,4 m), it could give some explanation by a strong erosion of the northern hillsides. This lagoon of 207 hectares among which protected 97 ha, surrounded with mangrove swamp, with savanna, with undergrowth and dry forest is the object of a protection since 1998 by the Conservatoire du Littoral.
Hydrodynamics:

The functioning of the pond is made by exchanges with the marine environment in a regular way by the tide, and exceptionally in the occassion of strong swells. These exchanges are mainly made by:
- a shortest, 400 meters long, south channel for an average width of 6 meters and a depth about 1 meter and communicating directly with Atlantic Ocean.
- A second channel in North, longer and of lower section, which extends over more than 1 km in length and crosses a swampy zone before succeeding in the Caribbean Sea. Considering its dimensions, and because he crosses a mangrove swamp before ending in the sea, this channel feeds the lagoon only during very strong tides.
Thus the water level of the pond varies according to the tide as the sea:
- filling with the rising tide.
- And emptying of his surplus in low tide. In low tide we can see the bottom of the pond, established mainly by soft mud which dries and cracks in the sun.
The water of the pond of saltworks is brackish. Indeed, the pond is fed at the same time with fresh water resulting from the streaming of hillsides surroundings and with salt water resulting from both channels.
It is necessary to note a very strong salinity of the water of the pond, superior to that of the sea water, being able to give some explanation by a too low contribution of fresh water coupled with a very strong evaporation.
Flora and fauna:
By getting into this lagoon, waters of the Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea, produce specific ecological conditions which favor the development of rich and diversified aquatic populations. The site establishes the last stage for numerous species of birds from North America getting ready to cross the channel of Saint Lucia. Mangrove swamps serve as zone of food for a lot invertebrate and other marine sorts
The Pond of yesterday:
This zone played an economic role mattering between the 18th and the 20th century thanks to the production of salt, where from the name attributed to the pond. From part its localisation and they get fresh ideas that it offers, the pond was formerly the object of multiple exploitations and varied, so playing an important role in the life of period.
The Pond of today:
Besides the threats which establish pesticides and streaming of polluting products, the tourism shows itself problematic because the site includes one of the busiest beaches of Martinique with near a million visitors a year.
The Etang des salines has the label " Site Ramsar " and to become " Big Site "
What a site Ramsar?
Since 1971, the Convention of Ramsar intends to protect the wet zones and to promote the rational use of their resources. It works to develop and to maintain an international network of wet zones important for the preservation of the world biodiversity and the returned ecosystematic services. Today more than 2 100 wet zones of world importance are registered on the list Ramsar among which 43 sites in France.
To understand better the functioning of the Etang des salines, the Conservatoire ofLittoral realized:
- A monitoring observatory of birds and Its panels Signs of discovery of the flora and fauna.
- A route of on piles walk with thematic and playful panels signs.
- An educational notebook on the mangrove swamp.
==================================================
TO VALID YOUR VISIT
Having visited the site: "Log this hiding place" Found it "and send me your proposals of answers either via my profile, or via the messaging geocaching.com (Center message) by specifying well the name of the earthcache, and I will contact you in case of problem." (No answers in logs PLEASE)::
1 - How was formed the Etang des Salines? And how many hectares are protected ?
2 - How It work?
3 - Why the level of the pond changes all the time?
4 - For centuries after Its formation, several varieties of exploitation succeded on the pond. What are they? Give at least five of them, and each their period ? For it, you will have to go on the site to the following coordinates to find the answers: (N 14 23.967 W 60 52.472).
5 - Go to the following coordinates (N 14 23.819 W 60 51.834), and admire the landscape everything around you:
a) - what do you see in your left hand ?
b) - and in your right hand ?
To immortalize your visit, a photo of the site, you or your GPS........ will be welcome, although optional.
Nota :
Reminder on "Earthcaches" There is no container or logbook to find information. Simply visit the site, to answer questions above and send us the answers.
==========================================================================================
Sources / Sources :
Wilkipedia, BRGM- FR, Conservatoire du littoral Martinique, UNRP 24//09/2014.
==========================================================================================
Since October, 24 2016
