
At the listed coordinates you will find ponor where River Dobra sinks underground. This ponor is known as Djula's Ponor and it is located in the middle of the town of Ogulin. The ponor is a nice example of karst geomorphology.
River Dobra
River Dobra is a karst river located in the Primorje-Gorski Kotar County and the Karlovac County in Croatia. It rises near Skrad and Ravna Gora in Gorski Kotar region, and flows into the River Kupa near Karlovac. It is 107.9 kilometres long and its basin covers an area of 900 square kilometres.
River Dobra
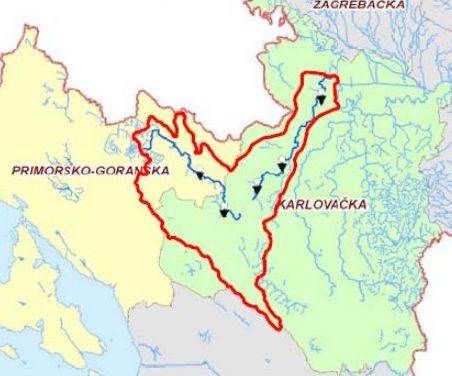 Source: Hydrological Analysis of Dobra River Catchment Area
Source: Hydrological Analysis of Dobra River Catchment Area
The flow of the River Dobra is divided into three parts: (1) Upper Dobra or Ogulin Dobra (51.2 km long - from spring to Djula's ponor); (2) River Dobra as subterranean river - flows through the system of karst channels and caverns in the total length of 16,396 meters and resurfaces near the village Gojak (aerial length of subterranean part is 4.6 km); (3) Lower Dobra (52.1 km long).
Karst Landscape
The term “karst” applies to a distinctive type of landscape that develops from the dissolving action of water on soluble bedrock - primarily limestone and marble but also dolostone, gypsum and halite.
Karst Landscape
 Source: wgnhs.uwex.edu
Source: wgnhs.uwex.edu
Karst landscapes are characterized by fluted and pitted rock surfaces, shafts, sinkholes, sinking streams, springs, subsurface drainage systems, and caves. The unique features and three-dimensional nature of karst landscapes are the result of a complex interplay between geology, climate, topography, hydrology, and biological factors over long time scales. Globally, examples of karst topography can be found at all latitudes and at all elevations, with rock types potentially containing karst covering approximately 20% of the Earth’s land surface.
Parts of Karst Landscape
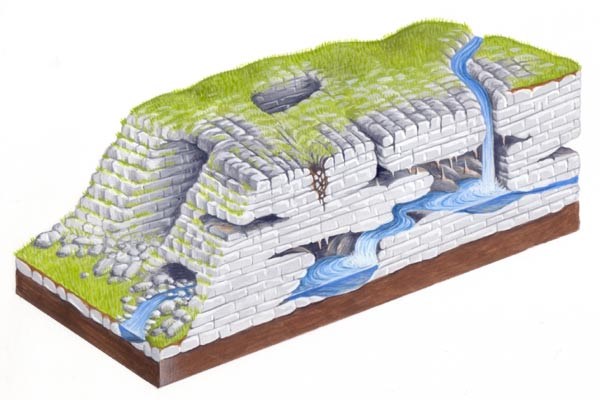
The three-dimensional nature of a karst landscape can be broken down into three parts: (1) exokarst, (2) epikarst, and (3) endokarst.
Parts of Karst Landscape
 Source: northpennines.org.uk
Source: northpennines.org.uk
Exokarst describes all features found on the surface of the karst landscape, ranging from small-scale to large-scale features (e.g., from karren to sinksinkholes to poljes). Epikarst is the zone of solutionally enlarged openings or fractures that extends from the surface (the exokarst) down as much as 10–30 m below the surface to the underlying endokarst. The endokarst describes all deeper components of the underground karst landscape, including the smallest cavities, cave speleothems, cave sediments, and cave passages. The epikarst zone plays a critical role in the karst system, allowing water, air, and other materials (sediment, organic debris, and nutrients) to be readily transferred from the surface to the subsurface.
Logging Tasks
To log this EarthCache answer the following questions:
1. Observe the rock formation above the ponor and describe its color and texture.
2. Observe the ponor itself. Does it belong to exokarst, epikarst or endokarst? Why?
3. Does the ponor represent also an entrance to the cave?
Send your answers through my profile at geocaching.com (through e-mail or message center) and NOT in a log. You don't have to wait for me to approve your answers. Once you send your answers feel free to log this EarthCache as found. If there are problems with your answers, I will contact you.
Sources
1. Alecia M. Spooner, Geology for Dummies, Hoboken: Wiley Publishing, Inc., 2011.
2. Tim Stokes, Paul Griffiths, Carol Ramsey, "Karst Geomorphology, Hydrology, and Management", Compendium of Forest Hydrology and Geomorphology in British Columbia, pp. 373-400, 2010.
3. Ognjen Bonacci, Ivo Andric, "Hydrological Analysis of the Karst River Dobra", Hrvatske Vode, 18(72), pp. 127-138, 2015.
4. Ivana Opala, Nevenka Ozanic, "Hydrological Analysis of Dobra River Catchment Area", Zbornik radova Gradjevinskog fakulteta Sveucilista u Rijeci, 13, pp. 11-32, 2010.
5. Wikipedia.org

Na izlistanim koordinatama pronaći ćete ponor u kojem rijeka Dobra ponire u podzemlje. Ovaj ponor je poznat kao Đulin ponor, a nalazi se u središtu grada Ogulina. Ovaj ponor predstavlja lijep primjer krške geomorfologije.
Rijeka Dobra
Rijeka Dobra je krška rijeka koja se nalazi u Primorsko-goranskoj i Karlovačkoj županiji. Izvire blizu Skrada i Ravne Gore u Gorskom kotaru, a utječe u rijeku Kupu blizu Karlovca. Duga je 107,9 kilometara, a njezin sliv obuhvaća površinu od 900 kvadratnih kilometara.
Rijeka Dobra
 Izvor: Hydrological Analysis of Dobra River Catchment Area
Izvor: Hydrological Analysis of Dobra River Catchment Area
Tijek rijeke Dobre se dijeli na tri dijela: (1) Gornja Dobra ili Ogulinska Dobra (51,2 km duljine - od izvora do Đulinog ponora); (2) rijeka Dobra kao ponornica - teče kroz sustav krških kanala i kaverni u ukupnoj dužini od 16.396 metara, te ponovo izvire blizu sela Gojak (zračna udaljenost podzemnog toka je 4,6 km); (3) Donja Dobra (52,1 km duljine).
Krški krajolik
Pojam "krš" se odnosi na zasebnu vrstu krajolika koji nastaje djelovanjem vode na topivim stijenama - u prvom redu vapnenca i mramora, ali i dolomit, gips i halit.
Krški krajolik
 Izvor: wgnhs.uwex.edu
Izvor: wgnhs.uwex.edu
Krški krajolik je karakteriziran naboranim i udubljenim kamenim površinama, vrtačama, ponornicama, izvorima, podzemnim tokovima i špiljama. Jedinstvena obilježja i trodimenzionalna priroda krškog krajolika predstavlja rezultat kompleksnog međuodnosa geologije, klime, topografije, hidrologije i bioloških faktora tijekom dugih vremenskih perioda. Globalno, primjeri krške topografije se mogu naći na svim geografskim širinama i na svim nadmorskim visinama. Vrste stijena koje potencijalno mogu sadržavati krš pokrivaju 20% zemljine kopnene površine.
Dijelovi krškog krajolika
Trodimenzionalna priroda krškog krajolika se može podijeliti u tri dijela: (1) egzokrš, (2) epikrš i (3) endokrš.
Dijelovi krškog krajolika
 Source: northpennines.org.uk
Source: northpennines.org.uk
Egzokrš obuhvaća krške pojave koje se nalaze na površini krškog krajolika, u rasponu od malih pojava do velikih (npr. od škrapa do vrtača do polja). Epikrš je zona otvora i pukotina koje se šire od površine (od egzokrša) u dubinu i do 10-30 metara ispod površine prema endokršu. Endokrš obuhvaća sve dublje komponente podzemnog krškog krajolika, uključujući najmanje otvore, špiljski ukrasi, špiljski sedimenti i špiljski prolazi. Zona epikrša ima ključnu ulogu u krškom sustavu, jer omogućava redoviti protok vode, zraka i ostalih materijala (sedimenata, organskih ostataka i hranjivih tvari) sa površine u podzemlje.
Zadaci za logiranje
Kako biste logirali ovaj EarthCache odgovorite na sljedeća pitanja:
1. Promotrite stijenu koja se nalazi iznad ponora i opišite njezinu boju i teksturu.
2. Promotrite ponor. Pripada li ponor egzokršu, epikršu ili endokršu? Zašto?
3. Predstavlja li ponor ujedno i ulaz u špilju?
Odgovore pošaljite preko mog profila na geocaching.com, a NE u Vašem logu! Ne morate čekati na moje potvrdjivanje Vaših odgovora. Jednom kada pošaljete Vaše odgovore slobodno logirajte pronalazak ovog EarthCachea. Ako Vaši odgovori budu pogrešni ja ću kontaktirati Vas.
Izvori
1. Alecia M. Spooner, Geology for Dummies, Hoboken: Wiley Publishing, Inc., 2011.
2. Tim Stokes, Paul Griffiths, Carol Ramsey, "Karst Geomorphology, Hydrology, and Management", Compendium of Forest Hydrology and Geomorphology in British Columbia, pp. 373-400, 2010.
3. Ognjen Bonacci, Ivo Andrić, "Hydrological Analysis of the Karst River Dobra", Hrvatske Vode, 18(72), pp. 127-138, 2015.
4. Ivana Opala, Nevenka Ožanić, "Hydrological Analysis of Dobra River Catchment Area", Zbornik radova Građevinskog fakulteta Sveučilišta u Rijeci, 13, pp. 11-32, 2010.
5. Wikipedia.org