Face the Marble

This is a Metamorphic Rock
Metamorphic rocks have been modified by heat, pressure, and chemical processes, usually while buried deep below Earth's surface. Exposure to these extreme conditions has altered the mineralogy, texture, and chemical composition of the rocks.
There are two basic types of metamorphic rocks. Foliated metamorphic rocks such as gneiss, phyllite, schist, and slate have a layered or banded appearance that is produced by exposure to heat and directed pressure.
Non-foliated metamorphic rocks such as hornfels, marble, quartzite, and novaculite do not have a layered or banded appearance.
Marble as mentioned above is a non-foliated metamorphic rock, it is produced from the metamorphism of limestone or dolostone. It is composed primarily of calcium carbonate.
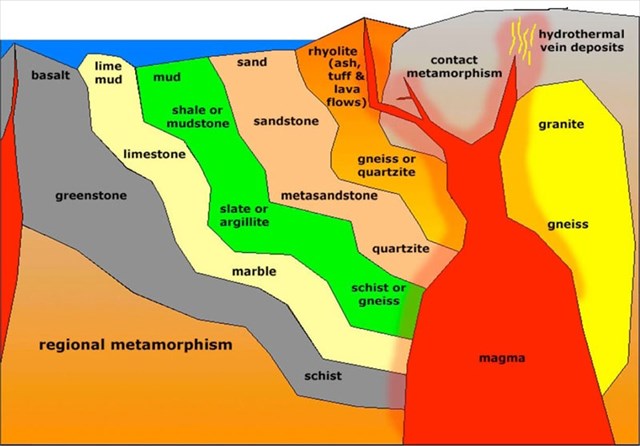
This simplified diagram illustrates the relationship of metamorphic rocks with their parent materials.

This is Marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock that forms when limestone is subjected to the heat and pressure of metamorphism. When it is formed from a limestone with very few impurities, it will be white in color. It is composed primarily of the mineral calcite (CaCO3) and usually contains other minerals, such as clay minerals, micas, quartz, pyrite, iron oxides, and graphite. Under the conditions of metamorphism, the calcite in the limestone recrystallizes to form a rock that is a mass of interlocking calcite crystals. A related rock, dolomitic marble, is produced when dolostone is subjected to heat and pressure.
Mineralogy: 95% calcite (CaCO3) or dolomite Ca,Mg(CO3)2. Impurities may give rise to new minerals such as olivine.

This is how Marble Forms

Most marble forms at convergent plate boundaries where large areas of Earth's crust are exposed to regional metamorphism. Some marble also forms by contact metamorphism when a hot magma body heats adjacent limestone or dolostone.
Before metamorphism, the calcite in the limestone is often in the form of lithified fossil material and biological debris. During metamorphism, this calcite recrystallizes and the texture of the rock changes. In the early stages of the limestone-to-marble transformation, the calcite crystals in the rock are very small. In a freshly-broken hand specimen, they might only be recognized as a sugary sparkle of light reflecting from their tiny cleavage faces when the rock is played in the light.
As metamorphism progresses, the crystals grow larger and become easily recognizable as interlocking crystals of calcite. Recrystallization obscures the original fossils and sedimentary structures of the limestone. It also occurs without forming foliation, which normally is found in rocks that are altered by the directed pressure of a convergent plate boundary.
Recrystallization is what marks the separation between limestone and marble. Marble that has been exposed to low levels of metamorphism will have very small calcite crystals. The crystals become larger as the level of metamorphism progresses. Clay minerals within the marble will alter to micas and more complex silicate structures as the level of metamorphism increases.

Color: Marble is usually a light-colored rock. When it is formed from a limestone with very few impurities, it will be white in color. Marble that contains impurities such as clay minerals, iron oxides, or bituminous material can be bluish, gray, pink, yellow, or black in color.
Marble of extremely high purity with a bright white color is very useful. It is often mined, crushed to a powder, and then processed to remove as many impurities as possible. The resulting product is called "whiting." This powder is used as a coloring agent and filler in paint, whitewash, putty, plastic, grout, cosmetics, paper, and other manufactured products.

Acid Reaction: Being composed of calcium carbonate, marble will react in contact with many acids, neutralizing the acid. It is one of the most effective acid neutralization materials. Marble is often crushed and used for acid neutralization in streams, lakes, and soils.
It is used for acid neutralization in the chemical industry as well. Pharmaceutical antacid medicines such as "Tums" contain calcium carbonate, which is sometimes made from powdered marble. These medicines are helpful to people who suffer from acid reflux or acid indigestion. Powdered marble is used as an inert filler in other pills.
Hardness: Being composed of calcite, marble has a hardness of three on the Mohs hardness scale. As a result, marble is easy to carve, and that makes it useful for producing sculptures and ornamental objects. The translucence of marble makes it especially attractive for many types of sculptures.
The low hardness and solubility of marble allows it to be used as a calcium additive in animal feeds. Calcium additives are especially important for dairy cows and egg-producing chickens. It is also used as a low-hardness abrasive for scrubbing bathroom and kitchen fixtures.

To log this cache.
To get to log this cache you will have to visit and answer the questions which are related to the coordinates given the earthcache.
When answers are collected, send them to CO for verification.
As I own about 50 earthcaches there are MANY mails/messages to answer back on, and I will not always be able to answer right-back, BUT I READ ALL SENT ANSWERS AND LOGS, so if anything is not correct or need an upgrade, you will indeed hear back from me.
Thanks for your understanding, and for picking one of my caches.
You can log immediately answers are sent CO. If there are any questions about your answers CO will contact you.
Logs without answers to CO or with pending questions from CO will be deleted without any further notice.
Please do not include pictures in your log that may answer the questions.
Questions
1. Answer the questions under by visiting the Coordinates.
A. Marble is a metamorphic rock that forms when limestone is subjected to the heat and pressure of metamorphism. What can you say about the Marble at gz? And as Marble is formed from limestone, you often find fossils in these types of stones. Can any fossils be seen here? If so, what types of fossils? (crinoids/corals/brachiopods)
B. Why is the stone color (light/medium colored/dark)?
C. From what you see at gz, what color is the Marble (white/brown/red/Green/Black)? And what is it that the impurities in the marble stone may give rise to?
D. How many % of calcite or dolomite would you guess is in this marble stone at gz?
E. The main Marble color is XXX, what color are the veins and impurities in the stone? (you can give your answer by showing to a couple of the once that is displayed above in the cache text photo under color.)
2. Take a photo of yourself, the group or your GPS when logging the cache.
Without revealing any answers!
(It’s voluntary to post a photo in your online log)