

ESPAÑOL
El Error Intencionado
Es frecuente en los registros de los cachés leer "fácil de encontrar, coordenadas precisas" ; esto es posible gracias a la precisión con que cuenta hoy en día el sistema de posicionamiento global (GPS) , pero no siempre ha sido así...
El proyecto GPS fue concebido inicialmente para uso militar, como un sistema de guía para la navegación tanto aérea como naval en tiempo real. Su propietario es el Departamento de Defensa de los Estados Unidos de América y comenzó a desarrollarse allá por 1973.
Durante las primeras pruebas, los responsables de su desarrollo se sorprendieron de las altas cotas de precisión que alcanzaba el sistema. El Departamento de Defensa, ante la posibilidad de que un servicio de posicionamiento tan preciso pudiera ser utilizado con intenciones hostiles contra los Estados Unidos o sus aliados, decidió degradar de manera intencionada la calidad de la posición proporcionada por el sistema, sin llegar a restringir el uso para fines civiles.
Estas alteraciones de la calidad de la posición, denominadas error intencionado o disponibilidad selectiva (SA) , se conseguían alterando la información sobre las coordenadas de los satélites o el estado de los relojes de los satélites.
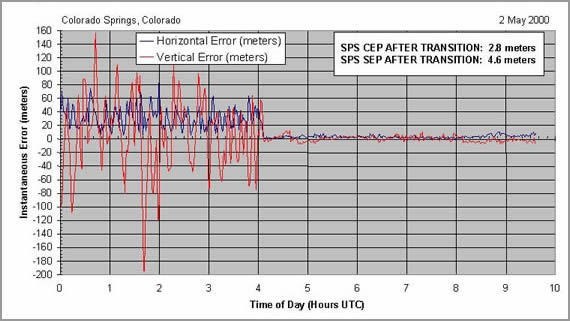
Error en la posición antes y después de eliminar el error intencionado el 2 de mayo de 2000.
Con disponibilidad selectiva las especificaciones del sistema señalaban que la posición horizontal podía encontrarse dentro de un círculo de 100 metros de diámetro el 95% del tiempo. Para el 5% restante el error podía llegar a rebasar los 300 metros.
El 2 de mayo del año 2000 y debido entre otras causas al desarrollo de nuevos y sofisticados métodos de degradación selectiva sobre zonas concretas del globo, a presiones internacionales y a intereses comerciales de Estados Unidos, el presidente Bill Clinton en una declaración presidencial, puso fin de modo permanente, al "error intencionado" (Ver declaración presidencial).
Ubicación del caché
El caché está próximo a monumentos como la Puerta del Carmen, la antigua Facultad de Medicina, el antiguo Palacio de Capitanía o la iglesia de Santa Engracia por lo que es muy recomendable para turistas.
Resolución del caché
Aunque la tecnología del sistema es bastante compleja, el fundamento de su funcionamiento es relativamente sencillo y se basa en que nuestro receptor GPS es capaz de medir la distancia a varios satélites que actúan como puntos de referencia en el espacio, y además conoce sus coordenadas, por lo que puede obtener sus propias coordenadas por triangulación.
Para obtener las coordenadas del caché tendrás que resolver el mismo problema que tu receptor GPS , aunque te lo pondremos más sencillo, sólo tendrás que hacerlo en 2D, en el plano.
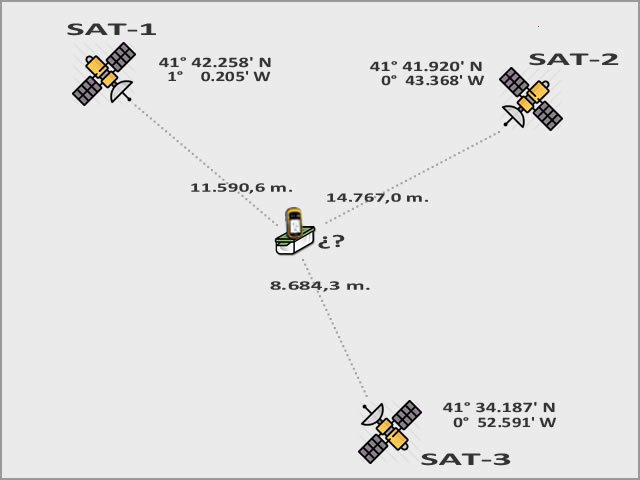
Triangulación GPS en el plano
Puedes comprobar si las coordenadas geográficas que has obtenido son correctas en: GeoChecker.com.
Opcionalmente también podrás resolver el caché contestando a las preguntas que se formularán a continuación sobre el sistema de posicionamiento global.
Entra en CERTITUDE con la concatenación de las respuestas en mayúsculas (Ejemplo: ACDBA) y tendrás la posibilidad de descargar un archivo pdf en el que se explica como resolver el problema utilizando el complemento solver de excel.
Pregunta nº 1
- ¿En qué fecha fue suprimido el error intencionado o disponibilidad selectiva?
A) 1 de mayo de 2001.
B) 2 de mayo de 2000.
C) 2 de mayo de 1808.
D) La disponibilidad selectiva no ha sido suprimida.
Pregunta nº 2
- ¿En qué estado se encuentra la Estación Master de Control del Sistema?
A) Kansas.
B) Utah.
C) Colorado.
D) Nebraska.
Pregunta nº 3
- ¿Cúal es el sistema geodésico de referencia empleado de modo nativo por GPS?
A) European Datum 1950 (ED50).
B) European Terrestrial Reference System 1989 (ETRS89).
C) UTM (Universal Transverse Mercator).
D) World Geodetic System 1984 (WGS84).
Pregunta nº 4
- El sistema de posicionamiento globlal (GPS), además de servicio de geolocalización proporciona...
A) Información meteorológica.
B) Tiempo coordinado.
C) Efemérides astronómicas.
D) Calendario perpetuo y santoral.
Pregunta nº 5
- Considerando las tres dimensiones ¿cuándo se dará la mejor geometría proporcionada por 4 satélites?
A) No son necesarios 4 sat´élites para obtener posición.
B) Uno de ellos situado en la vertical y los otros 3 repartidos regularmente sobre el horizonte.
C) Los 4 repartidos regularmente con un ángulo de elevación de 45º.
D) Los 4 situados lo más próximo posible en la vertical.

Puedes validar la solución a las preguntas y descargar el archivo para resolver el problema en certitude.
Otros cachés de la serie
ENGLISH
The Intentional Error
It is frequent in the logs of the caches to read "easy to find, precise coordinates" ; this is possible thanks to the accuracy of the global positioning system (GPS) , but this has not always been the case ...
The GPS project was initially designed for military use, as a guidance system for both aerial and naval navigation in real time. Its owner is the Department of Defense of the United States of America and began to develop it in 1973.
During the first tests, those responsible for its development were surprised at the high levels of accuracy achieved by the system. The Department of Defense, faced with the possibility that such a precise positioning service could be used with hostile intentions against the United States or its allies, decided to intentionally degrade the quality of the position provided by the system, without restricting the use for civil purposes.
These alterations in the quality of the position, called intentional error or selective availability (SA) , were achieved by altering the information about the satellite coordinates or the state of the satellites' clocks.

`Error in the position before and after removing the intentional error on May 2, 2000.
With selective availability, system specifications indicated that the horizontal position could be within a 100-meter diameter circle 95% of the time. For the remaining 5% the error could exceed 300 meters.
On May 2, 2000, and due to, among other causes, the development of new and sophisticated methods of selective degradation over specific areas of the globe, international pressure and to the commercial interests of the United States, President Bill Clinton, in a presidential statement, put an end to permanent mode, to "intentional error" (See statement by the President).
Location of the cache
The cache is close to monuments such as the Puerta del Carmen, the old Faculty of Medicine, the old Captaincy Palace or the church of Santa Engracia so it is highly recommended for tourists.
Resolution of the cache
Although the technology of the system is quite complex, the basis of its operation is relatively simple and is based on our GPS receiver is able to measure the distance to several satellites that act as reference points in space, and also knows their coordinates, so you can get your own coordinates by triangulation.
To obtain the coordinates of the cache you will have to solve the same problem as your GPS receiver , although we will make it simpler, you will only have to do it in 2D, in the plane.

GPS triangulation in the plane
You can check if the geographic coordinates that you have obtained are correct in: GeoChecker.com.
Optionally you can also solve the cache by answering the questions that will be formulated below about the global positioning system.
Enter at CERTITUDE with the concatenation of the answers in capital letters (Example: ACDBA) and you will have the possibility of downloading a pdf file in which it is explained how to solve the problem using the complement solver of excel.
Question nº 1
- On what date was the intentional error or selective availability suppressed?
A) May 1, 2001.
B) May 2, 2000.
C) May 2, 1808.
D) The selective availability has not been suppressed.
Question nº 2
- In what state is the Master System Control Station?
A) Kansas.
B) Utah.
C) Colorado.
D) Nebraska.
Question nº 3
- What is the reference geodesic system used in a native way by GPS?
A) European Datum 1950 (ED50).
B) European Terrestrial Reference System 1989 (ETRS89).
C) UTM (Universal Transverse Mercator).
D) World Geodetic System 1984 (WGS84).
Question nº 4
- The global positioning system (GPS), in addition to geolocation service provides ...
A) Meteorological information.
B) Coordinated time.
C) Astronomical ephemerides.
D) Perpetual and santoral calendar.
Question nº 5
- Considering the three dimensions, when will the best geometry provided by 4 satellites be given?
A) 4 satellites are not necessary to obtain position.
B) One of them located in the vertical and the other 3 regularly distributed over the horizon.
C) The 4 regularly distributed with a 45º elevation angle.
D) The 4 located as close as possible in the vertical.

You can validate the solution to the questions in order to download the file with the way to solve the problem in certitude.
Other caches of the serie