You do not have to walk out to the lighthouse to answer the questions, they can be answered from anywhere on the spit. Please ensure you have checked the tides beforehand if you do. The following website may be useful.
https://www.tidetimes.org.uk/rhu-marina-tide-times
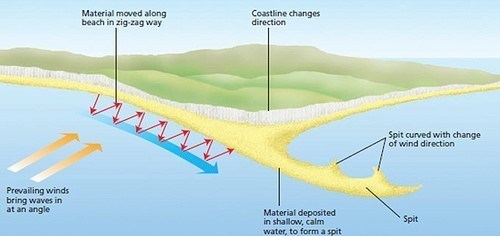
A SPIT is a stretch of sand and/or shingle that juts out into the sea from the land. Sediment is carried by the *Longshore drift and where there is a change in the coastline shape, deposition occurs.
*The longshore current transports sediments (sand, silt and shingle) along the coast parallel to the shoreline, this is called longshore drift. It is dependent on the prevailing wind blowing at an angle to the coastline. The incoming wind squeezes the water along the coast, generating a water current which continues parallel to the coast. The waves breaking on the beach carry the sediment up and along the beach. In order words, Longshore Drift is the sediment moved by the longshore current. Sediment from one location is eroded, transported and deposited onto the spit.
The diagram shows the creation of the spit by the longshore drift across the mouth of the loch. Sand spits often have a curved end as a secondary wind and wave direction curves the end of the spit as waves strike from this second and different direction. Waves cannot get behind the spit, creating a sheltered area where the silt is deposited and **mud flats form.
**Mud Flats are coastal wetlands that form when mud is deposited by the tide. If the coastal sediments are fine (ie. silt and clay), a mud flat is developed instead of a beach. Flats are typically found in areas where the tidal waters flow slowly, such as sheltered bays.
The size of the particles of sediment that make up a beach are usually a reflection of the energy of the waves that hit the shore. In low-energy environments, we see very fine particles such as silt or mud deposited. Higher-energy beaches are often characterised by larger particles, such as pebbles or even boulders.
To log this EarthCache, go to the listed coordinates and carry out the following tasks. The answers MUST be sent to us via email or message. IF ANSWERS ARE NOT RECEIVED WITHIN 4 WEEKS OF LOGGING IT WILL BE DELETED WITHOUT NOTIFICATION.
1. Compare the beaches to the north and south of the spit. What differences can you identify? For example, water depth, steepness of shore, what sediments (type and size) are they made of?
2. From what you can see and what you have learned above, which direction do you think the longshore current is coming from? North/West or South/East? Please provide a reason for your answer.
3. Why do you think that the spit has not extended all the way across the loch?
4. Please explain why this spit does not have a curved end?
5. Please attach a photo to your log of you, your dog, gps, thumb or something personal to prove you were here. Please do not show any spoilers in your photo.
June 2019 the logging tasks for EC were updated. COs can now insist on a photo as proof of visit.
| We have earned GSA's highest level: |
 |