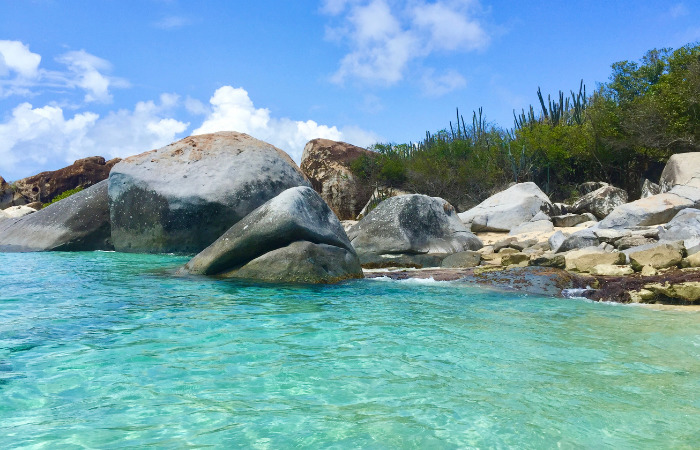
Formation of Sand on Virgin Gorda:
Where you are located is known as The Baths. This geological formation consists of massive igneous boulders. These batholiths were formed during the Tertiary period millions of years ago by rock under immense pressure up into existing volcanic rock layers under the Caribbean Sea. Initially, molten rock could not reach the surface and cooled underwater. This intrusive igneous rock, known as granite, contains large amounts of crystals and minerals. Once the volcanic rock reached the surface of Virgin Gorda due to tectonic uplift, weathering caused the massive formation to crack, forming the numerous smooth boulders on the island. Crevices, small sea pools, and even sand were created by mechanical weathering. Mechanical weathering is breaking down rock into smaller pieces due to natural processes. The Baths’ boulders and grains of beach sand were created due to millions of years of salt-crystal weathering and wave action. Sand that comes from granite rock can contain many minerals. The most common mineral found is quartz; this mineral often comes in a transparent white color in Virgin Gorda. Another mineral commonly found in granite, feldspar, can appear in beach sand. It has an off-white to beige color. Finally, mica can appear as specks of black sand. Another factor that forms beach sand is the build-up of marine debris. There are spectacular coral reef ecosystems in the waters surrounding Virgin Gorda and many islands of the Greater Antilles. When corals die or get bleached, small bits of debris can become dislodged from the reef and end up on shore. Biogenic sediment, or remains from corals or shells, is found on many beaches. Biogenic sediment is comprised mostly of calcium carbonate, a compound that takes an opaque (not transparent) white color in beach sand.

Sand Shape:
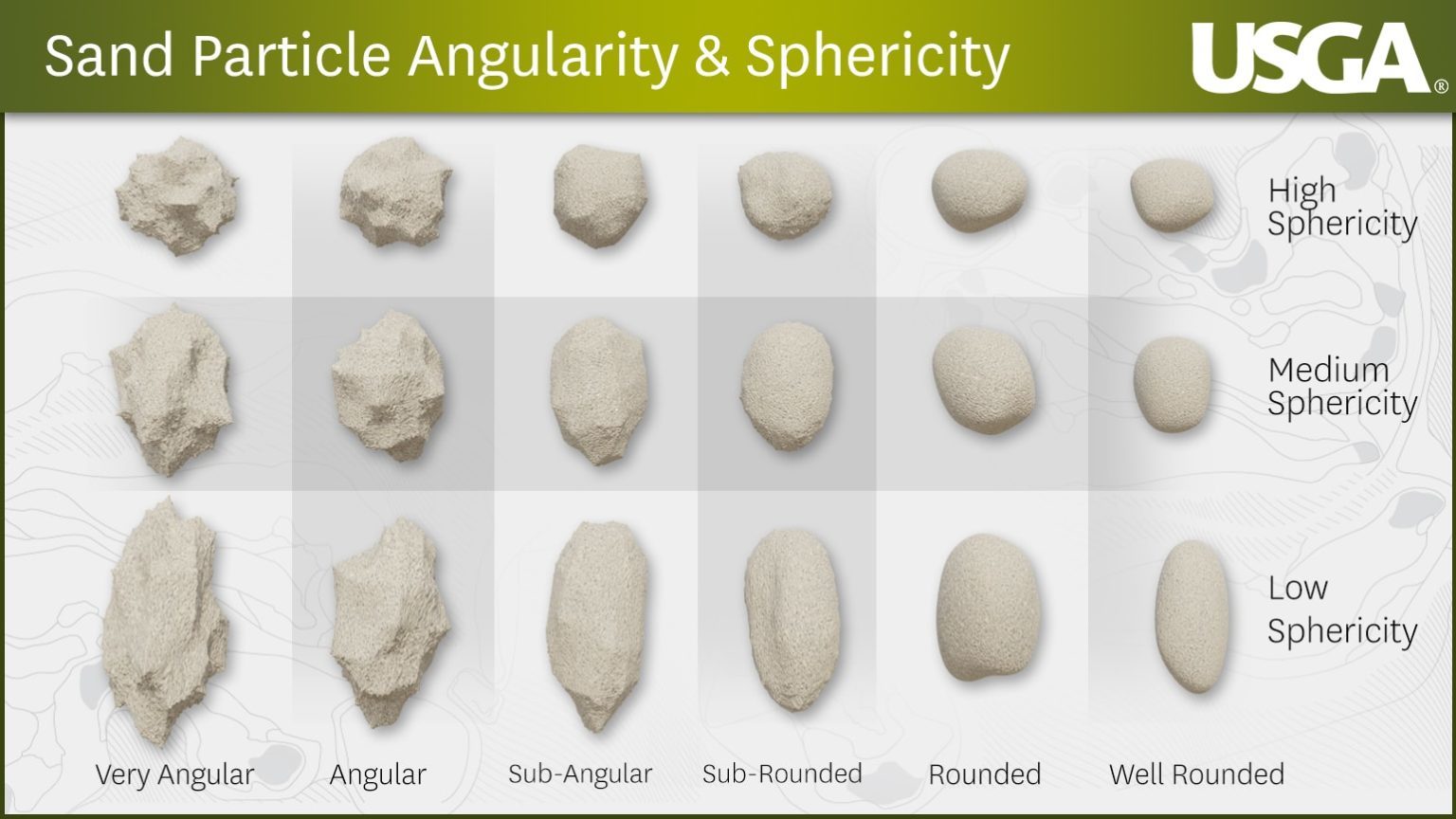
Sand particles can be classified by their shape. Geologists use the terms angularity and sphericity. Sphericity refers to a sand particle that is shaped similarly to a sphere. Round sand grains have high sphericity, and oval particles have lower sphericity. Angularity refers to sediment that looks pointed. Sands with sharp, jagged edges have a high angularity, while rounded sand is smooth. The image below has six categories used to describe angularity and three categories to describe sphericity.
Logging Tasks:
- Examine the sand at the location. What colors and corresponding minerals/compounds is it made up of?
- Does most of the sand appear to be biogenic sediment or formed from the weathering of granite? Explain your rationale.
- Feel the sand at the beach and classify it. Based on what you’ve learned in the description and your observations at the GZ, what is the sand’s sphericity and angularity?
- This is a required photo task. Please provide a photo of yourself, your GPS, or a personal item that proves that you have visited this site. Please post this in your log.
Sources:
https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Determination-of-the-shape-characteristics-a-sphericity-b-angularity-c-roughness_fig7_311531008
https://travelthruhistory.com/magnificent-baths-virgin-gorda/
https://www.worldatlas.com/articles/how-many-types-of-beaches-are-there-based-on-composition.html#:~:text=There%20are%20numerous%20ways%20of,boulder%20beaches%2C%20and%20shell%20beaches
| We have earned GSA's highest level: |
 |