

The Dinkey Dome Pluton is reached by a moderate to strenuous
hike into the Dinkey Lakes Wilderness. The area is at an elevation
of about 8800 feet. The parking area is accessible by unpaved
Forest Service access roads. The roads do get pretty rough, so a
high clearance vehicle would be a very good idea. Winter snows will
make the EarthCache inaccessible. Overnight stays in the wilderness
require a permit.
The Dinkey Lakes Wilderness has been covered in glaciers
numerous times. The two most recent events are called the Tahoe and
Tioga glaciations. While there is some discussion about the exact
dates of these events, the Tahoe glaciation is commonly thought to
have occurred in two stages, one stage between 200 and 140 thousand
years ago and the other from 50 to 42 thousand years ago. The more
recent Tioga glaciation probably occurred between 25 and 14
thousand years ago. Of the two, the Tioga glaciation is thought to
be just a little less extensive than the Tahoe.
Erosion from the glaciers left some distinctive features on the
104 to 90 million year old Dinkey Creek Pluton (see EarthCache).
Some of these features have been erased or hidden by more recent
erosion and deposition, but others glacial erosional features can
still be found throughout the Dinkey Creek Wilderness. One of these
features is chatter marks. Chatter marks are caused by rocks that
are embedded in the ice of the glacier. These rocks bounce across
the top of the bedrock gouging out a series of crescent shaped
indentations in the bedrock. These marks are usually in a line
parallel with the direction of the glacier’s flow.
Another erosional feature caused by glaciers is striations.
Striations are formed by the continuous scraping of small particles
across the bedrock. Like coarse sandpaper, the small rocks grind
small scratches in the bedrock below. Because these scratches are
not as deep as chatter marks, they are more quickly eroded away and
more difficult to find in this area.
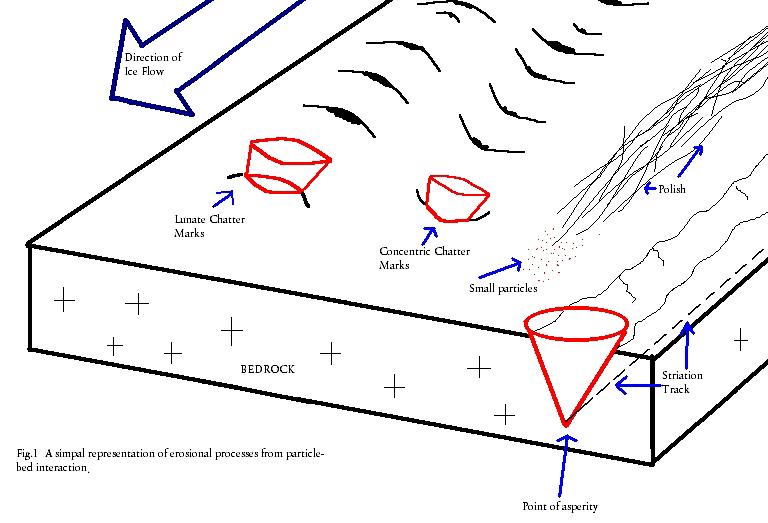 Image from Thomas Juon and Dak Helentjaris
Image from Thomas Juon and Dak Helentjaris
In other areas of the Sierra Nevada glacial polish can be found.
Glacial polish is bedrock that has been polished smooth by a
glacier grinding very small particles across the bare rock under
it. Today it is recognized by its high reflective quality and
smooth feel. Glacial polish only exists on the outer surface of the
rock, so it gets eroded away relatively quickly
Logging requirements:
Send me a note with :
- The number of people in your group.The text "GC30XK9 Dinkey
Creek Chatter Marks " on the first line.
- The number of people in your group (put in the log as
well).
- How many lines of chatter marks are found here?
- Using the line of chatter marks, what was the flow direction of
the glacier?
- Are there any striations or areas of glacial polish within 5
feet of the coordinates?
The above information was compiled from the
following sources:
- Petford, N., Cruden, A., McCaffrey, K and
Vigneresse, J-L., Granite magma formation, transport and
emplacement in the Earth's crust, Nature, V. 408, p. 669-673,
December 2000.
- Thomas Juon and Dak Helentjaris, Last modified
May 17, 1999,
http://gemini.oscs.montana.edu/~geol445/hyperglac/eroproc1/