From the guidelines: "People do not need to wait for permission to log your EarthCache. Requiring someone to wait is not supported by the EarthCache guidelines. People should send their logging task answers to you, then log your EarthCache. When you review their logging task answers, if there is a problem, you should contact them to resolve it. If there is no problem, then their log simply stands."

What can you learn from this EarthCache? - This is a very simple EarthCache and one that demonstrates the effect that faults have on the continuity of rock strata and the types of lateral movement associated with faults.
Location - The rock strata in question are Ordovician age quartzites that outcrop amongst softer, more friable metasediments of the Schist Greywacke Complex in Central Portugal.
What are faults? - In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock, across which there has been significant displacement along the fractures as a result of earth movement.
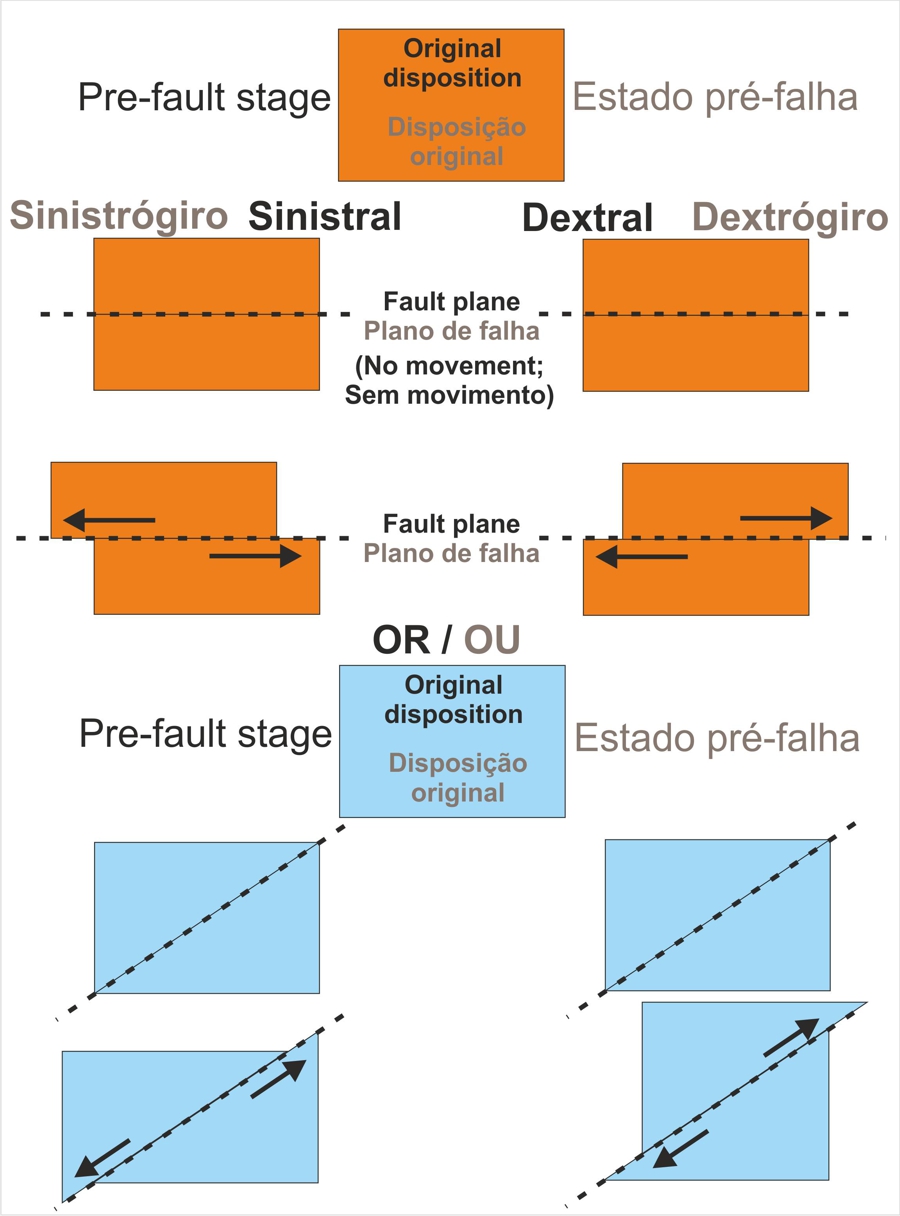
Lateral movement associated with faults – Movement can be of two types: sinistral or dextral.
In geology the terms sinistral and dextral refer to the horizontal component of movement of blocks on either side of a fault or the sense of movement within a shear zone. These are terms of relative direction, as the movement of the blocks are described relative to each other when viewed from above. Movement is sinistral (left-handed) if the block on the other side of the fault moves to the left, or if straddling the fault the left side moves toward the observer. Movement is dextral (right-handed) if the block on the other side of the fault moves to the right, or if straddling the fault the right side moves toward the observer (Observe the image).
How can you log this EarthCache? –
- Go the cache coordinates.
- Walk around to observe the quartzite layer from several angles.
- Identify the fault that has caused the discontinuity and tell me what is located on the fault plane (the imaginary line of the fault).
- What type of movement is associated with this particular fault? Sinistral or dextral?
If you think you have the right answers, log the cache but ALSO send me the answers via my profile with the following information:
- Identification of the cache
- Answers
- (please click: I want to send my e-mail along with this)
Note: No answers, no logs! / Logs with the answers in them will be deleted.

O que podes aprender com esta EarthCache? - Esta é uma EarthCache muito simples e uma que demonstra o efeito que as falhas têm sobre a continuidade de estratos de rocha e os tipos de movimento lateral associado às mesmas falhas.
Localização - As camadas de rocha em questão são quartzitos de idade Ordovícica que afloram dentro do Grupo das Beiras no Centro de Portugal.
O que são falhas? - Uma Falha geológica, ou simplesmente falha é uma superfície num volume de rocha onde se observa deslocamento relativo dos blocos paralelo à fractura.
Movimento lateral associado com falhas - O movimento pode ser de dois tipos: sinistrógiro (falha Esquerda) ou dextrógiro (Falha Direita).
Em geologia os termos sinistrógiro e dextrógiro referem-se ao componente horizontal do movimento de blocos de ambos os lados de uma falha ou o sentido de movimento dentro de uma zona de cizalhamento. Estes são termos de direcção relativa, como o movimento dos blocos são descritos em relação à outra quando visto de cima. O movimento é sinistrógiro (para a esquerda) se o bloco do outro lado da falha se move para a esquerda. O movimento é dextrógiro (para a direita) se o bloco do outro lado da falha se move para a direita (observe a imagem).
Como podes "logar" esta EarthCache? -
1 – Vai às coordenadas da cache.
2 – Dá umas voltas em torno do ponto zero para poderes observar a camada de quartzito de vários ângulos.
3 - Identifica a falha que causou a descontinuidade e diz-me o que está localizado no plano de falha (a linha imaginária da falha).
4 - Que tipo de movimento está associado a essa falha particular? sinistrógiro ou dextrógiro?
Se achas que tens as respostas certas, faz o log da cache, mas envia-me TAMBÉM as respostas através do meu perfil com as seguintes informações:
- Identificação do cache
- Respostas
- (Selecciona: Quero enviar meu e-mail junto com este - ver acima)
Nota: Sem respostas, não há logs! / Logs com as respostas serão eliminados.

 The most exciting way to learn about the Earth and its processes is to get into the outdoors and experience it first-hand. Visiting an Earthcache is a great outdoor activity the whole family can enjoy. An Earthcache is a special place that people can visit to learn about a unique geoscience feature or aspect of our Earth. Earthcaches include a set of educational notes and the details about where to find the location (latitude and longitude). Visitors to Earthcaches can see how our planet has been shaped by geological processes, how we manage the resources and how scientists gather evidence to learn about the Earth. To find out more click HERE.
The most exciting way to learn about the Earth and its processes is to get into the outdoors and experience it first-hand. Visiting an Earthcache is a great outdoor activity the whole family can enjoy. An Earthcache is a special place that people can visit to learn about a unique geoscience feature or aspect of our Earth. Earthcaches include a set of educational notes and the details about where to find the location (latitude and longitude). Visitors to Earthcaches can see how our planet has been shaped by geological processes, how we manage the resources and how scientists gather evidence to learn about the Earth. To find out more click HERE.