Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through space and time, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.
In physics, acceleration is the rate at which the velocity of a body changes with time. In general, velocity and acceleration are vector quantities, with magnitude and direction, though in many cases only magnitude is considered (sometimes with negative values for deceleration). Acceleration is accompanied by a force, as described by Newton's Second Law; the force, as a vector, is the product of the mass of the object being accelerated and the acceleration (vector). The SI unit of acceleration is the meter per second squared (m/s2).
For example, an object such as a car that starts from standstill, then travels in a straight line at increasing speed, is accelerating in the direction of travel. If the car changes direction at constant speedometer reading, there is strictly speaking an acceleration although it is often not so described; passengers in the car will experience a force pushing them back into their seats in linear acceleration, and a sideways force on changing direction. If the speed of the car decreases, it is usual and meaningful to speak of deceleration; mathematically it is acceleration in the opposite direction to that of motion.
In mathematical physics, equations of motion are equations that describe the behaviour of a physical system in terms of its motion as a function of time. More specifically, the equations of motion describe the behaviour of a physical system as a set of mathematical functions in terms of dynamic variables: normally spatial coordinates and time are used, but others are also possible, such as momentum components and time. The most general choice are generalized coordinates which can be any convenient variables characteristic of the physical system. The functions are defined in a Euclidean space in classical mechanics, but are replaced by curved spaces in relativity. If the dynamics of a system is known, the equations are the solutions to the differential equations describing the motion of the dynamics.

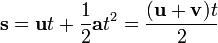
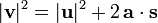
The speed of light in vacuum, commonly denoted c, is a universal physical constant important in many areas of physics. Its value is BCD,FGH,JKL metres per second, a figure that is exact because the length of the metre is defined from this constant and the international standard for time. In imperial units this speed is approximately 186,282 miles per second. According to special relativity, c is the maximum speed at which all energy, matter, and information in the universe can travel. It is the speed at which all massless particles and associated fields (including electromagnetic radiation such as light) travel in vacuum. It is also the speed of gravity (i.e. of gravitational waves) predicted by current theories. Such particles and waves travel at c regardless of the motion of the source or the inertial frame of reference of the observer. In the Theory of Relativity, c interrelates space and time, and also appears in the famous equation of mass–energy equivalence E = mc2.

In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity that is often understood as the ability of a physical system to do work on other physical systems

A Geocacher of mass 95kg is standing still having just found a cache, looking at their GPS they see the next closest is 162m away from them.. however, they are on a very tight schedule and only have 18 seconds to get there. If they accelerate uniformly and constantly, their velocity upon reaching the cache will be V, their acceleration will be A, their displacement will be NOP and their kinetic energy will be QRWXY
N 52° |AQ| |X-H| . |RY+L| |OP-BR| |BH|
W 001° |(C/D)+BB| |JY+C-A| . |NN| |(F-G)/H| |UG+YK|
Cache is best approached from Earth 

 First to find - Thornicus Maximus & Leaky Cauldrons
First to find - Thornicus Maximus & Leaky Cauldrons 
 Second to find - Peatie & Dobunnis
Second to find - Peatie & Dobunnis 
 Third to find - Dawesboy
Third to find - Dawesboy 
Links to other caches in the series:
 Maths
Maths
 Biology
Biology
 Chemistry
Chemistry
 Physics
Physics
 Computing
Computing
 More to come
More to come