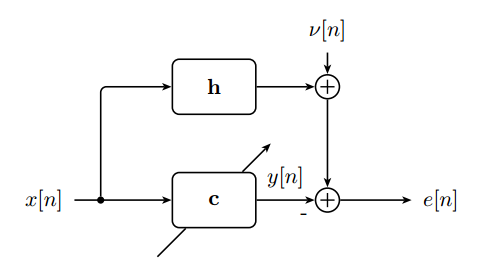
The first goal is to solve a mathematical problem: Consider the figure above, where c is an adaptive filter with three coefficients, i.e., c=[C,D,E]. h is a linear, time-invariant filter with two coefficients, h=[5,5]. x[n] is a unit-variance white noise process with zero mean. v[n] is jointly stationary with x[n], with cross-correlation
E(x[n-k]v[n]) = 2 if k=2 and 0 else.
The filter coefficient vector minimizing the mean-squared error E(e2[n]) is given by the following equation:
c = Rxx-1 p,
where Rxx is the autocorrelation matrix of the input process x[n], and p is the vector of cross-correlations between x[n] and d[n].
-- Let AB be the rank of the matrix Rxx (e.g., AB=07 or AB=15).
-- Compute the coefficient vector c=[C,D,E].
-- This theory behind this problem is intricately linked to a famous mathematician, who also investigated the mathematical aspects of Brownian motion and is considered the founder of cybernetics. He was born on DD-MM-YYYY; FG=DD+1.
-- It is also possible to get the solution without knowing the process statistics, by letting an algorithm run. This algorithm just takes measurements of the input process x[n], the desired output d[n], and the error e[n], and changes the coefficient vector c such that the squared error is minimized. The algorithm was developed by a professor and his PhD student. H is the second letter of the professor’s first name (e.g.: Sigurd, second letter = i, H=9). Hint: The professor also contributed greatly to the theory of quantization.
-- To which of the following applications of adaptive filters does the example above belong?
I=1: inverse modeling
I=2: prediction
I=3: system identification
I=4: interference cancellation
-- The matrix equation solving the problem above is also linked to an Austrian mathematician. He died in 1983. J = digit sum of his age - 3.
Please take care about muggles hiding behind windows! I recommend grabbing the cache during the night or on weekends.
Update 28.09.2017: Since the original cache location is being deconstructed, I had to move the cache a bit. It is now approx. 10 m to the north of the final coordinates. The cache container had to be downsized to a petling.