
The Mississippi River is the largest drainage system in North America. Flowing entirely in the United States (though its drainage basin reaches into Canada), it starts in northern Minnesota and meanders slowly southwards for 2,340 miles to the Mississippi River Delta at the Gulf of Mexico. With its many tributaries, the Mississippi's watershed drains all or parts of 31 US states and 2 Canadian provinces between the Rocky and Appalachian Mountains. The Mississippi ranks as the fourth longest and tenth largest river in the world. The river either borders or cuts through the states of Minnesota, Wisconsin, Iowa, Illinois, Missouri, Kentucky, Tennessee, Arkansas, Mississippi, and Louisiana.
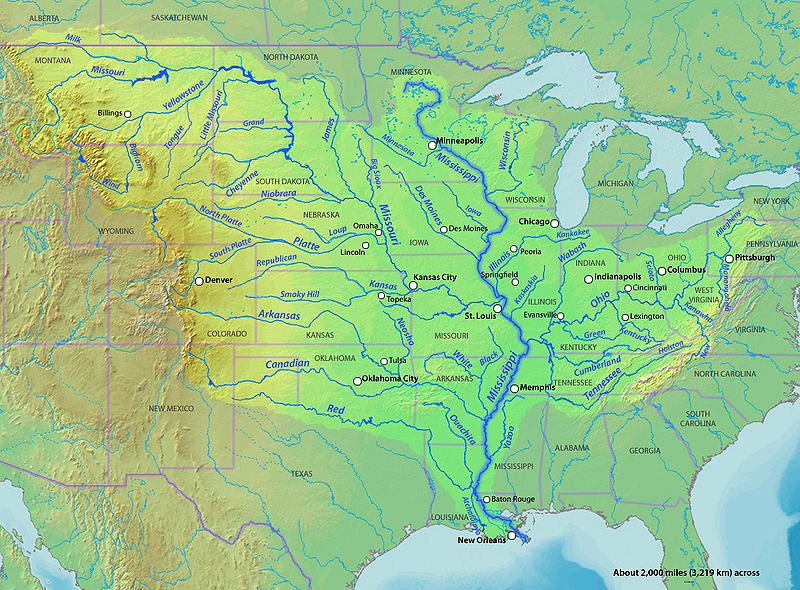
Flood plains are made by a meander eroding sideways as they travel downstream. When a river breaks its banks and floods, it leaves behind layers of alluvium (silt). These gradually build up to create the floor of the flood plain. A flood plain is an area of land adjacent to a stream or river that stretches from the banks of its channel to the base of the enclosing valley walls and experiences flooding during periods of high discharge. Formed from thick layers of this river's silt deposits, the Mississippi River Valley is one of the most fertile agricultural regions of the country.
Erosion
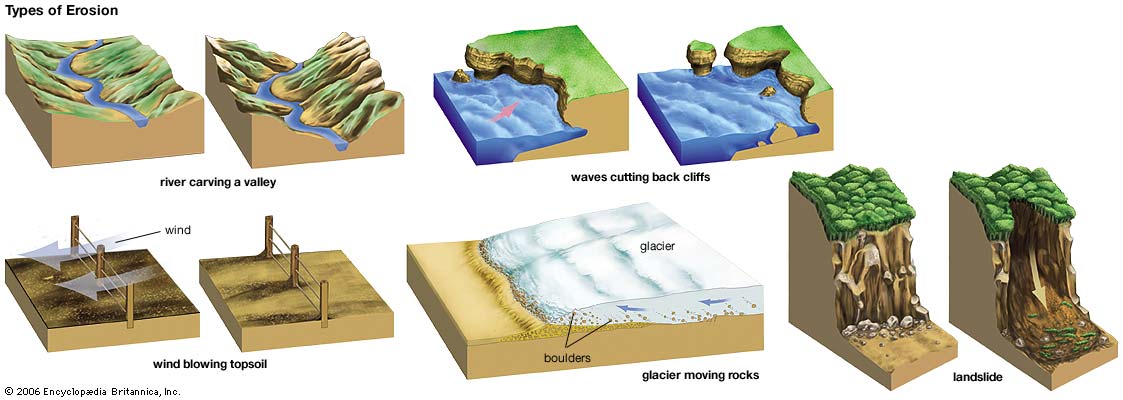
Erosion is the process by which soil and rock are removed from the Earth's surface by natural processes such as wind or water flow, and then transported and deposited in other locations. In this particular area at GZ, Water has caused most of the Erosion here.
Types of Erosion:
Splash Erosion: Small soil particles are detached and sent airborne through the impact of raindrops on soil.
Sheet Erosion: Raindrops break apart the soil structure and it's moved down-slope by water that flows overland as a sheet rather than definitive channels. This occurs frequently during cloud bursts.
Rill Erosion: This process develops small, short-lived, concentrated flow paths. These paths create a sediment source and delivery system for hill-slope erosion. Areas where precipitation rates exceed soil infiltration rates are more prone to this type of erosion.
Gully Erosion: Water flows in narrow channels during or directly following heavy rains or melting snow. The gullies can erode to considerable depths.
Valley or Stream Erosion: Continual water flow alongside land (along a linear feature) creates this type of erosion. It extends downward, deepening a valley, and head-ward, extending the valley into the hillside. This occurs most frequently in times of flooding.
Bank Erosion: Over time, banks of rivers and streams are naturally worn down.
Freezing and thawing: Cold weather causes water trapped in tiny rock cracks to freeze and expand, breaking the rock into several pieces.
Source: (water)
**Logging requirements**
DO NOT POST ANSWERS IN YOUR LOG.
Send the following answers to me via email.
- The text "GC5C8M7 Big Muddy" on the first line
- Name the creek that is farther up the river and is on this parks northern border?
- Name two types of rock that the bluff to the north is made of?
- What tower is up river?
- Across the river from here is what?
- Something is reshaping the shoreline up river what type of erosion is happening here (It's not water erosion), (Look up river at 331 degrees)?
- How wide is the river here, (see waypoint)?
- How wide is the floodplain here, (see waypoint)?
| I have earned GSA's highest level: |
 |