A Nebraska state park permit is required to enter. If you don't have one, daily and annual permits may be purchased at the park entrance. In 2015 the daily entrance fee was $5
Current fee schedule
Welcome to Eugene T. Mahoney State Park, here you will see incredible views of valley’s, and rugged hills.

Floodplain

A floodplain or flood plain is an area of land adjacent to a stream or river that stretches from the banks of its channel to the base of the enclosing valley walls and experiences flooding during periods of high discharge. It includes the floodway, which consists of the stream channel and adjacent areas that actively carry flood flows downstream, and the flood fringe, which are areas inundated by the flood, but which do not experience a strong current. In other words, a floodplain is an area near a river or a stream which floods when the water level reaches flood stage.
Formation
Flood plains are made by a meander eroding sideways as they travel downstream. When a river breaks its banks and floods, it leaves behind layers of alluvium (silt). These gradually build up to create the floor of the flood plain. Floodplains generally contain unconsolidated sediments, often extending below the bed of the stream. These are accumulations of sand, gravel, loam, silt, and/or clay, and are often important aquifers, the water drawn from them being per-filtered compared to the water in the river.
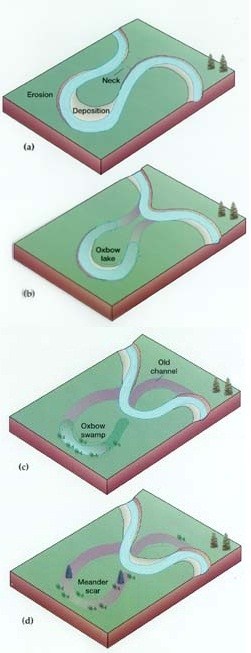
Meander
A meander, in general, is a bend in a twisting watercourse or river. A meander is formed when the moving water in a stream erodes the outer banks and widens its valley and the inner part of the river has less energy and deposits what it is carrying. A stream of any volume may assume a meandering course, alternately eroding sediments from the outside of a bend and depositing them on the inside. The result is a snaking pattern as the stream meanders back and forth. When a meander gets cut off from the main stream, an oxbow lake is formed.
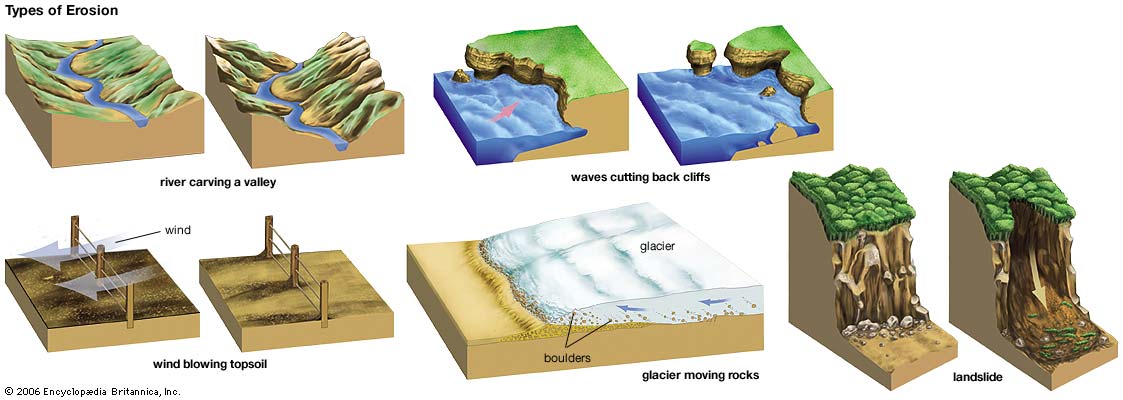
What is Erosion?
Erosion is the process by which soil and rock are removed from the Earth's surface by natural processes such as wind or water flow, and then transported and deposited in other locations.
Types of Erosion:
Splash Erosion: Small soil particles are detached and sent airborne through the impact of raindrops on soil.
Sheet Erosion: Raindrops break apart the soil structure and it's moved down-slope by water that flows overland as a sheet rather than definitive channels. This occurs frequently during cloud bursts.
Rill Erosion: This process develops small, short-lived, concentrated flow paths. These paths create a sediment source and delivery system for hill-slope erosion. Areas where precipitation rates exceed soil infiltration rates are more prone to this type of erosion.
Gully Erosion: Water flows in narrow channels during or directly following heavy rains or melting snow. The gullies can erode to considerable depths.
Valley or Stream Erosion: Continual water flow alongside land (along a linear feature) creates this type of erosion. It extends downward, deepening a valley, and head-ward, extending the valley into the hillside. This occurs most frequently in times of flooding.
Bank Erosion: Over time, banks of rivers and streams are naturally worn down.
Freezing and thawing: Cold weather causes water trapped in tiny rock cracks to freeze and expand, breaking the rock into several pieces.
Wind erosion is a major geomorphological force, especially in arid and semi-arid regions. Wind erosion is of two primary varieties: deflation, where the wind picks up and carries away loose particles; and abrasion, where surfaces are worn down as they are struck by airborne particles carried by wind.
Mass movement is the downward and outward movement of rock and sediments on a sloped surface, mainly due to the force of gravity. Mass movement is an important part of the erosional process, and is often the first stage in the breakdown and transport of weathered materials in mountainous areas. It moves material from higher elevations to lower elevations where other eroding agents such as streams and glaciers can then pick up the material and move it to even lower elevations. Mass-movement processes are always occurring continuously on all slopes; some mass-movement processes act very slowly; others occur very suddenly, often with disastrous results.
Source: (water)
**Logging requirements**
DO NOT POST ANSWERS IN YOUR LOG.
Send the following answers to me via email.
Climbing to the top is the only way to get the following answers accurately
- The text "GC5RDGN Mahoney State Park" on the first line
- How wide is the floodplain? (See waypoints)
- How many times do you see the river meander?
- How many sand bar's, which is sediment, are visible in the river?
| I have earned GSA's highest level: |
    |