Erosion
Erosion is the process by which soil and rock are removed from the Earth's surface by natural processes such as wind or water flow, and then transported and deposited in other locations.
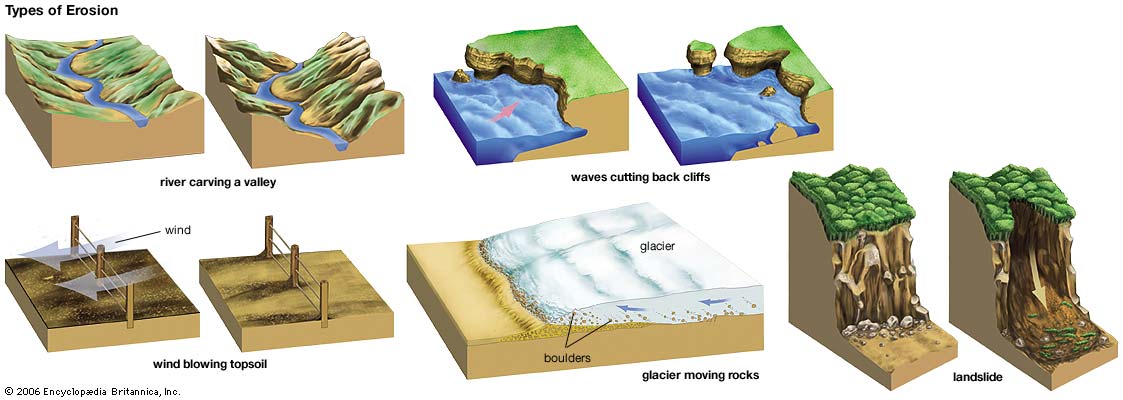
Types of Erosion:
Splash Erosion: Small soil particles are detached and sent airborne through the impact of raindrops on soil.
Sheet Erosion: Raindrops break apart the soil structure and it's moved down-slope by water that flows overland as a sheet rather than definitive channels. This occurs frequently during cloud bursts.
Rill Erosion: This process develops small, short-lived, concentrated flow paths. These paths create a sediment source and delivery system for hill-slope erosion. Areas where precipitation rates exceed soil infiltration rates are more prone to this type of erosion.
Gully Erosion: Water flows in narrow channels during or directly following heavy rains or melting snow. The gullies can erode to considerable depths.
Valley or Stream Erosion: Continual water flow alongside land (along a linear feature) creates this type of erosion. It extends downward, deepening a valley, and head-ward, extending the valley into the hillside. This occurs most frequently in times of flooding.
Bank Erosion: Over time, banks of rivers and streams are naturally worn down.
Freezing and thawing: Cold weather causes water trapped in tiny rock cracks to freeze and expand, breaking the rock into several pieces.
Wind erosion is a major geomorphological force, especially in arid and semi-arid regions. Wind erosion is of two primary varieties: deflation, where the wind picks up and carries away loose particles; and abrasion, where surfaces are worn down as they are struck by airborne particles carried by wind.
Mass movement is the downward and outward movement of rock and sediments on a sloped surface, mainly due to the force of gravity. Mass movement is an important part of the erosional process, and is often the first stage in the breakdown and transport of weathered materials in mountainous areas. It moves material from higher elevations to lower elevations where other eroding agents such as streams and glaciers can then pick up the material and move it to even lower elevations. Mass-movement processes are always occurring continuously on all slopes; some mass-movement processes act very slowly; others occur very suddenly, often with disastrous results.
Source: (water)
Limestone
Is a sedimentary rock composed largely of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). Limestone makes up about 10% of the total volume of all sedimentary rocks. The solubility of limestone in water and weak acid solutions leads to karst landscapes, in which water erodes the limestone over thousands to millions of years.
Granite
First, granite is made of large mineral grains (which is where its name came from) that fit tightly together. Second, granite always consists of the minerals quartz and feldspar, with or without a wide variety of other minerals (accessory minerals). The quartz and feldspar generally give granite a light color, ranging from pinkish to white. That light background color is punctuated by the darker accessory minerals. Thus classic granite has a "salt-and-pepper" look. The most common accessory minerals are the black mica biotite and sometimes black amphibole hornblende.
Biotite
Biotite is a common phyllosilicate mineral within the mica group; more generally, it refers to the dark mica series.
(basicly it's the black you see below)

Igneous rocks
Gabbro

Granite

basalt

**Logging requirements**
DO NOT POST ANSWERS IN YOUR LOG.
Send the following answers to me via email.
- The text "GC5RYZB Erosion of Big Spring park" on the first line
- While standing here look at the cliff wall (White’ish colors are chert, and the grey color is limestone.) what is the majority of the cliff made of?
- When looking at the grey gabbro what size are the black mica biotite crystals? (See waypoint Grey)
- When looking at the red granite what size are the black mica biotite crystals? (See waypoint Red) {it’s lying flat on the ground}
- Which of the above two look’s more eroded?
- What are the dimensions of the limestone marker (width X height X depth)? {See waypoint Marker}
| I have earned GSA's highest level: |
    |