Oil is formed from dead or decaying marine life. Over millions of years, the dead material is compacted as sediment falls on top of it. When it is compacted, it become dense and begins to sink into the crust. As it sinks, the temperature rises as it gets ever so closer to the earth's mantel. The heat helps separate the dead material. If the temperature is high enough, it becomes natural gas which we use in our kitchen stoves and propane tanks. When the temperature rises, it makes the dead material less dense and therefore it rises. As it cools, it slows down and eventually gets trapped by bedrock. Usually this occurs a few miles below the surface, but because California, especially southern California has many fault lines, the crude oil can make its way up to the surface.
Fault lines and oil field DO have a correlation as to where they are both found. If there is a fault near the coastline, there is a higher chance for oil to be found nearby. Although this might not be the case as several other factors go into how deep oil may be such as the type of rock that the oil is under and duration that the dead material is under high temperatures. With the help of seismic activity, oil can literally be driven out of the ground as seen with the nearby La Brea Tar Pits. Below is a map of fault lines and known oil fields. See a correlation?
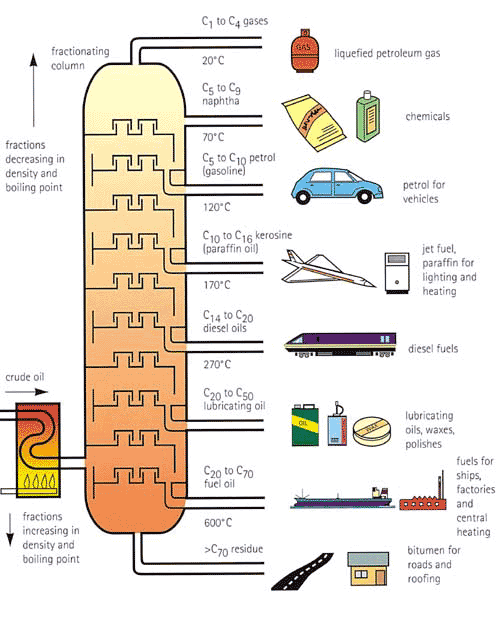
Crude oil is oil fresh out of the ground. It is sticky, black, and smells like tar. This type of oil is useless to us, unless we refine it in a refinery. Both time and temperature are the main two factors that go into oil refining. The length of time and how hot it is makes the crude oil burn off impurities. Different impurities are needed/unneeded depending on it's use. This can be best explained in the diagram below.
Works Cited
https://www.priweb.org/ed/pgws/backyard/signal_hill/signal_hill_oil.html
http://www.agiweb.org/education/energy/oil/
http://ffden-2.phys.uaf.edu/212_spring2011.web.dir/kristine_odom/temp/10956/ftddrops/Downstream.html
TO LOG A FIND ON THIS CACHE YOU MUST GIVE ME THE CORECT ANSWERS BEFORE YOU LOG A FIND. YOU CAN CONTACT ME THROUGH MY EMAIL OR THE GEOCACHING MESSAGE CENTER. ANY INCORRECT ANSWERS WILL RESULT IN A DELETED LOG
1. "Discovery Well" on the first line of your email.
2. How many barrels of oil per day did "The Expensive Dry Hole" produce AND what was the depth that it drilled at?
3. How many barrels of oil do engineers estimate still lie beneath the Long Beach Oil Field?
4. Look at the picture on the plaque in front of you. Estimate the height in feet that the cude oil shoots into the air AND explain what geologic forces/phenomena causes it.
5. Using the view as a reference point, list at least two fixed (stationary) objects/things that you can see that use/have oil AND state their distance AND compass orientation. In addition to this, and using the chart above, give the appropriate temperature that the object that uses/has oil was refined at. See "hints" for clarification.

