As you drive Highway 60, you notice exposed rock formations. So I decided to stop and put on my amateur geologist hat and investigate the road cut area. My investigation came up with sedimentary structures. What causes the sediments in this area to form or layer. My earthcache will explain the different structures and names of this process.
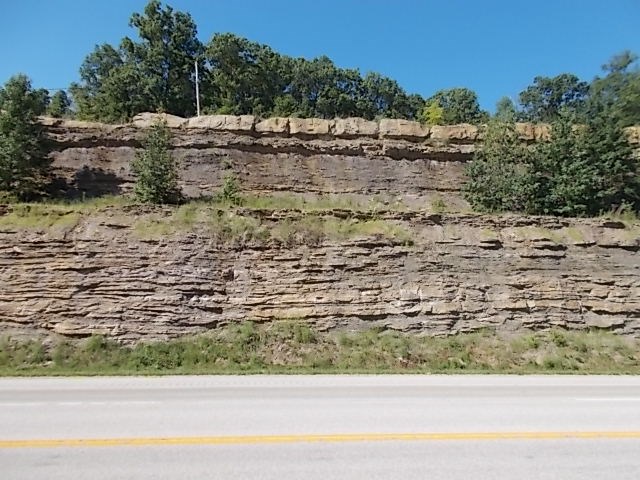

Sedimentary structures are visible features within sedimentary rocks (sandstone, limestone, shale, to name a few) that formed at the time of deposition and represent manifestations of the physical and biological processes that operated in depositional environments. The most commonly observed sedimentary structure is stratification. Stratification refers to the layering that occurs in sedimentary rocks as a result of different depositional episodes. Stratification is described by the thickness of the individual layers. Beds are layers of sediment that are thicker than 1 centimeter and are typically produced by coarser grained sediments such as sands and gravel. Laminations are layers thinner than 1 centimeter, These deposits are typically formed by fine sand sediments such as silts and clay and often represent seasonal deposition. Other sedimentary structures provide information about specific processes operating within depositional environments. These structures are observed within individual beds and laminations and can be quite useful in determining environmental conditions at the time of deposition.
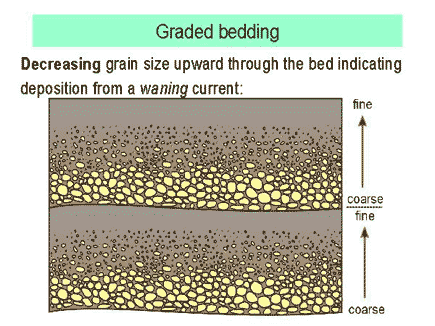
Graded bedding occurs when sediment loaded currents(turbity currents) experience a relatively quick drop in velocity causing the sediments to deposit. As the sediment settles larger, heavier, clasts settle first followed by the smaller, lighter clasts producing vertically sorted "graded" beds with large clasts on the bottom and finer clasts on top.
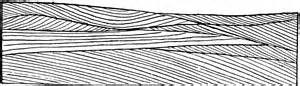
Cross-bedding forms when sediment come to rest at an angle and can form anywhere fluids, such as wind or water, carry sediment. The individual beds form as sediment moves up and over the windward or upstream side a ripple or dune and then become deposited on the downstream side. Small scale cross bedding creates ripple marks. These structures are common on stream beds and on beach and lake shores.
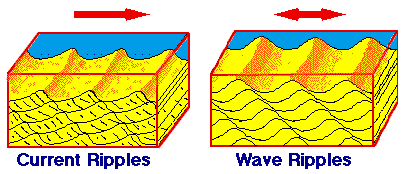
Ripple marks come in two forms, symmetric, or wave formed ripples and asymmetric, or current ripples. Wave-formed ripple result from the to and fro motion of waves and have a symmetrical profile. Current ripple marks form in response to water or wind currents flowing in one direction and have asymmetricc profiles. The asymmetric profiles allow geologists to determine paleocurrent directions, in other words, which direction the wind or water was flowing from when the cross beds were deposited. This is possible due to the fact the longer side of the ripple always faces the upstream direction.
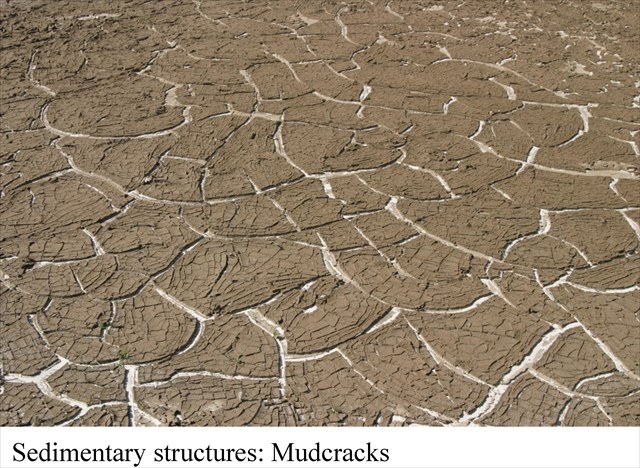

Mud cracks are another common sedimentary structure. These structures form when the clay rich sediments found in muds dry and shrink. As the sediment creating polygonal patterns called mud cracks. Over time these cracks become filled with other sediments which preserve the polygonal pattern formed by the cracking sediment. Mud cracks form in any environment that allows for the wetting and drying of sediment such as lakes, marshes, rivers, lake shores.
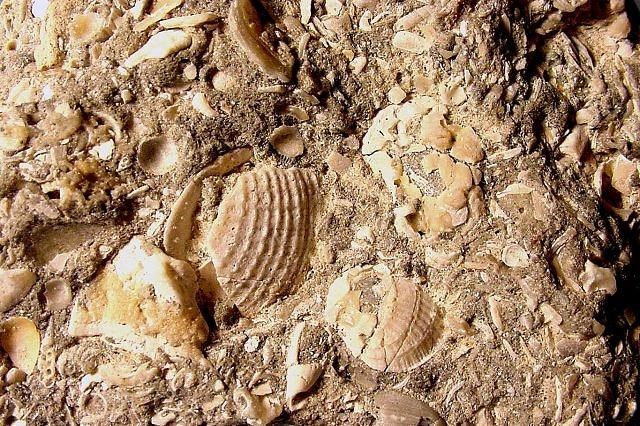

Finally, some structures are formed by the actions of living organisms. These structures are known as Biogenic sedimentary structures and are caused by the disruption of previously deposited sediment. Biogenic structure, also referred to as trace fossils, can take the form of tracks, burrows, or trails. Extensive burrowing by organisms within the sediment, called bioturbation, may alter sediments so thoroughly that other structures are disrupted or destroyed.
Now with all lessons you must answer question about the earthcache.
1. What type of sedimentary structure or structures is present at the location?
2. Now that you have the structure or structures. How did you come up with this answer?
3. How tall is the exposed road cut of the bottom terrace?
A. 5' to 10'
B. 10' to 15'
C. 15' to 20'
Optional pic of yourself at the road cut. THANKS
Please email the answers and do not log or will be deleted.
