The development and changes of the bay over the years is varied.
Sarasota Bay:
Sarasota Bay is a lagoon located off the west coast of Florida in the United States. Though no significant single stream of freshwater enters the bay, with a drainage basin limited to 150 square miles in Manatee and Sarasota Counties, it is generally treated as an estuary, with three "passes" or inlets, giving access from the Gulf of Mexico. Its source of freshwater has been increased from natural historical levels by urban surface runoff.
The Bay:
The bay and its surrounding area appeared on the earliest maps of the area, being named Sarasota on one dating from the early 18th century. Hunting in the area had supported native populations for more than ten thousand years as Florida attracted some of the earliest human settlements in the hemisphere. Following the retreat of the glaciers, ocean levels rose creating the current coastline and the natural bounty of Sarasota Bay provided food for inhabitants for over five thousand years before Europeans began exploration of the area in 1513 and later, establishing settlements along its shores. The below link provides an amazing history of the area.
http://www.sarasotagov.com/PDF/NDS/11%20-%20Historic%20Preservation%20Chapter%20(Support%20Document).pdf
Sarasota Bay, the largest and deepest coastal bay between Tampa Bay and Charlotte Harbor, is one of twenty-eight estuaries in the country that have been named by the U.S. Congress as an estuary of national significance. The bay lies between barrier islands called keys, that separate the body of water from the Gulf of Mexico and the Florida mainland. Longboat Key, Lido Key, Siesta Key, and Casey Key are the major keys that delineate the main bay and its smaller portions.
Since 1921, when Sarasota County was created, the bay lies in areas governed both by Manatee County and Sarasota County. After Florida became an American state in 1845, large counties were carved up from time to time, to form new and smaller counties. From 1855 to 1921 the bay was governed by Manatee County, and from 1834 to 1855 the bay was governed by Hillsborough County. Governance prior to that has been Spanish, French, English, and during the Civil War, Florida was Confederate. The concept of "governance of natural resources" did not exist among the American Indians who harvested the bounty of Sarasota Bay for thousands of years without diminishing it.
Sea Grass:
The sea grass ecosystem in the bay is directly connected to the bay's passes that are both naturally made and man made. The passes to the bay from the Gulf of Mexico provide nutrients and life to the bay of Sarasota along with fresh water run off to the bay from the land. When Big Pass was established or changed to allow more shipping it changed and affected Saraota Bay in more than just a shift Of sand. Nature took over after the Intercoastal water way project and over time effected Midnight pass.
When the intercostal waterway was deredged and deepened for commercial reasons, it affected Midnight pass. The land mass through the pass began to change.
Sediments:
Sediment that moves down a river and is deposited into a bay is both fine and coarse. Coarse sediments which usually consist of gravel and sand are deposited at the head where the river meets the bay and also sink to the bottom of the bay. Fine sediment which usually consists of muds, clays, and organic materials flow down to the center of the bay and are deposited along the edges of the bay. At the entrance where the ocean water comes into the bay tidal water moves coarse sediments of sand and gravel from the ocean into the bay. Fine sediments such as muds, clays, and organic material flow out into the ocean but at a much slower rate than the coarse sand and gravel coming in. The exception to more sediment going out the inlet than coming in is during spring tides or flood events.
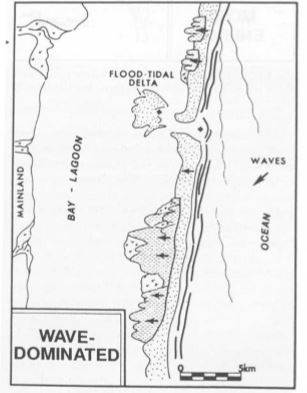
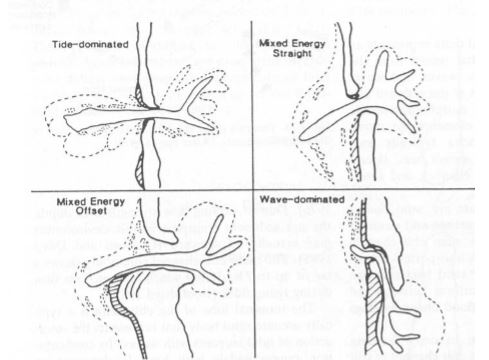
From this location you have a good view of the south part of the bay. As detailed in the reference page, the sea grass ecosystem here is large and diverse and seriously affected by both natural and man made events. Easily damaged by both and full of a wide variety of sea life.
Logging Requirements
1) Is sea grass visible at the closest point to the shore at this location?
2) Using the reference sheet, how did Big Pass affect Midnight Pass?
3) Do you believe that the passes to the Gulf of Mexico are interconnected?
4) How do you believe the passes are connected to each other being separated by such a large land mass?
5) While not required, please show your view from this location of the bay. (Optional)
The purpose of this Earthcache is to both learn a little bit about the geography of this area and hopefully gain some knowledge that you might not have known. More important than logging this cache is the hopes of gaining a little knowledge of this area! Thank you for visiting my Earthcache.
Please do not post your answers in the log and do not post a smiley without emailing your answers as your log will be deleted.
