Quaternary outwash from glaciers with layers and layers of sand and gravel laid to rest. This causes the ground to saturate with water and causes flooding. So help in the flooding in the Western part of Daviess County this part of Panther Creek was dug for flood control. If you ever came to Owensboro when raining water would be standing and drainage is the problem. So creeks, ditches help in getting the water moving not standing. But with all the ways to move the water erosion plays a part in the break down of the banks.

Erosion of creek beds and banks is a natural process. However erosion rates are significantly increased by human activities such as clearing land for farming and development. Erosion of bank soil by water during intense rainfall or flood events. The key principle in preventing or reducing along creeks is to maintain good ground cover over the surface of the banks. This reduces contact between falling rain or floodwaters and the banks, decreasing the amount of soil eroded. The roots of vegetation growing along and on top of the bank also help to reinforce the soil and reduce the erosion rate, while vegetation growing within the creek channel can also slow water flow and trap sediment.
Riparian means any land which adjoins, directly influences or is influenced by a creek or river. There are two common forms of creek erosion, bank erosion and bed erosion.
Bank Erosion
There are three processes at work when bank erosion occurs: sub-aerial erosion, fluvial scour and mass failure. These processes can occur singly or in combination and in different parts of the creek. Sub-Aerial erosion, this involves processes that loosen the soil of the creek bank, making it vulnerable to being carried away by water moving past in the next big flow.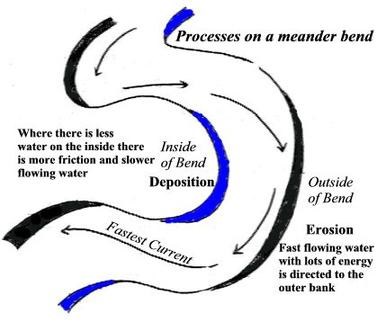 Fluvial scour occurs when a force applied to the bank by flowing water exceeds the resistance to erosion of the bank surface. On outer bends of creek meander, water flow is fast and there is strong contact between the flow and the bank itself. Scouring tends to take place in the area known as the toe of the bank, at the water's edge. Repeated scour at this point can undercut the bank, which then topples into the water or creek bed when its weight can no longer be supported. Mass failure can occur anywhere along a creek and often follows undercutting by scour. It can occur when the bank soil itself has been saturated, for example by heavy rain or from a flood peak and level of the flow in creek drops quickly, leaving the heavy saturated soil of the bank unsupported.
Fluvial scour occurs when a force applied to the bank by flowing water exceeds the resistance to erosion of the bank surface. On outer bends of creek meander, water flow is fast and there is strong contact between the flow and the bank itself. Scouring tends to take place in the area known as the toe of the bank, at the water's edge. Repeated scour at this point can undercut the bank, which then topples into the water or creek bed when its weight can no longer be supported. Mass failure can occur anywhere along a creek and often follows undercutting by scour. It can occur when the bank soil itself has been saturated, for example by heavy rain or from a flood peak and level of the flow in creek drops quickly, leaving the heavy saturated soil of the bank unsupported.
Bed Erosion
Erosion of the creek bed ( called bed deepening or incision) can occur due to a range of changes in the landscape over many years. The removal of vegetation by clearing of land, amount of surface water into creeks. Increased volume of flow, or increased flow, are main triggers for bed erosion. Once triggered, the power of the water flow work to expand the bed erosion and cause it to move upstream. Bed erosion usually shows up as a step in the stream bed that progressively moves upstream leaving behind a narrow channel in the bed of the stream. The erosion will continue to migrate until it reaches a control point in the creek. A control point is usually a rock bar or it can sometimes be a culvert. This will lower the creek bed deeper into the channel causing the creek banks to become steeper and more prone to collapse.
Creek erosion management
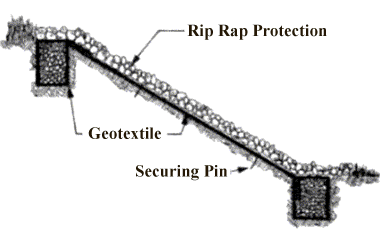
Maintaining good ground cover is the key to preventing or slowing the erosion of creek banks and beds. Vegetation cover on the banks reduce erosion due to both sub-aerial and scour processes as the bank soil is no longer directly exposed to the forces that cause erosion. Riparian vegetation also stabilizes creek banks, with roots acting like reinforcing rods, holding the soil together and reducing the risk of mass failure. Plants also help to dry the creek banks after rain or floods, reducing the risk of erosion. Inspect the banks to see if stable and have good cover. Decide whether the bed is deepening (bed is bare and banks vertical) or it is mainly the banks need attention. Other solutions which could be more expensive is rock riprap, geotextile mats or blankets, gabions (wire baskets filled with rock). With all the fixes mother nature will prevail in cycle. But with human disturbances, we must help in the slowing down of the erosion.
Now the fun part answering a few questions.
1. What type of erosion do you see present or if any? Explain.
2. What does Riparian mean?
3. Pic of yourself at the location.
Please send me answers thru my email and don't log the answers it will be deleted. THANKS
