- Explain how flowing water causes erosion.
- Describe how this locations runoff changes the Earth’s surface.
- Identify features caused by groundwater erosion and deposition.
- Understand the effects of particles based on water volume and velocity
- Recognize and point out the difference between Hydraulic Actions and Abrasion
- Classify differential erosion starting from the plunge pool and beyond
Introduction
So what is erosion anyway? Good question! The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language, defines erosion as: The group of natural processes, including weathering, dissolution, abrasion, corrosion, and transportation, by which material is worn away from the earth's surface. That's all fine and good, but what is it really? We see it all around us yet we can't really explain it. We know it usually involves water so lets start there.
Erosion and deposition are responsible for many landforms. Agents of erosion include flowing water, waves, wind, ice, and gravity. Sometimes all at the same time! In this exercise we will be focused on the effects primarily attributed with liquid water erosion. It is important to understand eroded material is eventually dropped somewhere else. This is called deposition. We won't be studying much on deposition other than the fact that particles eventually come to rest where water flow is weakest or non existent.
How Flowing Water Causes Erosion and Deposition
It is important to understand that flowing water is a very important agent of erosion and can erode rocks and soil. Water dissolves minerals from rocks, but if it doesn't flow it can't carry the particles. But when water does flow, say like from a steam or river, this process can happen really slow sometimes over millions of years! Or if in a flash flooding a bit faster. Regardless, flowing water can dissolve massive amounts of rock and other substances. The Grand Canyon is a good example of millions of years of erosion from the Colorado River.
Now the trick to waters ability to erode is found by the velocity, and volume of the water. The size of the eroded particles depends on the velocity of the water. As water slows, larger particles are deposited(aka: deposition). As the water slows even more, smaller particles are deposited. One should take note that at this location the slowest water movements here are during the winter and seasons of drought where as flooding and rainy seasons are the best time to view the water at work here.
In review: Flowing water erodes or deposits particles depending on how fast the water is moving and how big the particles are. Sometimes erosion takes millions of years especially when creating canyons.
Water Speed emulates Erosion
Obviously the faster moving water is the more energy it contains. Therefore, fast moving water can carry larger particles. There are many things that can make water flow faster. The slope of the land is one factor. The steeper the slope, the faster the water flows. Another factor is the amount of water that's in the stream. Streams with a lot of water flow faster than streams that are nearly dry. In this case, the erosion is caused by Lake Windsor's overflow and run off from collected waters from the Ozark mountain range and underground springs.
In review the faster the water movement, the greater the erosion, gravity plays are large part in water flow.
Particle Size and Erosion
The size of particles determines how they are carried by flowing water.
- Minerals that dissolve in water form salts,(ocean water is a good example). The salts are carried in solution. They are mixed thoroughly with the water aka: Salt Water.
- Small particles, such as clay and silt, are carried in suspension. They are mixed throughout the water. These particles are not dissolved in the water.
- Somewhat bigger particles, such as sand, are moved by saltation. The particles move in little jumps near the stream bottom. They are nudged along by water and other particles.
- The biggest particles, including gravel and pebbles, are moved by traction. In this process, the particles roll or drag along the bottom of the water.

In Review: Depending an the particle size, volume and velocity of water; particles can be in the form of solution, suspension, saltation, traction, or all of the above.
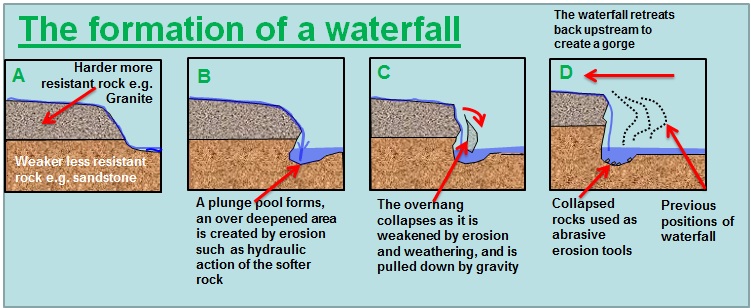
The Birth of a Waterfall
Waterfalls are found in areas with bands of hard and soft rock (otherwise known as resistant and less resistant rocks). The hard rock takes longer to erode than the soft rock, this is called (differential erosion,) so the water erodes the land at different rates. The water erodes the soft rock by a few different processes of erosion one including Hydraulic Action (the force and power of moving water) and the other is Abrasion (the scraping of the load {particles} against the bed and banks).
At first a small pitt or notch is created in the soft rock of the bedrock. The notch may only be a few inches in the from of a drop yet it increases the speed of the water falling over the edge. This encourages the water to erode vertically (downcutting) into the soft rock creating a vertical drop.
Over time the water deepens as the soft rock is continuously eroded. At the base of a waterfall a rounded pool is found. This is called a plunge pool. The force of the falling water causes the water to swirl in the pool in a movement called eddying.
As the water continues to fall, the hydraulic action may cause water to splash back against the back wall causing further erosion. This causes undercutting of the back wall,(and a good place for all the pirates to hide their treasures) Finally the overhang of hard rock is unstable and unsupported due to undercutting. It collapses and the rocks fall into the plunge pool.(maybe not such a good place for treasure after all).
Waterfalls continue to erode backwards in a process called headward erosion. This is when the hard and soft rock is all worn away and the river returns to its original slope. The process soon starts all over again, eventually creating gorges, canyons and other amazing feats of nature.
At this location, you will see many fine examples of the erosion you just learned about. Try and look for the signs of each specific erosion you learned about today, and then when you are ready (and tired of taking so many pictures of this beautiful location) try to answer the qualifying questions below. Please remember, DO NOT POST YOUR ANSWERS IN THE LOG. you must follow the directions in order to get you smily.
To Qualify for this Earthcache please email me via geocaching profile with the GC code, title and the answers to the following questions.
1. Define erosion.
2. What is the source of erosion found here? Hint: I'm looking for a name.
3. List Three (3) main erosions found at this site
4. List your estimated dimensions (in feet) of the current plunge pool. And what type of erosion is it called that made the plunge pool?
5. Looking at the rocks just beyond the plunge pool, would you classify the erosion seen here as Hydraulic Action or Abrasion?
6. Describe the rockbed that you see continuing into the gorge, in your own words decribe what kind of processes made the rocks look the way that they do.
7) How many Large Rocks can be seen immediately after the current plunge pool?
8) Because of the effects of Undercutting, Eddying and Headward erosion, how many plunge pools are there?
(Though it's not required) I would greatly apprciate if you took picture of yourself at GZ to add to the gallery of photos!.
You may go ahead and claim "found it" once you have come to ground zero, If I don't receive the information required from you within 24 hours, I will delete your "found it" log.