DIJKSTRA'S ALGORITHM
Edsger W. Dijkstra (1930-2002) was a Dutch computer scientist, pioneering early theories and research in the emerging world of computers. Among his accomplishments was Dijkstra's Algorithm, published in 1959. Edsger's work at the time was in graph theory- a mathematical concept which involves nodes (or vertices) connected by edges, as seen below:

Some graphs will include a weight (or length) to each line, allowing someone to calculate the distance between two nodes. Dijkstra's algorithm finds the shortest path between any 2 nodes in a graph, no matter how large or complicated a graph:
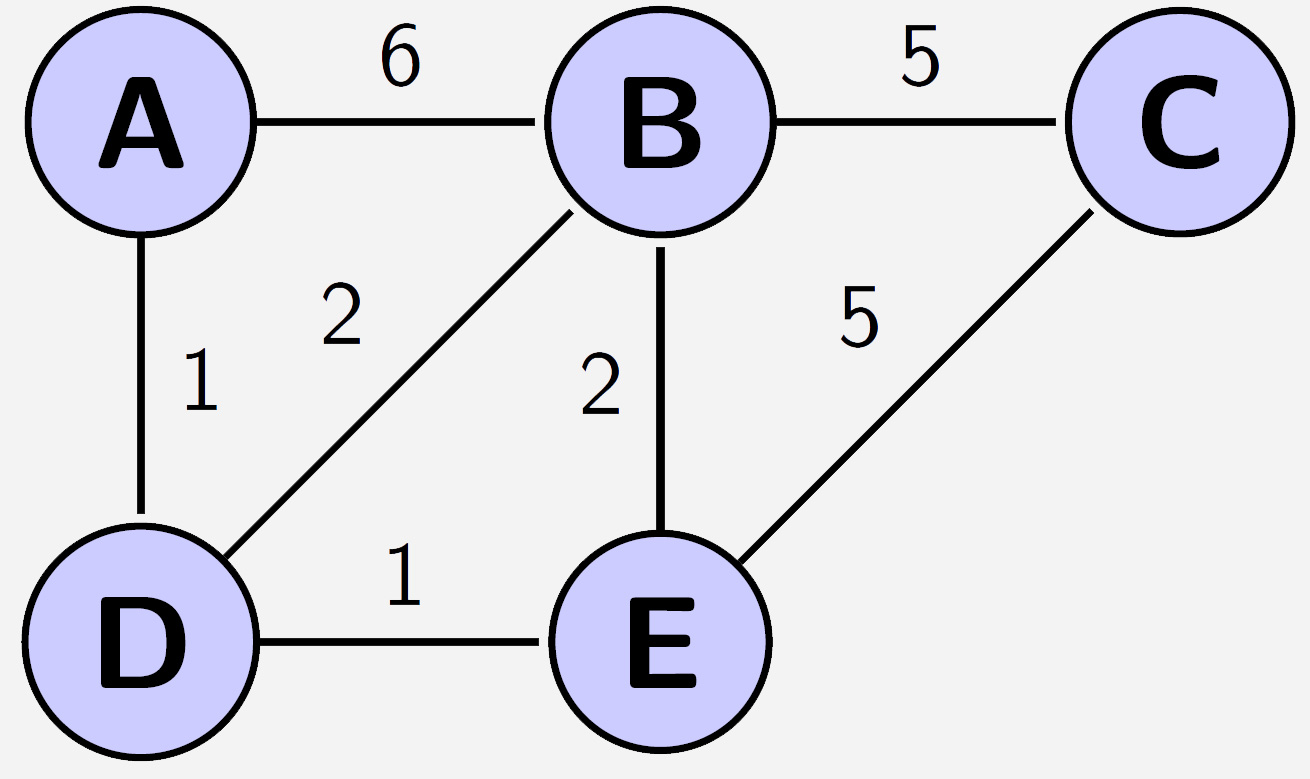
The algorithm works checking the minimum distance from the start (node A) to each node via a different path- if the new path is smaller, the node now has a shorter minium distance. By repeating this process for every node, we can methodically determine the shortest route from node A to node C. Here is the formal algorithm, courtesy of wikipedia:
- Assign to every node a tentative distance value: set it to zero for our initial node and to infinity for all other nodes.
- Set the initial node as current. Mark all other nodes unvisited. Create a set of all the unvisited nodes called the unvisited set.
- For the current node, consider all of its unvisited neighbors and calculate their tentative distances. Compare the newly calculated tentative distance to the current assigned value and assign the smaller one. For example, if the current node A is marked with a distance of 6, and the edge connecting it with a neighbor B has length 2, then the distance to B (through A) will be 6 + 2 = 8. If B was previously marked with a distance greater than 8 then change it to 8. Otherwise, keep the current value.
- When we are done considering all of the neighbors of the current node, mark the current node as visited and remove it from the unvisited set. A visited node will never be checked again.
- If the destination node has been marked visited (when planning a route between two specific nodes) or if the smallest tentative distance among the nodes in the unvisited set is infinity (when planning a complete traversal; occurs when there is no connection between the initial node and remaining unvisited nodes), then stop. The algorithm has finished.
- Otherwise, select the unvisited node that is marked with the smallest tentative distance, set it as the new "current node", and go back to step 3.
Let's work through the example above. We'll start by setting A to 0 and all other nodes to infinity:
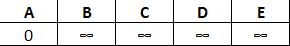
Next, we'll check the distances from A to B and D and update their values. All edges connected to A are complete, so we'll marked A as 'visited':
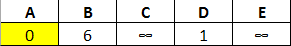
Of our unvisited nodes, D has the smallest value (2) so we'll check its out its edges, update B and E, and mark it as visited:
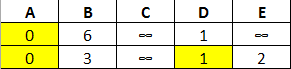
Now we'll repeat the process with node E and its neighbors. B does not change (as the route from E is length 4, shorter than its exisiting length of 3:
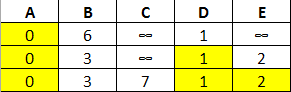
Finally, we'll check node B. Node C as an exisiting length of 7 (shorter than our new proposed route of 8), so nothing changes. There are no nodes left to examine, so our shortest route between A and C is 7.
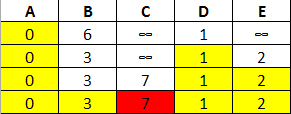
If you need additional information on how the algorithm works, please check wikipedia (the provided URL is at the top of the page as a related link). Now, onto the puzzle at hand:

You must find the shortest route between nodes A and X to get the final coordinates to this puzzle:
N41 3X.XXX
W83 3X.XXX
The missing 8 digits of the coordinate are the lengths along the shortest path. For example, if you though the shortest path was the top route ABEIMORUX, your coordinates would be N41 33.686, W083 34.245.
I recommend printing this out and solving on paper. Take your time, and work methodically. There will not be a checker for this one, partially due to the high difficulty and partially to prevent people from brute forcing the solution instead of solving. Good luck!