Earth Science Lesson
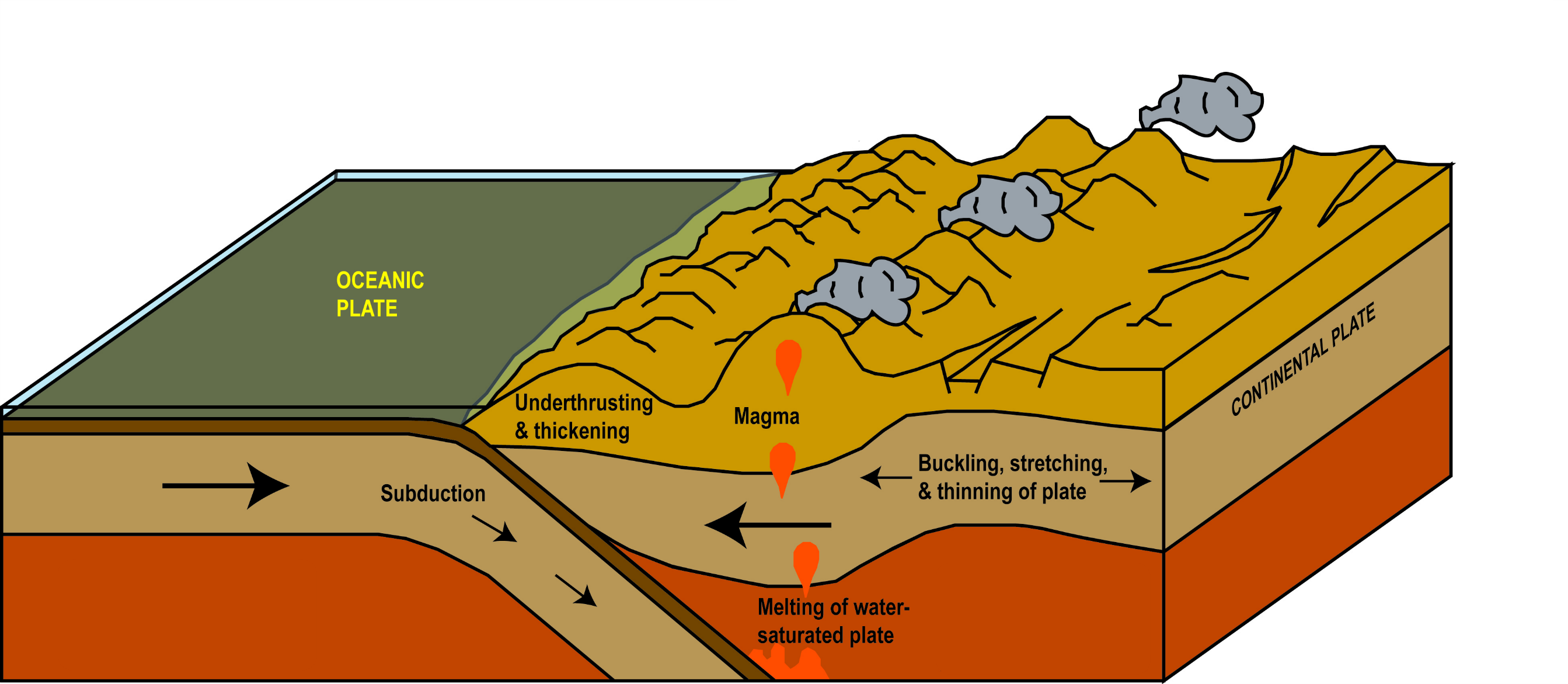
The granite that makes up Pikes Peak and the surrounding mountains that you can see from Crystal Reservoir was once molten rock. It slowly cooled and hardened miles beneath the surface, providing the crystals a very long time to grow. Over the last 500 million years numerous tectonic plates have collided forcing the now-cool granite lying below the surface upward. Around 65 million years ago a tectonic plate under the Pacific Ocean was driving into the North American continent which initiated tremendous, mountain building pressure below what is now Colorado and created Pikes Peak.
From two million to 10,000 years ago a series of Ice Age climates gripped the land. Alpine Glaciers formed on Pikes Peak. These rivers of ice gouged bowl-like hollows and U-shaped valleys. Since then, erosion has continued to sculpt the rugged mountain.
Logging Tasks
To earn credit for this Earthcache, please email me with the answers to these questions. Please do not include answers in your visit log. To assist with these questions, I have included properly labeled rock samples collected from this area.
1. How many u-shaped valleys can you identify from your present location (GZ)?
2. When you examine a piece of Pikes Peak granite you should be able to see evidence of a white material, a pink material, and possibly a clear shiny material. Name each material.
3. What do these crystals in the granite tell us about the rock’s origin?
4. Take a photo of yourself or a personal item to prove you were at the site. (REQUIRED).
Rock Examples
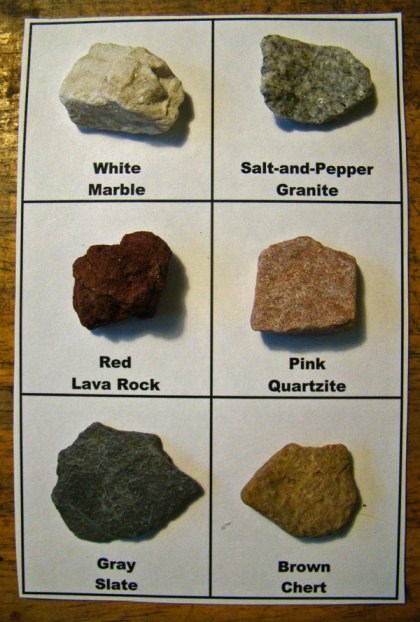



(Click photos to enlarge)
Rules of geocaching in National Forest
- When Geocaching, natural resources are not to be disturbed, nor are they allowed to be removed from NFS lands. That includes soil disturbance/digging, removal of vegetation, disturbance of natural features, etc.
- Avoid sensitive areas like wetlands or streams.
- When Geocaching, historical artifacts or features are not to be disturbed or removed. Geocaching shall not interfere with other permitted activities such as outfitter and guide designated campsites.
- When Geocaching, motorized vehicle use and parking shall be in compliance with PSICC travel regulations and Motor Vehicle Use Maps.
- Geocaching via horseback is not permitted in developed recreation sites other than those designated for equestrian use.
- Geocachers are not required to have a permit provided that they are in-compliance with all other FS regulations and policy concerning group size and fees.
CURRENT FEES AND HOURS FOR THE PARK
Resources
- Rogers, R. (2017). Pikes Peak Geology. Retrieved May 15, 2017, from http://www.pikespeak.us.com/Learn/geology.html
- Sarah. (2017). From Uplift to Glaciation: The Geological History of the Pikes Peak Region. Retrieved May 15, 2017, from http://www.amnh.org/learn-teach/young-naturalist-awards/winning-essays2/selected-winning-essays-1998-20032/from-uplift-to-glaciation-the-geological-history-of-the-pikes-peak-region/
- National Park Service. (2017). Stratigraphy. Retrieved May 15, 2017, from https://www.nps.gov/flfo/learn/education/stratigraphy.htm
- Esconi. (2016, March 04). Posts about Rock Hunters on Nature and Science Programs at Wonder Works. Retrieved May 16, 2017, from https://natureworksop.wordpress.com/category/rock-hunters/
