The listed coordinates indicate a monument of “the Birthplace of Fingerprint Research”. The cache is not hidden at the listed coordinates.
Dr. Henry Faulds, a Scottish surgeon, came to Japan in 1874 and settled in this place. He propagated Christianity as a missionary, and founded the Tsukiji hospital (present St. Luke International Hospital) and conducted medical treatment. He was interested in Japanese people using thumbprints to verify the identity of individuals and started researching fingerprints. In 1880, he submitted the world's first paper on scientific fingerprinting to the British scientific journal Nature from Japan.
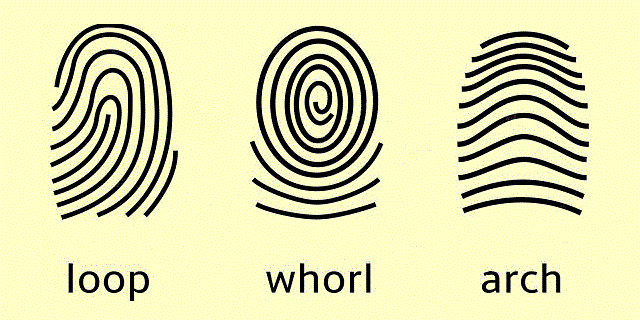
Faulds classified fingerprints into three basic patterns: loop, whorl, and arch, which constitute approximately 50%, 40%, and 10% of all fingerprints of Japanese people, respectively. The classification was later used for criminal investigations.
Actual cache coordinates:
N 35 40.(L-L)(A-L)(W*2-L)
E 139 46.(L)(W-W)(W*2-A)
Please bring your own pen.
===== Japanese =====
公開座標は、「指紋研究発祥の地」の碑を指しています。公開座標にキャッシュはありません。
英国人医師のヘンリー・フォールズは、明治7年(1874年)に来日し、この地に居を構え、宣教師としてキリスト教の布教を行うとともに、健康社築地病院(現在の聖路加国際病院)を設立し診療に従事しました。彼は日本人が拇印を利用して個人の同一性確認を行っていることに興味を持ち、指紋の研究を始めました。明治13年(1880年)に科学的指紋法に関する世界最初の論文を英国の科学雑誌Natureに日本から投稿しました。
フォールズは指紋を、蹄状紋(loop)、渦状紋(whorl)、弓状紋(arch)の3つの基本パターン(それぞれ日本人のおよそ50%、40%、10%)に分類しました。この分類は、後に犯罪捜査に利用されることになりました。

キャッシュは以下の座標にあります。
N 35 40.(L-L)(A-L)(W*2-L)
E 139 46.(L)(W-W)(W*2-A)
キャッシュにはペンが入っていませんのでお持ちください。

You can validate your puzzle solution with certitude.