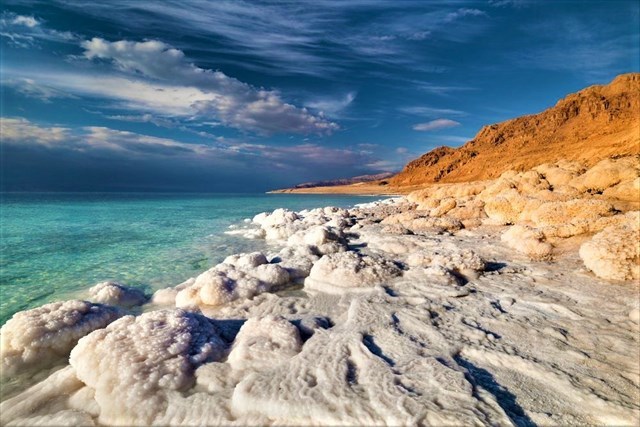

When you hear the name "Dead Sea," you might not picture your ideal vacation spot, yet this body of water has been attracting tourists for thousands of years. The minerals in the water are believed to offer therapeutic benefits, plus the high salinity of the water means it's super easy to float. Have you ever wondered why the Dead Sea is dead (or if it really is), how salty it is, and why so many people drown in it when you can't even sink?
Chemical Composition of the Dead Sea
The Dead Sea, nestled between Jordan, Israel, and Palestine, is one of the saltiest bodies of water in the world. In 2011, its salinity was 34.2%, which made it 9.6 times more salty than the ocean. The sea is shrinking each year and increasing in salinity, but it has been salty enough to prohibit plant and animal life for thousands of years.
The chemical composition of the water isn't uniform. There are two layers, which have different salinity levels, temperatures, and densities. The very bottom of the body has a layer of salt that precipitates out of the liquid. The overall salt concentration varies according to depth in the sea and the season, with an average salt concentration of about 31.5%. During flooding, the salinity can drop below 30%. However, in recent years the amount of water supplied to the sea has been less than the amount lost to evaporation, so the overall salinity is increasing.
The chemical composition of the salt is very different from that of sea water. One set of measurements of the surface water found the total salinity to be 276 g/kg and ion concentration to be:
- Cl-: 181.4 g/kg
- Mg2+: 35.2 g/kg
- Na+: 32.5 g/kg
- Ca2+: 14.1 g/kg
- K+: 6.2 g/kg
- Br-: 4.2 g/kg
- SO42-: 0.4 g/kg
- HCO3-: 0.2 g/kg
In contrast, the salt in most oceans is about 85% sodium chloride.
In addition to the high salt and mineral content, the Dead Sea discharges asphalt from seeps and deposits it as black pebbles. The beach is also lined with halite or salt pebbles.
Why the Dead Sea Is Dead
To understand why the Dead Sea doesn't support (much) life, consider how sal tis used to preserve food. The ions affect the osmotic pressure of cells, causing all of the water inside the cells to rush out. This basically kills plant and animal cells and prevents fungal and bacterial cells from thriving. The Dead Sea is not truly dead because it does support some bacteria, fungi, and a type of algae called Dunaliella. The algae supplies nutrients for a halobacteria (salt-loving bacteria). The carotenoid pigment produced by the algae and bacteria have been known to turn the blue waters of the sea red!
Although plants and animals don't live in the water of the Dead Sea, numerous species call the habitat around it their home. There are hundreds of bird species. Mammals include hares, jackals, ibex, foxes, hyraxes, and leopards. Jordan and Israel have nature preserves around the sea.
Why So Many People Drown in the Dead Sea
You might think it would be difficult to drown in water if you can't sink in it, yet a surprising number of people run into trouble in the Dead Sea. The density of the sea is 1.24 kg/L, which means people are unusually buoyant in the sea. This actually causes problems because it's hard to sink enough to touch the bottom of the sea. People who fall into the water have a hard time turning themselves over and may inhale or swallow some of the saltwater. The extremely high salinity leads to a dangerous electrolyte imbalance, which can harm the kidneys and heart. The Dead Sea is reported to be the second most dangerous place to swim in Israel, even though there are lifeguards to help prevent deaths.

10 Things you did not know about the Dead Sea:
1. The surface and shores of the Dead Sea are 423 metres (1,388 ft) below sea level, making it Earth’s lowest elevation on land.
2. The Dead Sea is 377 m (1,237 ft) deep, making it the deepest hypersaline lake in the world. A hypersaline lake is a landlocked body of water that contains significant concentrations of sodium chloride or other mineral salts, with saline levels surpassing that of ocean water.
3. With 33.7% salinity, the Dead Sea is one of the world’s saltiest bodies of water. Although Lake Assal (Djibouti), Garabogazköl and some hypersaline lakes of the McMurdo Dry Valleys in Antarctica (such as Don Juan Pond) have reported higher salinities.
4. The Dead Sea’s unusually high salt concentration means that people can easily float in the Dead Sea due to natural buoyancy. In this respect the Dead Sea is similar to the Great Salt Lake in Utah in the United States.
5. The Dead Sea is roughly 8.6 times saltier than the ocean. This salinity makes for a harsh environment in which animals cannot flourish (hence its name). The high salinity prevents macroscopic aquatic organisms such as fish and aquatic plants from living in it, though minuscule quantities of bacteria and microbial fungi are present.
6. The Dead Sea is 67 kilometres (42 mi) long and 18 kilometres (11 mi) wide at its widest point. It lies in the Jordan Rift Valley and its main tributary is the Jordan River.
7. The Dead Sea area has become a major center for health research and treatment for several reasons. The mineral content of the water, the very low content of pollens and other allergens in the atmosphere, the reduced ultraviolet component of solar radiation, and the higher atmospheric pressure at this great depth each have specific health effects.
8. Biblically, the Dead Sea was a place of refuge for King David. It was one of the world’s first health resorts (for Herod the Great), and it has been the supplier of a wide variety of products, from balms for Egyptian mummification to potash for fertilizers.
9. An unusual feature of the Dead Sea is its discharge of asphalt. From deep seeps, the Dead Sea constantly spits up small pebbles and blocks of the black substance. Asphalt coated figurines and bitumen coated Neolithic skulls from archaeological sites have been found. Egyptian mummification processes used asphalt imported from the Dead Sea region.
10. The world’s lowest road, Highway 90, runs along the Israeli and West Bank shores of the Dead Sea at 393 m (1,289 ft) below sea level.
Something about Salt
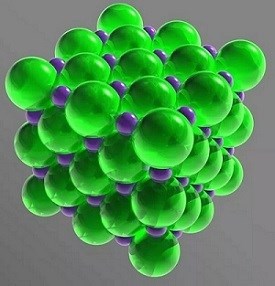
Salt is an ionic compound, which breaks into its component ions or dissociates in water. These ions are Na+ and Cl-. The sodium and chlorine atoms are present in equal amounts (1:1 ratio), arranged to form a cubic crystal lattice. The molecular formula of table salt—sodium chloride—is NaCl.
In the solid lattice, each ion is surrounded by six ions having an opposite electrical charge. The arrangement forms a regular octahedron. The chloride ions are much larger than the sodium ions. The chloride ions are arranged in a cubic array with respect to one another, while the small sodium cations fill the gaps between the chloride anions.
If you had a pure sample of sodium chloride, it would consist of NaCl. However, table salt actually is not pure sodium chloride. Anti-caking agents may be added to it, plus most table salt is supplemented with the trace nutrient iodin. While ordinary table salt is purified to contain mostly sodium chloride, sea salt contains many more chemicals, including other types of salt. The natural (impure) mineral is called halite.
One way to purify table salt is to crystallize it. The crystals will be relatively pure NaCl, while most impurities will remain the solution. The same process may be used to purify sea salt, although the resulting crystals will contain other ionic compounds.
Sodium chloride is vital for living organisms and important for industry. Most of the salinity of seawater is due to sodium chloride. The sodium and chloride ions are found in the blood, hemolymph, and extracellular fluids of multicellular organisms. Table salt is used to preserve food and enhance flavor. It's also used to de-ice roads and walkways and as a chemical feedstock. Salt may be used as a cleaning agent. Fire extinguishers Met-L-X and Super D contain sodium chloride to extinguish metal fires.
IUPAC Name: sodium chloride
Other Names: table salt, halite, sodium chloric
Chemical Formula: NaCl
Molar Mass: 58.44 grams per mole
Appearance: Pure sodium chloride forms odorless, colorless crystals. Many small crystals together reflect light back, making the salt appear white. The crystals may assume other colors if impurities are present.
Other Properties: Salt crystals are soft. They are also hygroscopic, which means they readily absorb water. Pure crystals in the air eventually develop a frosted appearance due to this reaction. For this reason, pure crystals are often sealed in a vacuum or completely dry environment.
Density: 2.165 g/cm3
Melting Point: 801 °C (1,474 °F; 1,074 K) Like other ionic solids, sodium chloride has a high melting point because significant energy is required to break ionic bonds.
Boiling Point: 1,413 °C (2,575 °F; 1,686 K)
Solubility in Water: 359 g/L
Crystal Structure: face-centered cubic (fcc)
Optical Properties: Perfect sodium chloride crystals transmit about 90% of light between 200 nanometers and 20 micrometers. For this reason, salt crystals may be used in optical components in the infrared range.


How to log this cache:
To log this cache you need to visit specific place in Dead Sea according to coordinations (access is free), where it is one of the highest salts / ooids concentrations on the coast of the Dead Sea, answers the following questions and reply me to an email in my profile.:
- Write me your own words why is the water in the Dead Sea so salty?
- Describe me shape, structure and color deposited salts on coords of earth cache.
- Number the steps of visible distance of salt on land from the sea on the coordinates of earth cache.
- Measure the altitude at the coordinates?
- Write me if it is possible to find a place with lower altitude on the Earth and walk on it with dry feet?
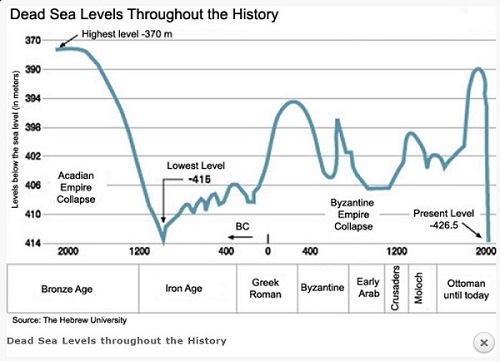
- Read from the chart: Dead Sea Levels Throughout the History of the Highest Level of Dead Sea in Bronze Age?
- Taste the salty water from the Dead Sea and write me your current feeling. Its really salty?
- Add to the log a photo of you on this salty place.
Feel free to log this cache. You do not need to wait for permission to log. If your answers are not correct, incomplete, I will contact you by e-mail. But if your e-mail is not coming to me within 3 days from your log, I will delete your log without notice.

كيفية تسجيل ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت هذه:
لتسجيل الدخول إلى ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت هذه ، يلزمك زيارة مكان محدد في البحر الميت وفقًا للإحداثيات (الوصول مجاني) ، حيث أنه أحد أعلى تركيزات الأملاح / السوائل على ساحل البحر الميت ، ويجيب على الأسئلة التالية ويجيبني على البريد الإلكتروني في ملفي الشخصي:
- اكتب لي كلماتك الخاصة لماذا المياه في البحر الميت مالحة جدًا؟
- صفني الشكل والبنية والأملاح المودعة بالألوان على رقائق ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت للأرض؟
- عدد خطوات المسافة الملح للملح على اليابسة من البحر على إحداثيات ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت للأرض؟
- قياس الارتفاع عند الإحداثيات؟
- اكتب لي إذا كان من الممكن العثور على مكان على ارتفاع منخفض على الأرض والمشي عليه بأقدام جافة؟
- قراءة من الرسم البياني: مستويات البحر الميت طوال تاريخ أعلى مستوى من البحر الميت في العصر البرونزي؟
- تذوق المياه المالحة من البحر الميت واكتب لي شعورك الحالي. انها حقا مالحة؟
- أضف إلى السجل صورة لك في هذا المكان المالح.
لا تتردد في تسجيل ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت هذه. لا تحتاج إلى الانتظار للحصول على إذن لتسجيل الدخول. إذا كانت إجاباتك غير صحيحة ، غير مكتملة ، سأتصل بك عن طريق البريد الإلكتروني. ولكن إذا لم يكن البريد الإلكتروني الخاص بك يأتي إلي في غضون 3 أيام من السجل الخاص بك ، فسوف أحذف السجل الخاص بك دون إشعار.
