What is basalt?
This EarthCache focuses on the igneous rock basalt, a common rock found at the GZ and all over St. Thomas. Magma that contains basalt is melted in the mantle, a portion of the Earth that sits below the crust. When this magma reaches the surface of the Earth via a hot spot or plate boundary, it can cool, building seamounts, islands, and mid-ocean ridges. The US Virgin Islands sits above the Carribean-North American Plate boundary (see image below). In the Early Cretaceous period, pillow basalt erupted, forming the US Virgin Islands. Most basalt worldwide is gray or black in color due to the high presence of iron and magnesium. However, when large amounts of pyroxene and olivine are present in basalt, it can appear greenish-gray.

Mafic or Felsic?
A mafic rock is rich in magnesium and iron. Most mafic minerals are dark in color, and common rock-forming mafic minerals include olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, and biotite. Common mafic rocks include diabase and gabbro.
A felsic rock is rich in feldspar and quartz. Most felsic rocks are lighter than mafic rocks and have beige or light brown hues. The most common felsic rock is granite. Common felsic minerals include quartz, muscovite, and orthoclase.

Characterizing Rocks/minerals:
Geologists use an array of terms to help characterize and examine the properties of a rock/mineral. Here are a few below:
- Cleavage: the rock/mineral breaks along a smooth, relatively flat surface.

- Fracture: the rock/mineral breaks along irregular and pointed edges.
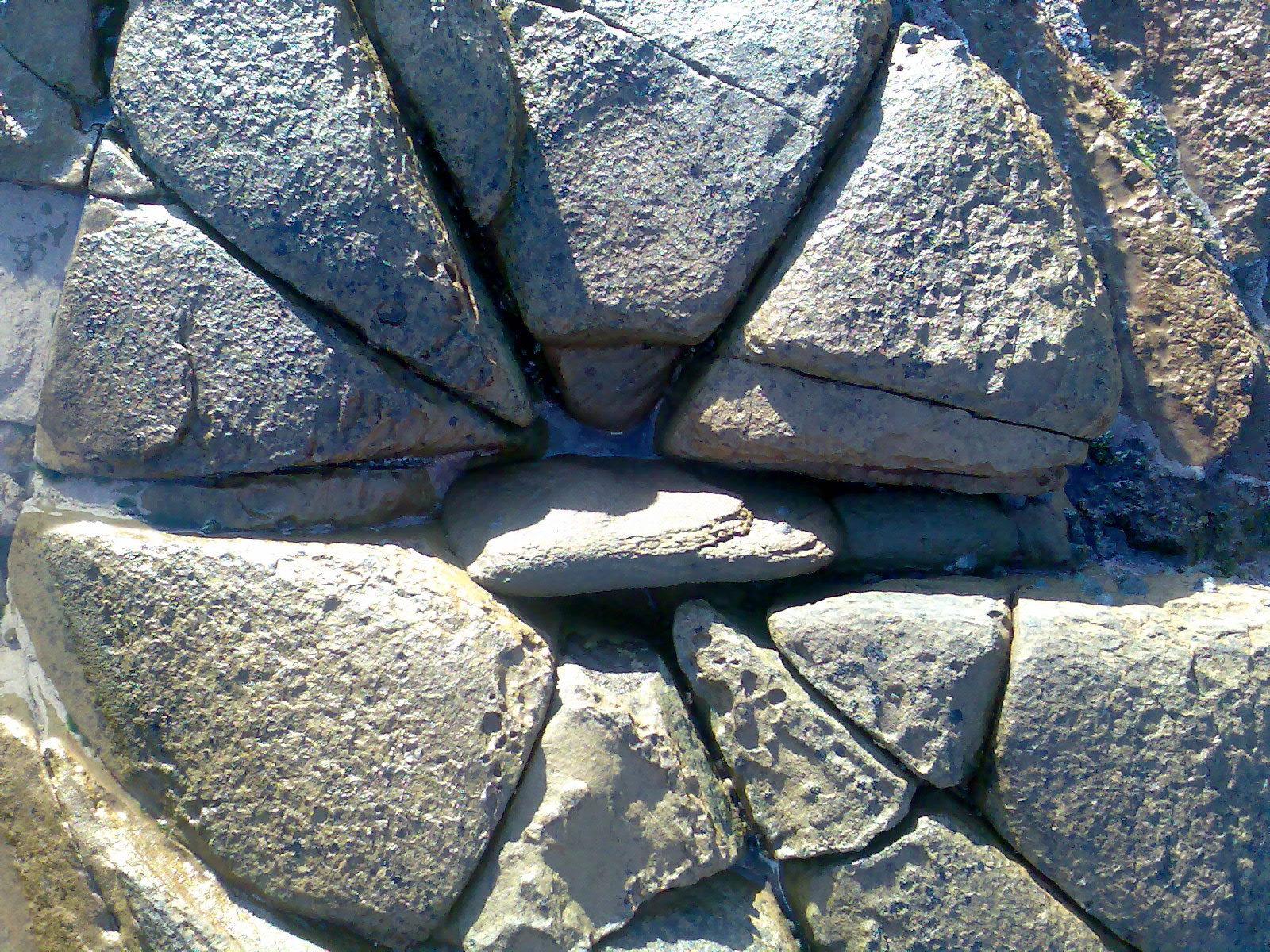

- Luster: the way that a rock/mineral gives off light. There are two main types of luster. Metallic luster resembles how metals give off light (ie: the mineral pyrite has a metallic luster). Nonmetallic luster is associated with rocks/minerals that do not resemble a metal.
Logging Tasks:
- Near the fountain, you should observe several examples of basalt boulders. What is the color of the boulders? What does this tell you about the minerals present in these specimens of basalt?
- Would you consider this rock to be mafic or felsic? Explain your rationale.
- Describe the appearance of the boulders. Note the following:
- What is the luster of the boulders?
- Do these specimens of basalt have cleavages or fractures?
- Please provide a photo of yourself, your GPSr, or a personal item that proves that you have visited this site. Please post this in your log.
Sources:
http://www.geologyin.com/2015/11/how-do-geologists-identify-minerals.html
https://www.forbes.com/sites/davidbressan/2022/06/09/new-map-shows-earths-tectonic-plates-in-unprecedented-detail/
https://pubs.usgs.gov/pp/p1631/P1631-tag.pdf
| We have earned GSA's highest level: |
 |