Welcome to the New Quay Wales Cliff Erosion Earth Cache! In this educational journey, we will explore the fascinating geological features and processes related to cliff erosion in New Quay, Wales. New Quay, a charming coastal town located on the west coast of Wales, is not only known for its stunning views but also for its dramatic cliffs that showcase the ongoing forces of nature.
To unlock the cache, you will need to visit the designated location and answer the following questions based on your observations and the information provided. Let's begin!
Now, let's delve into some background information to help you find the answers.
New Quay's cliffs are composed primarily of sedimentary rocks, which were formed over millions of years through the accumulation of layers of sediment. These sediments were eventually compressed and cemented together to form solid rock. The predominant rock type in this area is often sandstone or shale, which exhibit different erosion patterns due to their varying resistance to weathering.
Cliff erosion in New Quay is driven by several factors. Firstly, the relentless force of waves crashing against the cliffs plays a significant role. The power of these waves can exert immense pressure, leading to the gradual breakdown and removal of rock particles. Secondly, weathering processes such as freeze-thaw cycles, chemical weathering, and biological activity further weaken the cliff face, making it more susceptible to erosion.
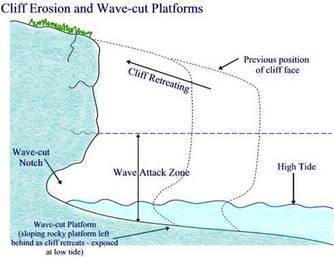
The constant wave action in New Quay has a profound impact on the cliffs. Waves erode the base of the cliffs, creating wave-cut notches and caves. Over time, these features can cause the overlying cliff sections to become unstable and collapse, resulting in the formation of sea stacks, arches, and other unique landforms.
Evidence of ongoing erosion can be found in the form of fallen rocks or debris at the base of the cliffs, exposed layers of rock that display signs of weathering, and the presence of erosional features such as caves or notches.
The significance of cliff erosion in shaping the coastal landscape of New Quay cannot be understated. As the cliffs recede over time, the coastline undergoes constant change. This natural process contributes to the formation of picturesque bays, headlands, and other coastal landforms, creating a dynamic and ever-evolving environment.
Remember to take caution during your exploration of the cliffs, as they can be unstable and dangerous. Please adhere to any safety guidelines and signs provided in the area.
Question 1: Describe the type of rock formations you see at the cliffs in New Quay.
Question 2: What forces contribute to the erosion of these cliffs?
Question 3: How does wave action affect the cliffs in New Quay?
Question 4: What evidence can you find that demonstrates the ongoing erosion of the cliffs?
Question 5: Explain the significance of cliff erosion in shaping the coastal landscape of New Quay.
Once you have your answers, please submit them through my profile or email me at 'euan.morris@yahoo.com.'
Enjoy your journey of discovery through the New Quay Wales Cliff Erosion Earth Cache, and may you gain a deeper understanding of the fascinating geological processes shaping our world!
Key Words:
-
Sedimentary rocks: Rocks formed through the accumulation and compression of layers of sediment over time.
-
Sandstone: A type of sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized grains.
-
Shale: A fine-grained sedimentary rock that tends to split into thin layers.
-
Erosion: The process of wearing away or removal of soil, rock, or other materials by natural agents, such as water, wind, or ice.
-
Wave-cut notch: A concave indentation formed at the base of a cliff by wave action.
-
Weathering: The breakdown and alteration of rocks and minerals at or near the Earth's surface by various chemical, physical, and biological processes.
-
Freeze-thaw cycles: Repeated cycles of freezing and thawing that can cause the expansion and contraction of water within rocks, leading to their disintegration.
-
Chemical weathering: The breakdown of rocks through chemical reactions, such as dissolution, oxidation, or hydrolysis.
-
Biological activity: The role of organisms, such as plants and burrowing animals, in weathering and breaking down rocks.
-
Sea stacks: Isolated columns of rock that are left standing as the result of the collapse and erosion of cliffs.
Here are some images:
Rock formations:
Wave erosion diogram:
Congratulations ScottP55 on the FTF 1.6.2023
Cliff Retreat Diogram.
