このレッスンの目的は、小石とは何かを知ることです!
(難しい課題はないので、初心者の方でも簡単に始められるアースキャッシュのつもりです。だからD1 / T1です)。
小石とは、堆積学のクランバイン・ファイ尺度に基づく粒径2~64ミリの*岩石の塊である。小石は一般に、顆粒(直径2~4ミリメートル)より大きく、玉石(直径64~256ミリメートル)より小さいと考えられている。小石を主成分とする岩石は礫岩と呼ばれる。小石器は、人類史上最古の人工物のひとつであり、旧石器時代のものである。
The purpose of this lesson is to get to know what pebbles are!
(This intends to be an easy earthcache for new beginners to start off with, as there is not any hard tasks to go through with. So it is rated D1 / T1.)
A pebble is a *clast of rock with a particle size of 2 to 64 millimetres based on the Krumbein phi scale of sedimentology. Pebbles are generally considered larger than granules (2 to 4 millimeters diameter) and smaller than cobbles (64 to 256 millimeters diameter). A rock made predominantly of pebbles is termed a conglomerate. Pebble tools are among the earliest known man-made artifacts, dating from the Palaeolithic period of human history.

主に表面の小石で構成されたビーチは、一般にシングル・ビーチと呼ばれる。このタイプのビーチは、波による浸食に対する鎧のような特性を持っており、また、動物や植物に生息域を提供する生態学的ニッチを備えている。
鉱石川の入り口のようないくつかの場所には、海岸礫(大量の小石)の海岸堤防があり、海岸礫の移動する堤防は、航海に大きな困難をもたらす。
小石にはさまざまな色や質感があり、石英や異なる色の堆積岩の筋が見られることもある。小石のほとんどは滑らかだが、海との接触頻度によっては、他の岩や他の小石と接触した跡が残ることもある。高水位にある小石には、海水と接触していないことを示す地衣類などの生物が繁殖していることがある。
*砕屑物-砕屑岩は、既存の鉱物や岩石の破片(クラスト)で構成されている。砕屑物とは、物理的風化作用によって他の岩石から砕け散った岩石の塊や小さな粒のことである。地質学者は、**堆積岩を指して砕屑岩という言葉を使う。
**堆積岩は、通常、湖や海の底に堆積した堆積物によって形成される。堆積物には鉱物、植物の小片、その他の有機物が含まれる。堆積物は長い時間をかけて圧縮され、固まった岩石の層になる。その結果、地層と呼ばれる層が形成される。
堆積岩は地球の岩石表面の大部分を占めているが、変成岩や火成岩に比べると地殻に占める割合は小さい。堆積岩の例としては、石灰岩、砂岩、泥岩、灰岩、チョーク、石炭、粘土岩、火打石などがある。石灰岩は、長い年月をかけて極度の熱と圧力を受けると(変成作用)、変成岩の大理石を形成する。砂岩は変成岩の石英岩を形成する。泥岩は変成岩の粘板岩を形成する。白亜は石灰岩の軟らかい白色である。火打石は、石英という鉱物の硬い堆積岩である。
A beach composed chiefly of surface pebbles is commonly termed a shingle beach. This type of beach has armoring characteristics with respect to wave erosion, as well as ecological niches that provide habitat for animals and plants.
Inshore banks of shingle (large quantities of pebbles) exist in some locations, such as the entrance to the River Ore, where the moving banks of shingle give notable navigational challenges.
Pebbles come in various colors and textures, and can have streaks of quartz and different colored sedimentary rock. Pebbles are mostly smooth but, dependent on how frequently they come in contact with the sea, they can have marks of contact with other rocks or other pebbles. Pebbles left above the high water mark may have growths of organisms such as lichen on them, signifying the lack of contact with seawater.
*Clast - Clastic rocks are composed of fragments, or clasts, of pre-existing minerals and rock. A clast is a fragment of geological detritus, chunks and smaller grains of rock broken off other rocks by physical weathering. Geologists use the term clastic with reference to **sedimentary rocks.
**Sedimentary rocks are formed by sediment that is deposited over time, usually as layers at the bottom of lakes and oceans. The sediment can include minerals, small pieces of plants and other organic matter. The sediment is compressed over a long period of time before consolidating into solid layers of rock. It forms layers called strata which can often be seen in exposed cliffs.
Sedimentary rocks cover the majority of the Earth's rocky surface but only make up a small percentage of the Earth’s crust compared to metamorphic and igneous types of rocks. Examples of sedimentary rocks include limestone, sandstone, mudstone, greywacke, chalk, coal, claystone and flint. Limestone forms the metamorphic rock marble when subjected to extreme heat and pressure over time (metamorphism). Sandstone forms the metamorphic rock quartzite. Mudstone forms the metamorphic rock slate. Chalk is a soft, white form of limestone. Flint is a hard, sedimentary form of the mineral quartz.
岩石の3つのタイプ
# 火成岩(火山性) 結晶のある典型的なもの
# 変成岩:典型的な変形岩。
# 堆積岩(層状)
Three Types of Rock:
# Igneous (Volcanic) typical with crystals
# Metamorphic (Changed) typial deformed
# Sedimentary (Layered)
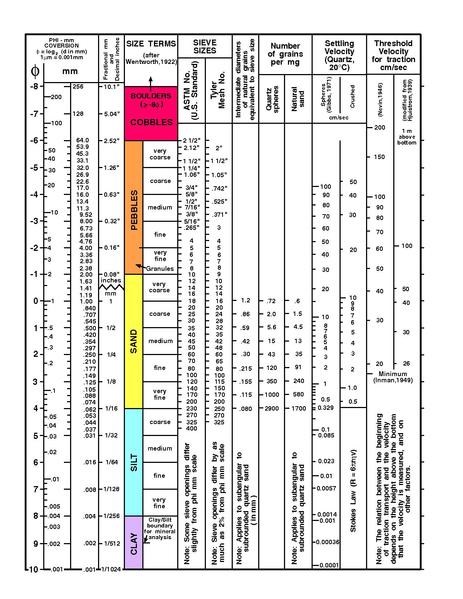
上のリンクをクリックすると、見やすいサイズのチャートが表示されます。
下の質問の答えにお使いください。
By clicking on the link above you will get to this chart in a good size to look at.
Use it for answering you question below.
このキャッシュを記録する
このキャッシュを記録するためには、アースキャッシュの座標に関連した質問に答えなければなりません。
答えが集まったら、確認のためCOに送ってください。
回答がCOに送られた後、すぐにログを取ることができます。あなたの答えに質問がある場合は、COがあなたに連絡します。
COへの回答がないログや、COからの質問が保留されているログは予告なく削除されます。
質問の答えとなるような写真をログに含めないでください。
To log this cache.
To get to log this cache you will have to visit and answer the questions which are related to the coordinates given the earthcache.
When answers are collected, send them to CO for verification.
You can log immediately after answers are sent CO. If there are any questions about your answers CO will contact you.
Logs without answers to CO or with pending questions from CO will be deleted without any further notice.
Please do not include pictures in your log that may answer the questions.
質問
1. 以下の質問に答えてください。
A. 小石にはいろいろな色があります!gzで一度見つかった主な色は?
B. gzであなたが隣に立っている小石の大きさは?リンク先のスケールを使って、どのスケールに属するか教えてください。
明るい色の石と黒い色の石です。
C. この場所にある小石は、両方ともどんな種類の石ですか?
# 火成岩
# 変成岩
# 堆積岩(層状)
D. 石が丸みを帯びていて、尖った端や角がないのはなぜだと思いますか?
2. その場所から、あなた、グループ、またはGPSが写った写真を、答えを明かさずに撮ってください。
Questions
1. Answer the questions under by visiting the Coordinates.
A. Pebbles can be found in many colors! What main colors are the once found at gz?
B. The pebbles you stand next to at gz, what size are they? Use the scale (linked to above) to tell where in the scale they belong.
There are two main areas to study, the light coloured stones and the black coloured stones.
C. What type of stone are the pebbles at the location, both types?
# Igneous (Volcanic)
# Metamorphic (Changed)
# Sedimentary (Layered)
D. Why do you think the stones are round/rounded and not with sharp ends/corners?
2. Take a photo of you, the group or the GPS from the location without revealing any of the answers.