|

🇭🇺 Esztergomban rengeteg geológiai titok rejlik. Üdvözöllek a következő EarthCache helyszínemen!
🇬🇧 Esztergom has plenty of geological secrets. Welcome to my next EarthCache!

Geology
🇭🇺
A víz eróziója a víz zavaró hatása a kőzetalapra. Lejtőkön, ahol a talaj gyenge, a csapadék hatására felszíni erózió alakul ki. A folyómederben a víz saját áramlása idézi elő a hátrafelé, mély és oldalsó erózió jelenségeit. A hátrafelé és mély erózió jellemzően a folyók felső szakaszán hat, ahol „V” alakú völgyeket formál, vagy vízeséseket, lépcsőzetes szinteket hoz létre a folyó esésgörbéjén.
Az oldalsó erózió főként a folyók középső és alsó szakaszán jelentkezik, ahol kanyarulatokat és part menti üledékeket alakít ki. Az úgynevezett abraszió pedig a hullámzás és szél hatására keletkezik, elsősorban a tározók, tavak partvidékén. Ezek a folyamatok folyamatosan formálják a tájat, és nagyban befolyásolják a vízfolyások fejlődését és viselkedését.
A folyami üledékek különféle szemcseméretű anyagokat tartalmaznak, amelyeket a víz rak le. Gyakoriak a durva szemcséjű anyagok, például kavics és homok, de előfordulnak finomabb, iszapos árterületi lerakódások is. Ezekből fluviolakusztrikus üledékek is kialakulhatnak, amelyek szabályosabb, rétegzett szerkezetűek, mint például folyóvízi tavak üledékei. Az olvadó gleccserek által szállított és lerakott anyagokat glacifluviális üledékeknek nevezzük.
🇬🇧 Water erosion is the disruptive action of water on rock or soil substrates. It appears on slopes with weak bases due to rainfall as so-called surface erosion. In riverbeds, it takes the form of backward, deep, and lateral erosion. Backward and deep erosion occur mainly in the upper course of rivers, creating steep, V-shaped valleys or – in the case of backward erosion – waterfalls and other steps in the stream’s slope profile.
Lateral erosion dominates in the middle and lower river courses. The flowing water causes the widening of the riverbed, the formation of meanders, and riparian deposits along the banks. Additionally, there is abrasion, which occurs on reservoir banks due to wave action and surf. These types of erosion constantly reshape the landscape and influence the direction and nature of the river flow.
Fluvial (river) sediments are deposits formed by river activity. They are often coarse-grained (e.g., gravel and sand), but in floodplains, fine-grained clays are also deposited. These sediments can transition into fluviolacustrine (river-lake) deposits, which are characterized by regular, rhythmic layering. Sediments created by melting glaciers are known as glacifluvial deposits.

River terraces
🇭🇺 A folyó teraszok többé-kevésbé jelentős lépcsőzetek a folyóvölgyek lejtőin, amelyeket a vízfolyás eróziója és felhalmozódása hozott létre. Lényegében ezek a völgy egykori fenekének maradványai, amelyeket a következő szakaszban a vízfolyás levágott (erodált). A teraszok lépcső alakúak, amelyek egyik oldalon sík felületből (úgynevezett teraszplatform) állnak, a másik oldalon pedig meredek lejtőből (teraszlejtő), és ezen a határon található a teraszél.
Gyakran több terasz (teraszlépcső) található egymás fölött. A legtöbb folyóterasz felhalmozódó eredetű, ahol a terasz alapja is kialakult, amelyen folyami üledékek, különösen kavics és homok pihen. Ritkábbak az eróziós teraszok, azaz sziklás, fedetlen üledékek. Vannak beágyazott teraszok is, amelyeknél a vízfolyás eróziója csak a folyami allúviumban történt, és nem érte el az alapkövet.
A folyó teraszok kialakulásának okai elsősorban tektonikus mozgások, amelyek az adott terület emelkedését eredményezik, éghajlatváltozás (különösen a jégkorszakok és interglaciális idők váltakozása) és a fő eróziós alap változásai.
🇬🇧 River terraces are more or less significant steps on the slopes of river valleys, created by erosion and accumulation of water flow. In essence, this is the rest of the former bottom of the valley, which was in the next phase cut (eroded) by a watercourse. The terraces have the shape of a step, formed on the one hand by a flat surface (the so-called terrace platform) and on the other hand by a steep slope (terrace slope), at their junction there is a terrace edge.
There are often several terraces (terrace steps) on top of each other. Most of the river terraces are of accumulative origin, where the base of the terrace is also developed, on which river sediments, especially gravel and sand, rest. More rare are erosive terraces, i.e., rocky, uncovered sediments. There are also embedded terraces, in which the erosion of the flow took place only in river alluvium and did not reach the bedrock.
The causes of river terraces are mainly tectonic movements, leading to the uplift of the relevant part of the territory, climate change (especially the alternation of ice and interglacial times), and changes in the main erosion base.
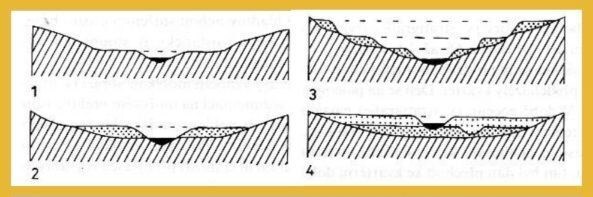
Terrace types
🇭🇺 [1] A szikla terasz akkor alakul ki, amikor a folyó erodálja a üledékrétegeket, és eléri az alatta lévő alapkövet, így feltárulnak a sziklafelszínek. Ezek a teraszok olyan területeket jelölnek, ahol a folyó mélyen belevágott a völgy aljába.
[2] Ez a típusú terasz akkor jön létre, amikor a folyó saját magától lerakott üledékeibe, mint például homokba és kavicsba, vág bele. A folyó erodálja az összegyűlt anyagot, és lapos teraszplatformot hagy maga után, amely a tömörített üledékből áll.
[3] Idővel a folyó fokozatosan erodálja a tájat, több teraszlépcsőt kialakítva. A legöregebb terasz a legmagasabb ponton van, a legfiatalabb pedig az alacsonyabb ponton, tükrözve az erózió és a lerakódás folyamatos folyamatát.
[4] Ez a terasz akkor alakul ki, amikor a folyó hosszú időn keresztül rak le anyagot, új teraszokat képezve a régebbiek fölött. A fiatalabb terasz a régebbi teraszon pihen, jelezve a folyamatos lerakódást és a folyó szintjének emelkedését.
🇬🇧 [1] A rock terrace is formed when the river erodes through sediment layers and reaches the underlying bedrock, leaving behind exposed rock surfaces. These terraces indicate areas where the river has deeply cut into the valley floor.
[2] This type of terrace occurs when the river cuts into its own deposited sediments, such as sand and gravel. The river erodes the accumulated material, leaving behind a flat terrace platform made of the compacted sediment.
[3] Over time, the river gradually erodes the landscape, forming multiple terrace steps. The oldest terrace lies at the top, and the youngest terrace is at the lowest point, reflecting the ongoing process of erosion and deposition.
[4] This terrace forms when the river deposits material over a long period, creating new terraces above older ones. The younger terrace rests on top of the older one, indicating continuous deposition and rising river levels.
🇭🇺 A "found it" naplóhoz kérem küldje el nekem a válaszokat a profilomon keresztül:
1) Írd le saját szavaiddal a víz eróziójának folyamatát.
2) A víz eróziója itt lassú vagy gyors? Miért gondolod ezt?
3) Milyen típusú folyóterasz [1, 2, 3, 4] található az induló koordinátákon? Indokold meg a válaszodat.
4) Készíts képet magadról vagy a GPS-edről a folyóterasszal a hídról, és töltsd fel a képet a naplódba.
🇬🇧 For log as "found it" please send me answers for those questions via my profile:
1) Describe in your own words the process of water erosion. 2) Is water erosion slow or fast here? Why do you think that?
3) What type of river terrace [1, 2, 3, 4] is located at the initial coordinates? Justify your statement. 4) Take a picture of you or your GPS with the river terrace from the bridge and upload the picture to your log.
🇭🇺 A válaszok elküldése után azonnal jelentkezzen be, köszönöm.
🇬🇧 Please log the cache immediately after sending your answers, thanks. Photos by DanielKotmel, 2025. Sources -
Water erosion [online]. Available from https://eos.com/blog/water-erosion/ [21. 04. 2025]
Fluvial features [online]. Available from https://www.nps.gov/articles/ meandering-stream.htm [21. 04. 2025]
Stream bank [online]. Available from https://www.lakesuperiorstreams.org/ understanding/streambank.htm [21. 04. 2025]

|