이 강의의 목적은 자갈이 무엇인지 알아보는 것입니다!
(이것은 어려운 작업이 없으므로 초보자가 시작하기에 쉬운 어스캐시가 되도록 의도된 것입니다.)
자갈은 퇴적학의 크룸베인 파이 척도에 따라 입자 크기가 2~64밀리미터인 암석의 파편입니다. 자갈은 일반적으로 입자(직경 2~4mm)보다 크고 자갈돌(직경 64~256mm)보다 작습니다. 자갈이 주성분인 암석은 응집암이라고 합니다. 자갈로 만든 도구는 인류 역사상 구석기 시대부터 사용된 가장 오래된 인공 유물 중 하나입니다.

주로 표면 자갈로 구성된 해변을 일반적으로 자갈 해변이라 부른다. 이 유형의 해변은 파도 침식에 대한 방어 특성을 지닐 뿐만 아니라 동식물의 서식지를 제공하는 생태적 틈새를 형성한다.
일부 지역, 예를 들어 오어 강 입구에는 연안 자갈 둑(대량의 자갈)이 존재하며, 이동하는 자갈 둑은 항해에 상당한 어려움을 초래한다.
자갈은 다양한 색상과 질감을 지니며, 석영 줄무늬나 다색의 퇴적암 성분을 포함할 수 있다. 대부분 매끄럽지만, 바다와의 접촉 빈도에 따라 다른 암석이나 자갈과의 접촉 흔적이 남을 수 있다. 만조선 위쪽에 위치한 자갈에는 이끼 같은 생물체의 부착물이 생기기도 하는데, 이는 해수와 접촉하지 않음을 의미한다.
*클라스트 - 클라스트암은 기존 광물과 암석의 파편(클라스트)으로 구성됩니다. 클라스트는 물리적 풍화로 다른 암석에서 떨어져 나온 암석 파편, 덩어리 및 작은 입자로 이루어진 지질학적 잔해의 일부입니다. 지질학자들은 **퇴적암을 지칭할 때 클라스트라는 용어를 사용합니다.
퇴적암은 오랜 시간에 걸쳐 호수나 바다 바닥에 주로 층을 이루며 쌓인 퇴적물에 의해 형성됩니다. 이 퇴적물에는 광물, 식물의 작은 조각 및 기타 유기물이 포함될 수 있습니다. 퇴적물은 오랜 기간 압축된 후 단단한 암석층으로 굳어집니다. 이는 지층이라고 불리는 층을 형성하며, 노출된 절벽에서 흔히 관찰할 수 있습니다.
퇴적암은 지구의 암석 표면 대부분을 덮고 있지만, 변성암 및 화성암 유형에 비해 지각에서 차지하는 비율은 매우 적습니다. 퇴적암의 예로는 석회암, 사암, 이암, 회색사암, 백악, 석탄, 점토암, 부싯돌 등이 있습니다. 석회암은 오랜 시간 극한의 열과 압력을 받으면(변성작용) 변성암인 대리석으로 변합니다. 사암은 변성암인 규암으로 변합니다. 이암은 변성암인 슬레이트로 변합니다. 백악은 부드러운 흰색 석회암 형태입니다. 부싯돌은 광물인 석영의 단단한 퇴적 형태입니다.
암석의 세 가지 유형:
# 화성암 (화산암) - 결정 구조가 특징
# 변성암 (변형된 암석) - 변형된 형태가 특징
# 퇴적암 (층상 구조)
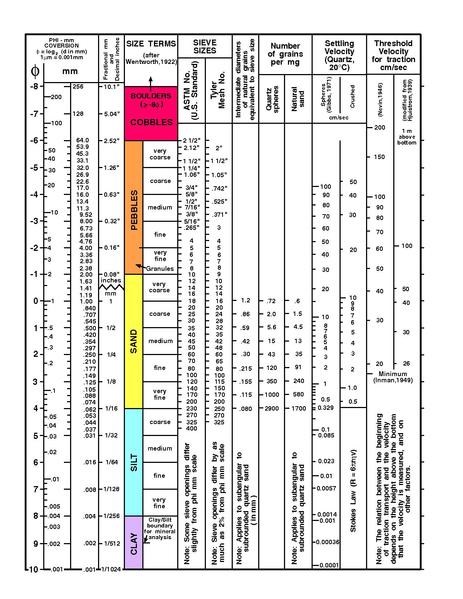
위 링크를 클릭하면 보기 좋은 크기의 차트를 확인할 수 있습니다.
아래 질문에 답할 때 이 차트를 활용하세요.
이 캐시를 기록하려면.
이 캐시를 기록하려면 지오캐시에 제공된 좌표와 관련된 질문들을 방문하여 답변해야 합니다.
답변을 수집한 후, 확인을 위해 CO에게 보내주십시오.
답변을 CO에게 보낸 직후 기록할 수 있습니다. 답변에 대해 질문이 있을 경우 CO가 연락할 것입니다.
CO에게 답변을 제출하지 않았거나 CO의 미해결 질문이 있는 로그는 별도의 통보 없이 삭제됩니다.
질문에 대한 답이 될 수 있는 사진을 로그에 포함하지 마십시오.
질문
1. 좌표를 방문하여 아래 질문에 답하세요.
A. 자갈은 다양한 색상으로 발견됩니다! gz에서 발견되는 자갈의 주요 색상은 무엇인가요?
B. gz에서 여러분이 서 있는 자갈의 크기는 어떻게 되나요? 위 링크된 척도를 사용하여 해당 자갈이 척도상 어디에 속하는지 설명하세요. 연구해야 할 주요 영역은 밝은 색 돌과 검은색 돌로 구분됩니다.
C. 해당 위치의 자갈은 어떤 종류의 돌인가요? 두 종류 모두 설명하세요.
# 화성암(화산암): 결정이 특징
# 변성암(변형된 암석): 변형 흔적이 특징
# 퇴적암(층상 구조):
D. 대부분의 돌이 날카로운 모서리/끝이 아닌 둥글거나 둥글게 다듬어진 형태인 이유는 무엇이라고 생각하나요?
2. 답변 내용이 노출되지 않도록 해당 위치에서 본인, 그룹 또는 GPS를 촬영하세요.
The purpose of this lesson is to get to know what pebbles are!
(This intends to be an easy earthcache for new beginners to start off with, as there is not any hard tasks to go through with.)
A pebble is a *clast of rock with a particle size of 2 to 64 millimetres based on the Krumbein phi scale of sedimentology. Pebbles are generally considered larger than granules (2 to 4 millimeters diameter) and smaller than cobbles (64 to 256 millimeters diameter). A rock made predominantly of pebbles is termed a conglomerate. Pebble tools are among the earliest known man-made artifacts, dating from the Palaeolithic period of human history.

A beach composed chiefly of surface pebbles is commonly termed a shingle beach. This type of beach has armoring characteristics with respect to wave erosion, as well as ecological niches that provide habitat for animals and plants.
Inshore banks of shingle (large quantities of pebbles) exist in some locations, such as the entrance to the River Ore, where the moving banks of shingle give notable navigational challenges.
Pebbles come in various colors and textures, and can have streaks of quartz and different colored sedimentary rock. Pebbles are mostly smooth but, dependent on how frequently they come in contact with the sea, they can have marks of contact with other rocks or other pebbles. Pebbles left above the high water mark may have growths of organisms such as lichen on them, signifying the lack of contact with seawater.
*Clast - Clastic rocks are composed of fragments, or clasts, of pre-existing minerals and rock. A clast is a fragment of geological detritus, chunks and smaller grains of rock broken off other rocks by physical weathering. Geologists use the term clastic with reference to **sedimentary rocks.
**Sedimentary rocks are formed by sediment that is deposited over time, usually as layers at the bottom of lakes and oceans. The sediment can include minerals, small pieces of plants and other organic matter. The sediment is compressed over a long period of time before consolidating into solid layers of rock. It forms layers called strata which can often be seen in exposed cliffs.
Sedimentary rocks cover the majority of the Earth's rocky surface but only make up a small percentage of the Earth’s crust compared to metamorphic and igneous types of rocks. Examples of sedimentary rocks include limestone, sandstone, mudstone, greywacke, chalk, coal, claystone and flint. Limestone forms the metamorphic rock marble when subjected to extreme heat and pressure over time (metamorphism). Sandstone forms the metamorphic rock quartzite. Mudstone forms the metamorphic rock slate. Chalk is a soft, white form of limestone. Flint is a hard, sedimentary form of the mineral quartz.
Three Types of Rock:
# Igneous (Volcanic) typical with crystals
# Metamorphic (Changed) typial deformed
# Sedimentary (Layered)
By clicking on the link above you will get to this chart in a good size to look at.
Use it for answering you question below.

To log this cache.
To get to log this cache you will have to visit and answer the questions which are related to the coordinates given the earthcache.
When answers are collected, send them to CO for verification.
You can log immediately after answers are sent CO. If there are any questions about your answers CO will contact you.
Logs without answers to CO or with pending questions from CO will be deleted without any further notice.
Please do not include pictures in your log that may answer the questions.
Questions
1. Answer the questions under by visiting the Coordinates.
A.Pebbles can be found in many colors! What main color are the once found at gz?
B. The pebbles you stand next to at gz, what size are they? Use the scale (linked to above) to tell where in the scale they belong. There are different main areas to study, the light coloured stones and the black coloured stones.
C. What type of stone are the pebbles at the location, both types?
# Igneous (Volcanic) typical with crystals
# Metamorphic (Changed) typial deformed
# Sedimentary (Layered)
D. Why do you think most of the stones are round/rounded and not with sharp ends/corners?
2. Take a photo of you, the group or the GPS from the location without revealing any of the answers.