 |
Gully Erosion |
 |
A gully is a landform created by running water, eroding sharply into soil, typically on a hillside. Gullies resemble large ditches or small valleys. When the gully formation is in process, the water flow rate can be substantial, which causes the significant deep cutting action into soil.
Gully erosion is the process by which gullies are formed. Hillsides are more prone to gullying when they are cleared of vegetation, through deforestation, over-grazing or other means. The eroded soil is easily carried by the flowing water after being dislodged from the ground, normally when rainfall falls during short, intense storms such as during thunderstorms.
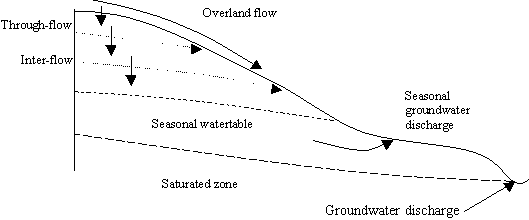 Process of formation: The gully moves upward at a nick point. This is from interflow as well as surface runoff. This interflow is quite important for the propagation of the nick point and its migration upstream.
Process of formation: The gully moves upward at a nick point. This is from interflow as well as surface runoff. This interflow is quite important for the propagation of the nick point and its migration upstream.
Gullies reduce the productivity of farmland where they incise into the land, and produce sediment that may clog downstream waterbodies. The total soil loss from gully formation and subsequent downstream river sedimentation can be sizable.
Slope Gradient and Length Naturally, the steeper the slope of a field, the greater the amount of soil loss from erosion by water. Soil erosion by water also increases as the slope length increases due to the greater accumulation of runoff. Consolidation of small fields into larger ones often results in longer slope lengths with increased erosion potential, due to increased velocity of water which permits a greater degree of scouring (carrying capacity for sediment).
Vegetation Soil erosion potential is increased if the soil has no or very little vegetative cover of plants and/or crop residues. Plant and residue cover protects the soil from raindrop impact and splash, tends to slow down the movement of surface runoff and allows excess surface water to infiltrate.
Your picture is welcome

To log your find you must send me a mail, answering the following questions:
1 -Look up the slope. How do you think that the erosion started?
2 - In the Erosion and Sediment Control Guidelines, Built Environment (NRETAS, 2012), what is one of the ways to prevent further erosion?
3 -Walk down the path (take care) to the final waypoint. What is the depth of the gully here? (approximately)